Cd19
-
Official Full Name
CD19 molecule -
Overview
Lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate in response to various concentrations of different antigens. The ability of the B cell to respond in a specific, yet sensitive manner to the various antigens is achieved with the use of low-affinity antigen receptors. This gene encodes a cell surface molecule which assembles with the antigen receptor of B lymphocytes in order to decrease the threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation. -
Synonyms
B4;CVID3;MGC12802;CD19;B-lymphocyte antigen CD19;OTTHUMP00000122551;differentiation antigen CD19;T-cell surface antigen Leu-12;B-lymphocyte surface antigen B4
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Monkey
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus
- Canine
- Rabbit
- HEK293
- CHO
- C-His
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- N-His
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- GST
- T7
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- mFc
- lIgG2b
Background
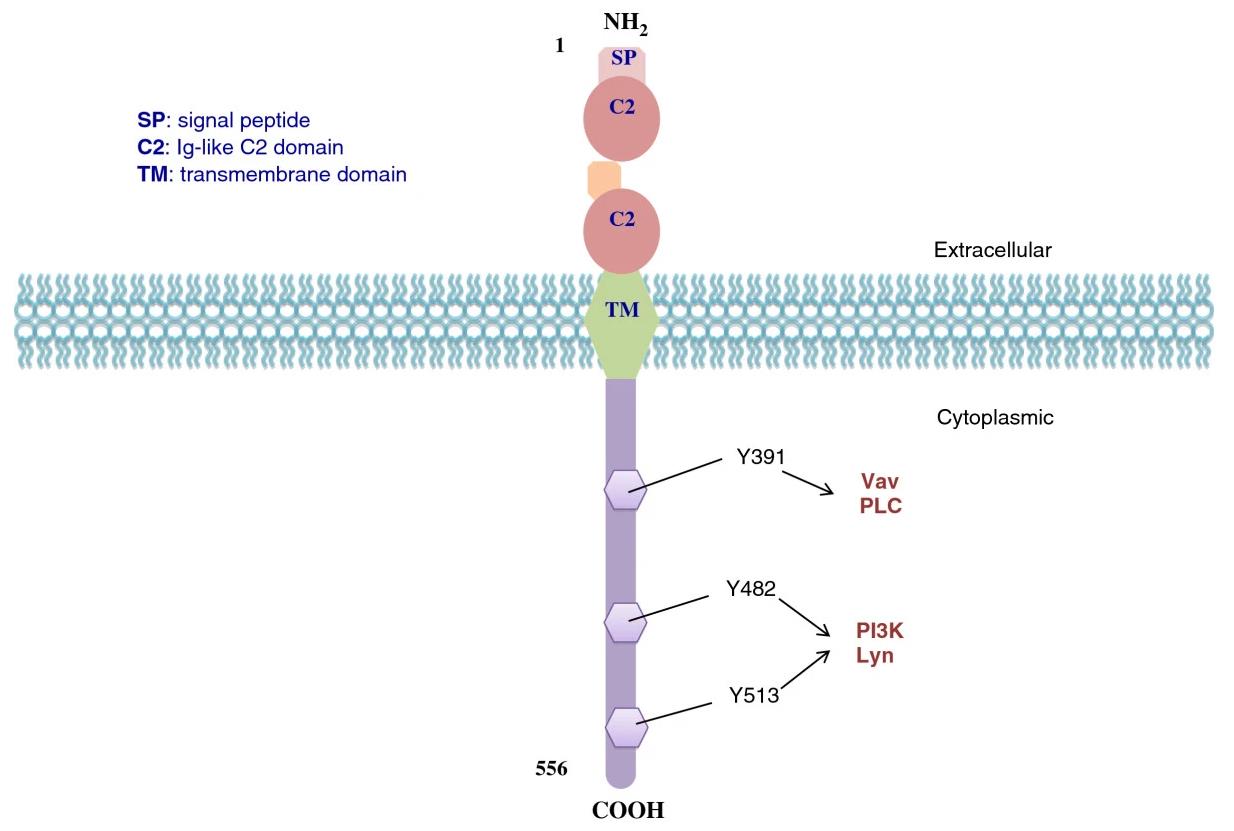
Fig1. CD19 molecular structure. (Kemeng Wang, 2012)
What is CD19 protein?
