Principle and Protocol of Bradford Method
Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 method is a complex method combining colorimetry and pigment method. It is simple, fast, highly sensitive and stable. It is a commonly used method. Through this experiment, learn the principle of protein content determination by Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 method, and understand the structure, principle and application of spectrophotometer in colorimetry.
Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 is an organic dye, which is brown in free state. It becomes blue when combined with basic amino acids (especially arginine) and aromatic amino acid residues of proteins in dilute acid solution, and its maximum absorption wavelength changes from 465nm to 595nm. Protein content is 0-1000 μ Within the range of g, the absorbance of protein and pigment conjugate at 595nm is in direct proportion to the protein content, in accordance with Beer's law. The protein mass combined with the dye can be obtained by measuring the increase of light absorption at 595nm. Therefore, the advantages of this method are simple, rapid, less interference and high sensitivity.
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Micropipette, ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer, quartz cuvette, balance.
2. Experimental Materials
Protein samples extracted by various methods.
3. Main reagents
Sample solution*1
Protein standard solution (1mg/mL): accurately weigh 10mg of bovine serum albumin and prepare 1mg/mL with 10mL of sample solution.
Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 protein reagent: weigh 100 mg of Coomassie brilliant blue G-250, dissolve it in 50 mL of 90% ethanol, add 100 mL of 85% phosphoric acid, and finally dilute it to 1000 mL*2 with distilled water.
1. Standard Curve Method
(1) Take 7 tubes and add reagents according to Table 2-1-2
Table 2-1-2 Preparation of Protein Standard Curve*3
| Reagent | Test tube number | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Standard solution /mL | - | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.1 |
| Sample solution /mL | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | - |
| Protein concentration mass /(mg/mL) | - | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Figure 2-1-2 Standard Curve of Coomassie Brilliant Blue Dyeing Method
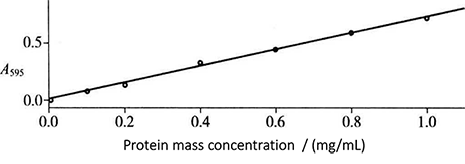
(2) Add 3.0 mL Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 protein reagent into each test tube, mix well and place for 2 min, and then conduct colorimetric determination*4 at 595nm wavelength. The standard curve is drawn with the mass concentration of protein (mg/mL) as the abscissa and the absorbance as the ordinate (Fig. 2-1-2).
2. Determination of Protein Content in Samples
Take 10μL of protein sample to be tested, add 90μL of sample solution for dilution (the mass concentration should be within the range of protein standard curve), add 3.0mL of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 protein reagent, mix it well and place it for 2 min, then measure the absorbance value*5 at the wavelength of 595 nm, find out the protein mass concentration according to the standard curve, and multiply it by the dilution multiple to obtain the true mass concentration of protein sample to be tested.
1. Note that after adding Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 protein reagent, the colorimetry should be completed within 1h. It is better to measure the light absorption within 5-20min after the reagent is added, because the complex is most stable during this period.
2. In the determination, a small part of the protein dye complex will be adsorbed on the cuvette wall, but the adsorption amount of this complex can be ignored. After the determination, wash the blue cuvette with ethanol.
3. The Coomassie brilliant blue method is simple, easy to dry, uses less reagents and is easy to prepare color reagents. Few interfering substances, such as sugar, buffer, reducing agent and complexing agent, do not affect the color development. The disadvantage of this method is that because the contents of arginine and aromatic amino acids in various proteins are different, there will be large deviation when it is used for the determination of different proteins.
* 1 This can be distilled water, protein buffer solution or salt solution. Depending on the sample dissolution solution.
* 2 This solution can be left for 1 month at room temperature.
* 3 Standard solution preparation.

* 4 The colorimetry should be completed within 1h.

* 5 Avoid bubbles when homogenizing, which have an effect on the absorbance.


