CD79B
-
Official Full Name
CD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta -
Overview
CD79 is a heterodimeric molecule comprised of an alpha-chain (CD79a) and beta-chain (CD79b). A 37-39 kD type I integral membrane protein CD79b is non-covalently associated with CD79a and cell surface IgM to form the B-cell receptor (BCR) complex. CD79b is -
Synonyms
CD79B;CD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta;CD79B antigen (immunoglobulin associated beta) , IGB;B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein beta chain;B29;Ig-beta;B-cell-specific glycoprotein B29;immunoglobulin-associated B29 protein;CD79b antigen (immunoglobulin-associated beta);IGB;AGM6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Cynomolgus
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Fc
- T7
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Avi
- rFc
Background
What is CD79B protein?
CD79B protein, also known as B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein beta chain, is a protein that is involved in B-cell receptor signaling. It is a component of the B-cell receptor (BCR) complex, which plays a crucial role in the activation and function of B cells in the immune system.
CD79B protein is specifically expressed in B cells and is responsible for transducing signals from the BCR to downstream signaling pathways upon antigen recognition. It forms a heterodimer with CD79A protein to form the B-cell antigen receptor complex, which is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin (Ig) molecule and associated CD79A/CD79B heterodimers. This complex is required for the surface expression and signaling of the BCR.
What is the function of CD79B protein?
The main function of CD79B is to transduce signals from the BCR upon antigen recognition. It contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in its cytoplasmic tail. Upon binding of antigens to the BCR, CD79B is phosphorylated by the Src family kinases. This phosphorylation leads to the recruitment and activation of downstream signaling molecules, such as Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), which ultimately triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling events necessary for B-cell activation, proliferation, and antibody production.
CD79B related signaling pathway
The CD79B protein is involved in the activation of several signaling pathways, including the BCR signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in B cell development, differentiation, and immune responses. This pathway involves the recruitment and activation of various intracellular signaling molecules, ultimately leading to the activation of transcription factors and gene expression necessary for B cell proliferation, survival, and antibody production.
CD79B Related Diseases
- B Cell Lymphomas: CD79B is a key component of the B cell receptor (BCR) complex, which plays a crucial role in B cell activation and survival. Mutations or dysregulation of CD79B can contribute to the development of B cell lymphomas, such as diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and Burkitt lymphoma.
- Agammaglobulinemia: CD79B mutations can also lead to a rare genetic disorder known as X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA). XLA is characterized by a severe deficiency in B cells, resulting in a lack of antibody production and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Dysregulation of CD79B signaling has been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis. Abnormal activation of B cells through the BCR complex, including CD79B, can contribute to the production of autoantibodies and the breakdown of self-tolerance.
- B-cell lymphomas: Alterations in CD79B expression or mutations in the CD79B gene have been found in different types of B-cell lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and Burkitt lymphoma. These abnormalities can lead to constitutive BCR signaling and contribute to the growth and survival of lymphoma cells.
- Autoimmune diseases: CD79B has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis. Dysregulated BCR signaling mediated by CD79B can result in the production of autoantibodies and immune dysregulation.
- B-cell lymphomas: Alterations in CD79B expression or mutations in the CD79B gene have been found in different types of B-cell lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and Burkitt lymphoma. These abnormalities can lead to constitutive BCR signaling and contribute to the growth and survival of lymphoma cells.
- Autoimmune diseases: CD79B has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis. Dysregulated BCR signaling mediated by CD79B can result in the production of autoantibodies and immune dysregulation.
Case Study
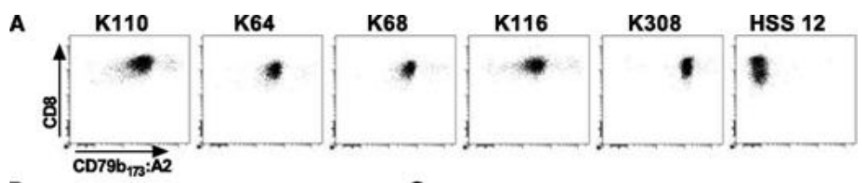
(Lokenz jahn, 2017)
Fig3. pMHC tetramer CD8+ T cells exhibit different degrees of CD79b peptide sensitivity and specificity. T cells were clonally expanded by single-cell sorting of CD8+ T cells binding to pMHC tetramers containing CD79b peptides. (A) Shown are pMHC-tetramer staining of 5 representative clones (K110, K64, K68, K116, and K308) isolated using pMHC tetramer CD79b173:A2. Control includes clone HSS12 specific for USP11-derived peptide FTWEGLYNV bound to HLA-A2. Shown are CD8+ cells.
