Fc Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
- FCAMR
- CD89
- FCER1A
- FCER1G
- FCER2
- CD64
- CD32A
- Fcgr2b
- CD16
- FCGR3
- CD16a
- FCGR3B
- FCGR4
- FCGRT
- FCGRT
- FCRL1
- FCRL3
- FCRL4
- MS4A2
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Fc Receptors Research
At Creative BioMart you can find a wide range of products related to Fc receptors, including recombinant proteins and other key products. In addition, we offer customized services to meet your specific requirements, ensuring you get the product you need.
In addition to our products and services, we offer a wealth of resources for your reference. Our resources cover all aspects of Fc receptors, including the involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics. These resources will be invaluable to researchers wishing to deepen their understanding of Fc receptors and their role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
About Fc Receptors
Fc receptors, abbreviated as FcRs, are a group of cell surface receptors found on various immune cells that play a crucial role in the recognition and binding of the Fc region of antibodies. Fc receptors are a part of the immune system and are involved in the effector functions mediated by antibodies, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), phagocytosis, and the release of inflammatory mediators.
The Fc region of an antibody is the tail portion that interacts with Fc receptors. Fc receptors recognize and bind to the Fc region of antibodies, which allows immune cells to recognize and respond to foreign pathogens or cells targeted by antibodies. The antibody subclasses (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE) have distinct Fc regions, leading to different interactions with Fc receptors.
There are several types of Fc receptors expressed on various immune cells, including:
- Fcγ Receptors (FcγRs): These receptors bind to the Fc region of IgG antibodies. FcγRs are expressed on various immune cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells. They play a crucial role in ADCC, phagocytosis, cytokine release, and immune complex clearance.
- Fcε Receptors (FcεRs): FcεRs specifically bind to the Fc region of IgE antibodies. They are primarily expressed on mast cells and basophils, which are involved in immediate hypersensitivity reactions, such as allergies and asthma. Cross-linking of FcεRs by allergens triggers the release of inflammatory mediators, leading to allergic responses.
- Fcα Receptors (FcαRs): FcαRs bind to the Fc region of IgA antibodies. They are found mainly on phagocytic cells, including neutrophils and macrophages, and are involved in the clearance of pathogens and immune complexes coated with IgA.
- Fcμ Receptors (FcμRs): FcμRs are expressed on B cells and bind to the Fc region of IgM antibodies. They play a role in the regulation of B cell activation and antibody production.
- FcRn (Neonatal Fc Receptor): FcRn is a unique Fc receptor that is involved in the transport of maternal IgG antibodies across the placenta to provide passive immunity to the developing fetus. It is also present in the intestinal epithelium, where it mediates the transfer of IgG from the mother's milk into the bloodstream of neonates.
The interaction between Fc receptors and antibodies is crucial for the immune system's recognition and elimination of pathogens, immune complex clearance, and regulation of immune responses. Dysregulation or genetic variations in Fc receptors can impact immune responses and contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases, allergies, and other immune-related disorders.
Understanding the function and regulation of Fc receptors is essential for developing therapeutic strategies that modulate immune responses, enhance antibody-mediated effector functions, and improve the efficacy of antibody-based therapies.
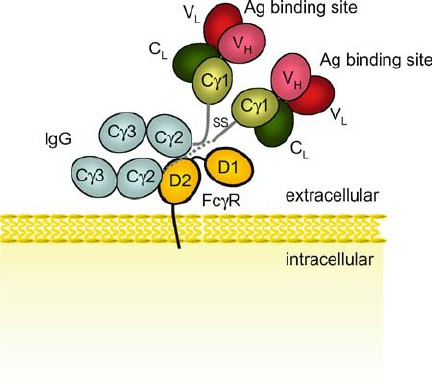 Fig.1 Schematic 3-dimensional structure of Fc γ RIII. (Takai T, 2005)
Fig.1 Schematic 3-dimensional structure of Fc γ RIII. (Takai T, 2005)
Functions of Fc Receptors
Fc receptors (FcRs) play several major functions in the immune system, primarily through their interaction with the Fc region of antibodies. Here are the key functions of FcRs:
- Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC): Fc receptors, particularly Fcγ receptors (FcγRs), are involved in ADCC. When antibodies bind to their target antigens on the surface of infected or tumor cells, FcγRs on immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, recognize and bind to the Fc region of these antibodies. This binding triggers the immune cells to release cytotoxic granules or induce apoptosis, leading to the destruction of the target cells.
