Activity Kits
🧪 Kit-0337
Source:
Species:
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
Background
Overview
Activity Kits are specialized sets of reagents and protocols designed to measure specific biological activities or substances within a sample. These kits streamline the experimental process by providing all necessary components, such as enzymes, substrates, buffers, and standards, and are widely used in research and diagnostic laboratories.
Classifications
Enzyme Activity Assay Kits
These kits are designed to measure the activity of specific enzymes within a biological sample. They typically include a substrate that reacts in the presence of the enzyme, producing a detectable product. The rate of this reaction is directly proportional to the enzyme concentration. Common examples include kinase and phosphatase activity assays.
Protein Detection Assay Kits
Protein detection kits allow for the quantification of protein concentrations in a sample. The most common type is the Bradford Assay, which uses a dye that binds to protein, changing its color intensity in proportion to the protein concentration. Other methods include the BCA (Bicinchoninic Acid) and Lowry assays.
Cytokine Detection Kits
Cytokines are signaling proteins involved in cell communication and immune responses. These kits are used to detect and quantify specific cytokines in cell culture supernatants or body fluids. They often employ ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) technology, which relies on antibodies to capture and detect the target cytokine.
Hormone Detection Kits
Hormone detection kits are used to measure levels of specific hormones in biological samples. These kits are crucial for diagnosing and monitoring endocrine disorders. They typically use immunoassays, such as radioimmunoassay (RIA) or ELISA, which are highly sensitive and specific.

How Activity Kits Work
Activity kits typically follow a standardized protocol that involves the following steps:
Sample Preparation: The biological sample is prepared according to the kit's instructions, which may involve dilution, centrifugation, or other processing steps.
Reaction: The sample is mixed with the provided reagents, which initiate a reaction specific to the target molecule or activity.
Detection: The reaction produces a signal (colorimetric, fluorescent, or luminescent) that is detected using a spectrophotometer, plate reader, or other detection equipment.
Quantification: The intensity of the signal is compared to a standard curve generated using known concentrations of the target molecule, allowing for the quantification of the target in the sample.
Advantages of Activity Kits
Standardization: Kits provide a consistent and standardized approach to measurements, reducing variability and improving reproducibility.
Sensitivity and Specificity: High-quality kits are designed to have high sensitivity and specificity for the target molecule or activity, minimizing false positives and negatives.
Ease of Use: Kits simplify the experimental process, making it accessible to a wider range of researchers.
Time-Saving: The use of kits can significantly reduce the time required to perform assays compared to setting up the experiments from scratch.
Cost-Effective: While individual reagents may be more expensive, kits are often more cost-effective due to the bundled components and reduced waste.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ammonia Colorimetric Assay Kit (Kit-0085)
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychiatric complication of cirrhosis associated with poor survival and adverse effects on quality of life (QOL). The drawbacks of long-term use of rifaximin in HE require the search for alternative therapies. In this context, the aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of nitazoxanide (NTZ) versus rifaximine (RFX) in preventing recurrence of HE and to assess its impact on quality of life. This prospective, randomized, double-blind controlled study included 60 patients randomly assigned to receive rifaximin 550 mg twice daily (group 1; N = 30) or nidazolide 500 mg twice daily (2 groups; N = 30) for 24 weeks. During the study period, patients were monitored for neurological symptoms, mental status, and work performance. Serum levels of HE triggers (ammonia, TNF-α, and octopamine) were assessed. Patients' health-related quality of life was also assessed.