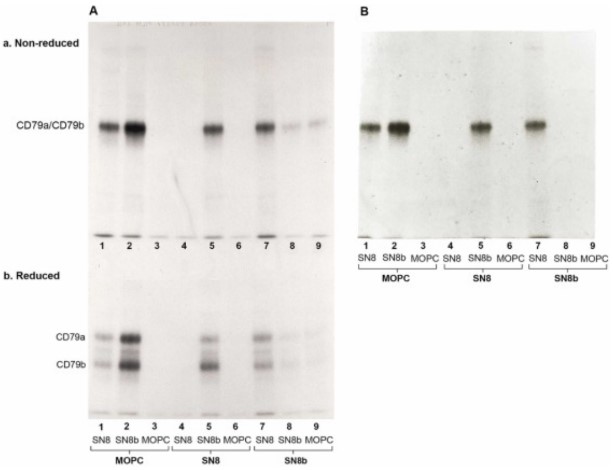
(Ben K. Seon, 2024)
Fig4. SDS-PAGE analysis of CD79a/CD79b complex or CD79a and CD79b molecules that are generated by reduction of the disulfide bonds between CD79a and CD79b molecules. Data in Section A are those of SDS-PAGE analysis of the immunoprecipitates from Experiment 1 of Table 1, whereas data in Section B are those of SDS-PAGE analysis of the immunoprecipitates from Experiment 2 of Table 1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
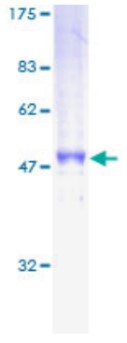
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: CD79B-0858H)
High Bioactivity & Detection Sensitivity
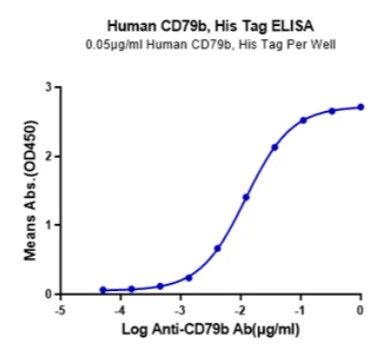
Fig2. CD79B is a 36-40 kDa member of the Ig-Superfamily. It is required in cooperation with CD79A for initiation of the signal transduction cascade activated by the B-cell antigen receptor complex (BCR) which leads to internalization of the complex, trafficking to late endosomes and antigen presentation. Enhances phosphorylation of CD79A, possibly by recruiting kinases which phosphorylate CD79A or by recruiting proteins which bind to CD79A and protect it from dephosphorylation.
Involved Pathway
CD79B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD79B participated on our site, such as B cell receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD79B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | BLK,PDK2B,CD81,RASGRP3,PRKCB,PPP3R2,RAC2,MAP4K1,CD22,PILRB |
Protein Function
CD79B has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,transmembrane signaling receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD79B itself. We selected most functions CD79B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD79B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | OR103-4,ADCYAP1R1A,LILRB5,ERBB2,SLC22A17,OR6K3,IL11RA,FCAMR,OR115-6,MPL |
| protein binding | CLK2,TRPC2,PMM1,UTF1,ARHGEF3,RBX1,TNNI3,EMP2,PPP1R9B,TBC1D17 |
Interacting Protein
CD79B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD79B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD79B.
SGTA;q8ckf8_yerpe
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lu, D; Jin, JY; et al. POPULATION PHARMACOKINETICS AND EXPOSURE-RESPONSE ASSESSMENT OF ANTI-CD79B ANTIBODY DRUG CONJUGATE IN PATIENTS: INTERIM ANALYSIS RESULTS.. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS 97:S88-S89(2015).
- Chang, CH; Wang, Y; et al. Extensive crosslinking of CD22 by epratuzumab triggers BCR signaling and caspase-dependent apoptosis in human lymphoma cells. MABS 7:199-211(2015).