CD19 gene (CD19 molecule) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 16 at locus 16p11. This gene encodes a member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Expression of this cell surface protein is restricted to B cell lymphocytes. This protein is a reliable marker for pre-B cells but its expression diminishes during terminal B cell differentiation in antibody secreting plasma cells. This protein forms a complex with several membrane proteins including complement receptor type 2 (CD21) and tetraspanin (CD81) and this complex reduces the threshold for antigen-initiated B cell activation. Activation of this B-cell antigen receptor complex activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signalling pathway and the subsequent release of intracellular stores of calcium ions. This protein is a target of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells used in the treatment of lymphoblastic leukemia. The CD19 protein is consisted of 556 amino acids and CD19 molecular weight is approximately 61.1 kDa.
What is the function of CD19 protein?
CD19 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is a type I transmembrane protein with a single transmembrane domain, cytoplasmic C-terminal and extracellular N-terminal. As the main signaling component of a multimolecular complex, CD19 acts together with complement receptor CD21, quadritransmembrane protein CD81 (TAPA-1) and CD225 on the surface of mature B cells to increase the sensitivity of B cells to antigens and promote the proliferation and differentiation of B cells. In addition, CD19 plays a crucial role in the development, maturation and immune response of B cells by interacting with intracellular signaling kinases to enhance BCR-activated signaling and is essential for the expansion and humoral immune response of B cells. CD19, whose expression begins in pre-B cells until it finally differentiates into plasma cells, is one of the most reliable surface biomarkers for B cells.
CD19 related signaling pathway
CD19 regulates the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of B cells by forming multimolecular complexes with BCR and other surface molecules such as CD21, CD81, and CD225. CD19 plays a critical role in the maturation and survival of B cells by enhancing BCR-induced signaling, lowering the signaling threshold required for B cell activation, and amplifies BCR signaling by recruiting and activating downstream protein kinases such as SrC-family kinases, Ras family kinases, Abl, Btk, Vav, Grb2, and PI3K. In addition, CD19 is involved in signaling independent of BCR, for example by binding to CD21 in response to activation of the complement fragment C3d.
CD19 related diseases
CD19 is a B-cell surface marker that has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially B-cell-associated blood tumors. Expression of CD19 is highly conserved in most acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALL), chronic lymphoblastic leukemias (CLL), and B-cell lymphomas, making it a therapeutic target for these diseases. For example, CAR T-cell therapies targeting CD19 have been approved to treat certain types of B-cell malignancies, such as relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). In addition, CD19-targeted therapies also include monoclonal antibodies, immunotoxins, bisspecific antibodies and antibody drug conjugations, and are being evaluated in clinical trials for their potential and efficacy in the treatment of B-cell-related diseases.
Bioapplications of CD19
CAR-T cell therapies targeting CD19, such as axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) and tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), have been approved for the treatment of certain types of B-cell malignancies and are continuing to expand their indications. CD19 targeting therapy also includes monoclonal antibodies, such as rituximab; Bisspecific antibodies, such as blinatumomab, promote the killing of tumor cells by T cells by simultaneously binding to CD19 and CD3 molecules. Antibody drug conjugators (ADCs) technology also involves CD19 targeted therapy, which enables precise killing of tumor cells by coupling cytotoxic drugs to anti-CD19 antibodies via specific linkers.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Asen Bagashev, 2018
To distinguish between epitope loss and surface localization defects, researchers used retrovirus transduction and gene editing techniques to create cell lines expressing the CD19 exon 2 variant (CD19ex2vs) with vesicular stomatitis virus G protein (VSVg) tag. These cell lines were negative in live cell flow cytometry using anti-VSVG antibodies and were resistant to killing by VSVG-directed antibody drug conjugators (ADCs), indicating a defect in surface localization. In fact, pulse-tracking and α-mannosidase inhibitor experiments showed that all CD19ex2vs acquired high mannose-type sugars specific to the ER, but not complex sugar chains synthesized in the Golgi. When fusing with green fluorescent protein (GFP), CD19ex2vs (including mutants lacking relevant disulfide bonds) co-localised with ER markers, suggesting a misalignment of the protein. Mass spectrometry analysis of CD19 interacting proteins revealed that CD19ex2vs failed to bind to the key quad-transmembrane protein CD81, but instead interacted with endoplasmic reticulum resident molecular chaperones such as calnexin and ER transporters involved in antigen presentation.