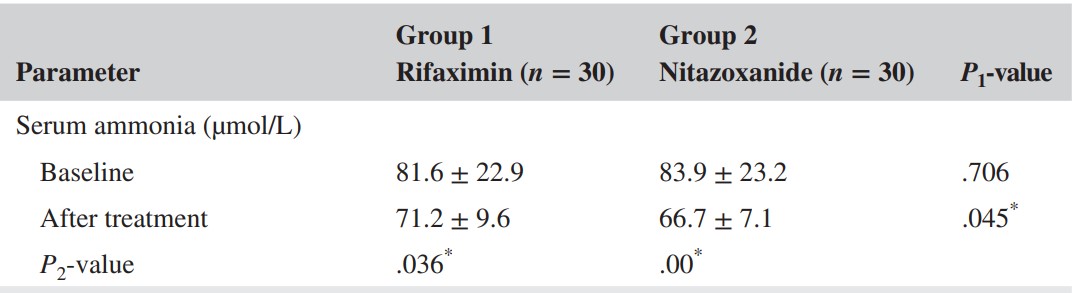
The results showed that six months after treatment, patients treated with NTZ showed statistically significant improvements in chess scores and mental state. In addition, NTZ showed statistically significant reductions in serum levels of ammonia (as detected by the kit), TNF-α, and octopamine compared with rifaximine. In terms of quality of life, the Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire (CLDQ) scores improved in the NTZ group. Both groups had mild, manageable side effects.
(Khadija A M Glal, 2021)
Fig1. During the current study, the nitazoxanide group showed statistically significant reduction in serum ammonia level as compared to rifaximin group.
Case Study 2: Aspartate Transaminase Assay Kit (Kit-0110)
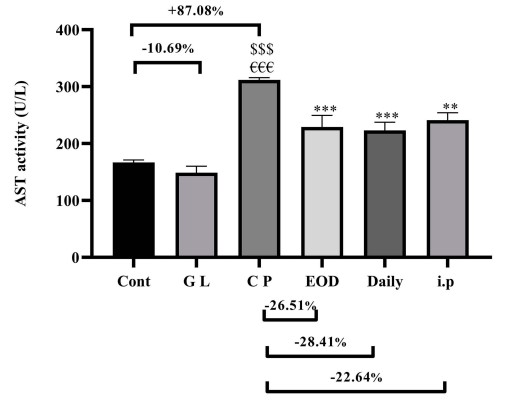
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is the most common cause of acute liver failure. The aim of this study was to investigate the molecular mechanisms by which Ganoderma lucidum mushroom (GLM) may ameliorate cisplatin (CP)-induced hepatotoxicity theoretically and experimentally. Thirty-six male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into six groups, two of them are normal and Ganoderma lucidum control groups. Liver injury was induced by a single dose of CP (12 mg/kg i.p) in four groups, one of them is CP control group. The biochemical markers of liver injury, including serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and total bilirubin (T. bilirubin) levels were assessed using commercial colorimetric assay kits. The results showed that GLM treatment significantly decreased serum levels of hepatic injury markers; ALT, AST, T. bilirubin as well as oxidative stress markers; MDA and H2O2 with a concomitant increase in hepatic GSH and SOD. GLM attenuated hepatic injury through downregulation of HMGB-1/NF-kB and caspase-3 resulted in modulation of the induced oxidative stress and the subsequent cross-talk between the inflammatory and apoptotic cascade indicating its promising role in DILI.
(Hanan M Hassan, 2020)
Fig2. Hepatoprotective effects of GLM (500 mg/kg/day) on serum levels of AST in CP-induced liver injury in rats.