- Phagocytosis: Fc receptors, including FcγRs and Fcα receptors (FcαRs), facilitate phagocytosis, the process by which immune cells engulf and internalize pathogens or antibody-coated cells. When antibodies bind to their targets, Fc receptors on phagocytes recognize and bind to the Fc region of these antibodies, promoting the engulfment and subsequent destruction of the target by the phagocytic cell.
- Immune Complex Clearance: Fc receptors are involved in the clearance of immune complexes, which are formed when antibodies bind to antigens, forming complexes that can be deposited in tissues. Fc receptors on cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, recognize and bind to the Fc portion of these immune complexes, triggering their internalization and subsequent degradation, thus preventing tissue damage caused by the accumulation of immune complexes.
- Regulation of Immune Responses: Fc receptors can modulate immune responses by transmitting activating or inhibitory signals upon binding to antibodies. For instance, activating FcγRs on immune cells can trigger pro-inflammatory responses, such as the release of cytokines and chemokines, promoting inflammation. On the other hand, inhibitory FcγRs can dampen immune responses by inhibiting the activation of immune cells.
- Maternal-Fetal Immune Transfer: FcRn (Neonatal Fc Receptor) is responsible for the transport of maternal IgG antibodies across the placenta, providing passive immunity to the developing fetus. FcRn binds to the Fc region of IgG antibodies in the maternal circulation, protecting them from degradation and facilitating their transfer to the fetal circulation.
The precise balance and regulation of Fc receptor activities are essential for maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing immune-related disorders.
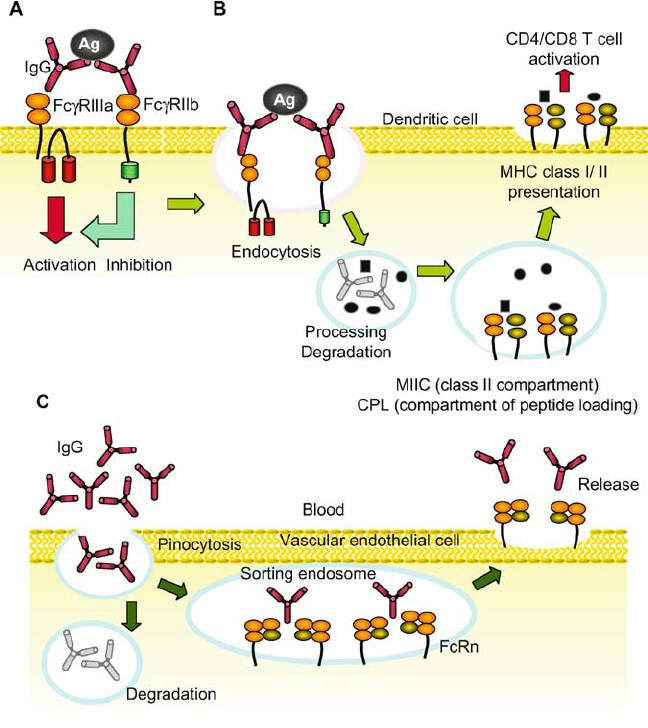 Fig.2 Major functions of FcRs. (Takai T, 2005)
Fig.2 Major functions of FcRs. (Takai T, 2005)
(A) Positive and negative regulation of cellular signaling. FcRs play a central role in controlling immune responses following interaction with ICs. The activation cascade through FcR γ -associating FcR results in cellular activation, which leads to phagocytosis, antibody- dependent cellular cytotoxicity, superoxide generation, and production and release of cytokines and proinflammatory mediators. In contrast, Fc γ RIIb harbors ITIM, and mediates inhibition of ITAM- induced activation cascade. (B) Clearance of ICs and MHC class I- and class II-restricted antigen presentation. After phagocytosis or endocytosis via a FcR-mediated process, the ICs are efficiently broken down intracellularly followed by antigen presentation in both class I- and class II-restricted manner. (C) Ig transport and recycling of IgG. FcRn and polymeric Ig receptor transport Ig transcel- lularly and FcRn contribute to regulate plasma IgG concentration.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- Takai T. Fc receptors and their role in immune regulation and autoimmunity. J Clin Immunol. 2005;25(1):1-18. doi:10.1007/s10875-005-0353-8
- Kim J, Lee JY, Kim HG, Kwak MW, Kang TH. Fc Receptor Variants and Disease: A Crucial Factor to Consider in the Antibody Therapeutics in Clinic. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179489
- Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch J V. Fcγ receptors as regulators of immune responses[J]. Nature Publishing Group, 2008(1). DOI:10.1038/NRI2206.