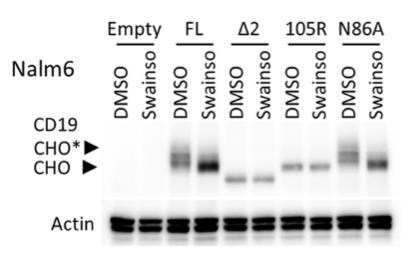
Fig1. Western blot with anti-CD19 or antiactin antibody of protein extracts from the transduced Nalm6 cell lines after treatment with DMSO or swainsonine.
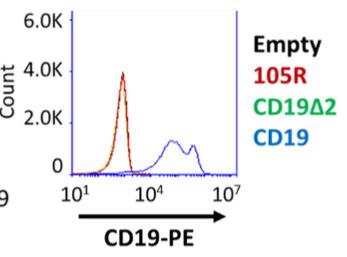
Fig2. Live-cell flow cytometry for empty (black), CD19-FL (blue), CD19-Δex2 (green), and CD19-105R (red).
Case Study 2: Xiaocui He, 2018
BCR is essential for the development and maturation of B cells, and many B-cell lymphomas, such as Burkitt Lymphoma (BL), rely on sustained BCR signaling to promote tumor growth, a process driven by the immune receptor tyrosine activation motif (ITAM) and PI3 kinase (PI3K) signaling pathways. In this study, researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 technology to knock out the BCR and B cell co-receptor genes in the human BL cell line Ramos. The study found that Ramos B cells require the expression of the BCR signaling component Igβ (CD79b) and co-receptor CD19 to maintain their adaptive and competitive growth. In addition, even in the absence of any other BCR component, Igβ can still be expressed on the surface of B cells and is close to CD19, transmitting signals in an ITAM-dependent manner.
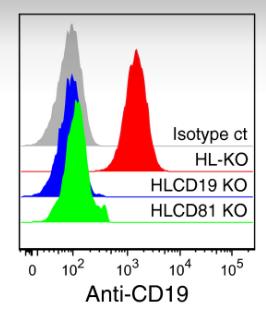
Fig3. The expression of CD19 on the surface of different Ramos KO cells was determined by flow cytometry.
Fig4. Measurement of the Igβ:CD19 proximity by Fab-PLA.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD19-12H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD19-07H)
Involved Pathway
Cd19 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Cd19 participated on our site, such as PIK-Akt signaling pathway,Hematopoietic cell lineage,B cell receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Cd19 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Primary i | CD40LG,CD8A,RAG1,AIRE,UNG,BTK,DCLRE1C,AICDA,ZAP70,PTPRC |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | INPPL1,ARPC2,PLEKHA2,PIK3CD,IKBKG,CRKL,HRAS,VAV1,SYK,AKT2 |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | HDAC4,HSPA1A,NFKBIB,RAN,TRAF3,AKT2,CDK1,NCOR2,PIK3R3,PRKACA |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | IFNA4,GNGT2,FGFR3,IKBKB,MAPK3,Reln,COL24A1,TCL1B1,CCNE1,RPS6KB2 |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | ITGA3,CD33,FCGR1A,MME,DNTT,Il4ra,ITGA6,IL11RA2,IL6,HLA-DRB1 |
| nodeficiency | ZAP70,AICDA,ORAI1,RAG2,PTPRC,TNFRSF13B,TAP1,CD3D,IL7R, Cd79b |
Protein Function
Cd19 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,receptor signaling protein activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Cd19 itself. We selected most functions Cd19 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Cd19. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | COPE,GPBP1,RASGRP3,HSPA13,ABCF3,PRADC1,HIST1H2AI,IL33,AACS,FBXO17 |
| receptor signaling protein activity | TIAM2,cgr2b,NGF,TRAIP,NSMAF,PDCL,DOK2,IFITM1,BAG4,FLRT3 |
Interacting Protein
Cd19 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Cd19 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Cd19.
IGHM;IGHD;CD82;PIK3R3;CD9;PIK3R1;BTK;ARID3A
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Xu, ZS; Zhang, JS; et al. Constitutive activation of NF-kappa B signaling by NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. ONCOLOGY REPORTS 33:1609-1614(2015).
- Strauss, V; Kolle, SN; et al. Immunophenotyping does not improve predictivity of the local lymph node assay in mice. JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY 35:434-445(2015).