Case Study 3: Protease Assay Kit (Kit-2416)
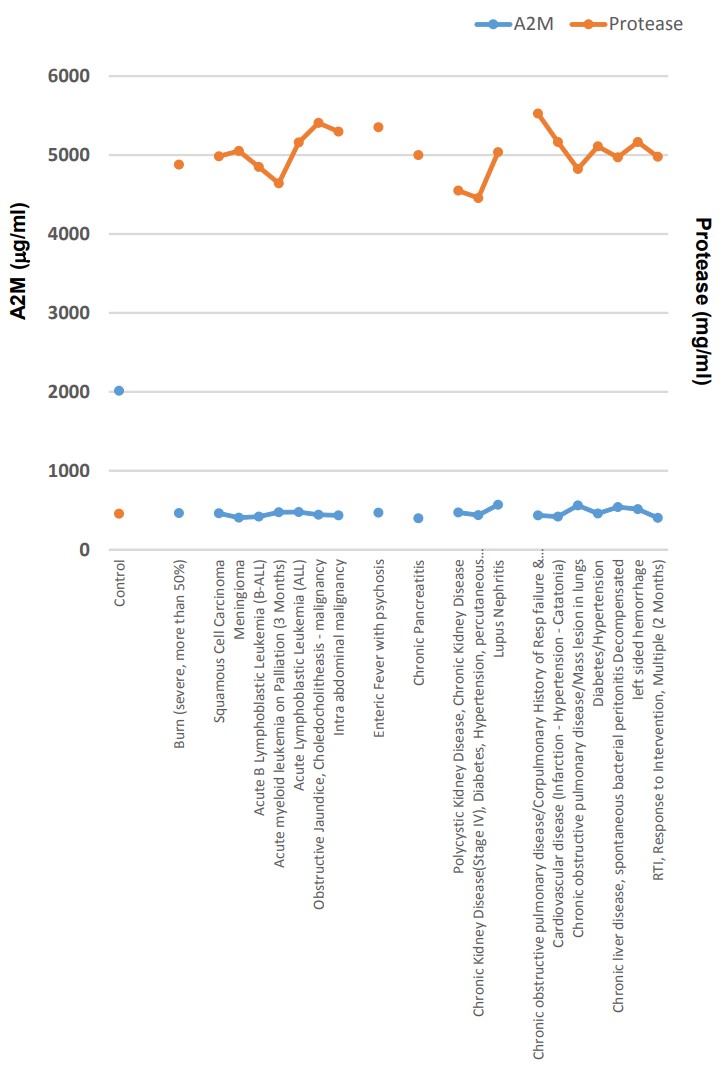
The activity of the broad spectrum protease inhibitor, alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M) may hold unexplored roles in diseases as well. Clinically measuring levels of variant proteases in combination with the monitoring of A2M, in plasma, can be a novel approach to further our understanding of diseases related to protease activity. They investigated the relationship of protease activity and concentration of A2M in plasma of chronic ill patients in Bangladesh. Blood was collected to prepare plasma from patients (n=20) of different categories: severe burn, cancer of different types, enteric fever with psychosis, chronic pancreatitis, chronic liver diseases, different types of kidney diseases, different types of pulmonary diseases, diabetes and hypertension. As control, plasma was prepared from healthy volunteers (n=20) without any known disease(s). Plasma concentrations of A2M were measured by sandwich ELISA (Enzyme–Linked Immunosorbent Assay) and protease activity assay were done by protease activity assay kit.
(Khan MM, 2016)
Fig3. A2M and protease level in plasma of patients of different diseases (n=20) compared with normal healthy individuals (control) (n=20).
Advantages
- Technical specialization. The activity test kits we offer cover a wide range of biological research areas, and our R&D team is dedicated to developing all kinds of test kits.
- Product diversity. Our extensive product line includes activity detection kits for different biological applications to detect a variety of biological processes such as reactive oxygen species, cell proliferation, apoptosis, immune response and oxidative stress.
- Customized service. We not only provide standardized test kits, but also provide customized test kits according to customer needs. The flexibility of this service can better meet specific research needs and provide customers with more personalized solutions.
Creative BioMart contains activity detection kits for different biological applications to detect enzyme activity, protein level, cytokine expression, etc. You can also let us know if you have any customized requirements. Please contact us for more product details.
References
- Glal KAM.; et al. Nitazoxanide versus rifaximin in preventing the recurrence of hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021;28(10):812-824.
- Hassan HM.; et al. Suppression of Cisplatin-Induced Hepatic Injury in Rats Through Alarmin High-Mobility Group Box-1 Pathway by Ganoderma lucidum: Theoretical and Experimental Study. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:2335-2353.
- Khan MM.; et al. Measurement of Protease Activity and Concentration of a Broad Spectrum Protease Inhibitor; Alpha 2-Macroglobulin (A2m) in Plasma of Severely Chronic Ill Patients in Bangladesh. J Clin Exp Pathol. 2016, 6:4.













