FGF2
-
Official Full Name
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (basic) -
Overview
roblast growth factors, or FGFs, are a family of growth factors involved in angiogenesis, wound healing, and embryonic development. The FGFs are heparin-binding proteins and interactions with cell-surface associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans have been shown to be essential for FGF signal transduction. FGFs are key players in the processes of proliferation and differentiation of wide variety of cells and tissues. -
Synonyms
FGF2;fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic);BFGF;FGFB;HBGF-2;heparin-binding growth factor 2;prostatropin;OTTHUMP00000037513;basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF;Fgf-2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Bovine
- Rabbit
- Mouse
- Porcine
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- Duck
- Bovine/Porcine
- Cattle
- Pig
- E.coli
- Yeast
- Insect Cells
- Barley Grain
- Sf21 Cells
- Hordeum Vulgare
- CHO
- HEK293
- Bovine Pituitary
- Bovine brain
- Oryza Sativa
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- yeast
- Mouse
- Human Cells
- Baculovirus
- Non
- His
- ERHV
- Flag
- S
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- MBP
- Fc
- SUMO
- HA
Background
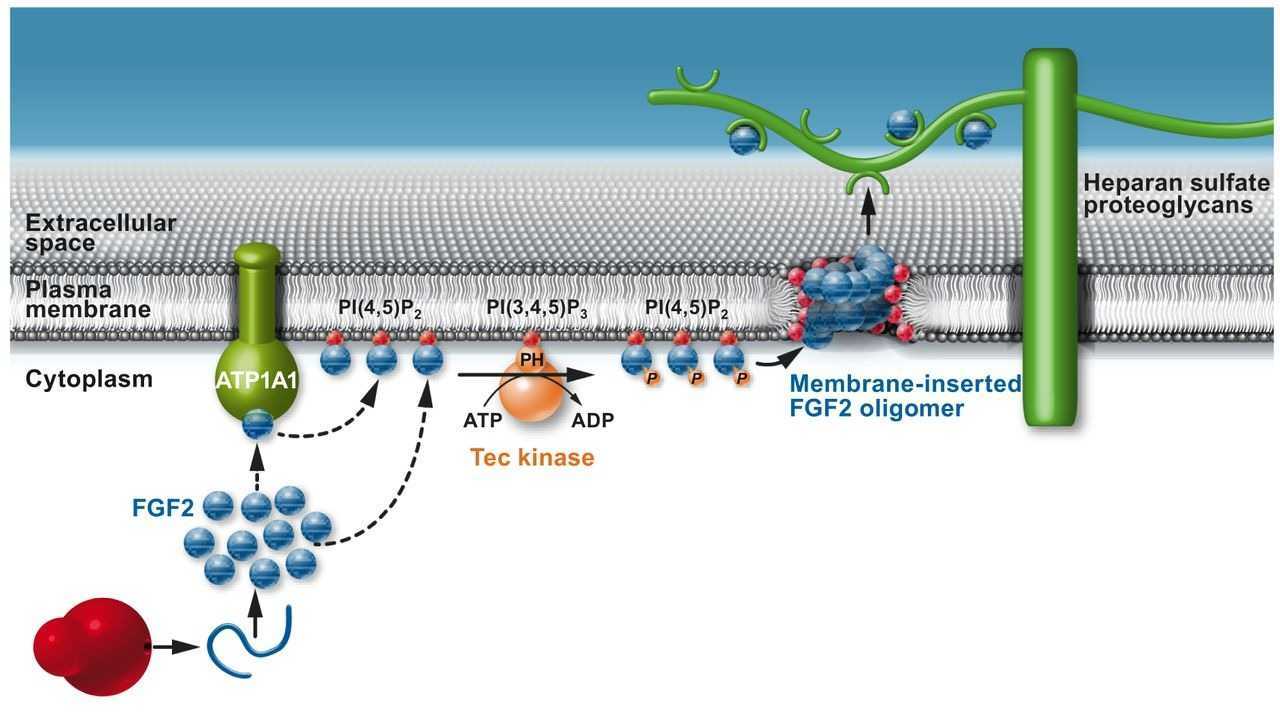
Fig1. A schematic diagram illustrating the PI(4,5)P2-dependent formation of FGF2 pores in the plasma membrane and FGF2 secretion. (David Brough, 2017)
What is FGF2 protein?
FGF2 gene (fibroblast growth factor 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4q28. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members bind heparin and possess broad mitogenic and angiogenic activities. This protein has been implicated in diverse biological processes, such as limb and nervous system development, wound healing, and tumor growth. The mRNA for this gene contains multiple polyadenylation sites, and is alternatively translated from non-AUG (CUG) and AUG initiation codons, resulting in five different isoforms with distinct properties. The CUG-initiated isoforms are localized in the nucleus and are responsible for the intracrine effect, whereas, the AUG-initiated form is mostly cytosolic and is responsible for the paracrine and autocrine effects of this FGF. The FGF2 protein is consisted of 288 amino acids and FGF2 molecular weight is approximately 30.8 kDa.
What is the function of FGF2 protein?
FGF2 is a protein with a wide range of biological functions. It is a mitogenic, angiogenic, and neurotrophic factor that is expressed at low levels in many tissues and cell types, with higher concentrations found in the brain and pituitary. FGF2 plays a role in numerous physiological and pathological processes such as limb development, angiogenesis, wound healing, and tumor growth. It is also involved in the proliferation, differentiation, and migration of various cell types of mesodermal and neuroectodermal origin . Furthermore, FGF2 is implicated in tissue repair and regeneration after injury, acting as a potent angiogenic factor and a mitogen for many cell types, including cardiomyocytes. It binds to four related tyrosine kinase receptors (FGFR1-4) and is involved in the regulation of cell growth, tissue repair, wound healing, and angiogenesis, among other functions. FGF2 also exhibits neuroprotective activity and can stimulate neurogenesis, playing a role in the central nervous system's differentiation and function.
FGF2 Related Signaling Pathway
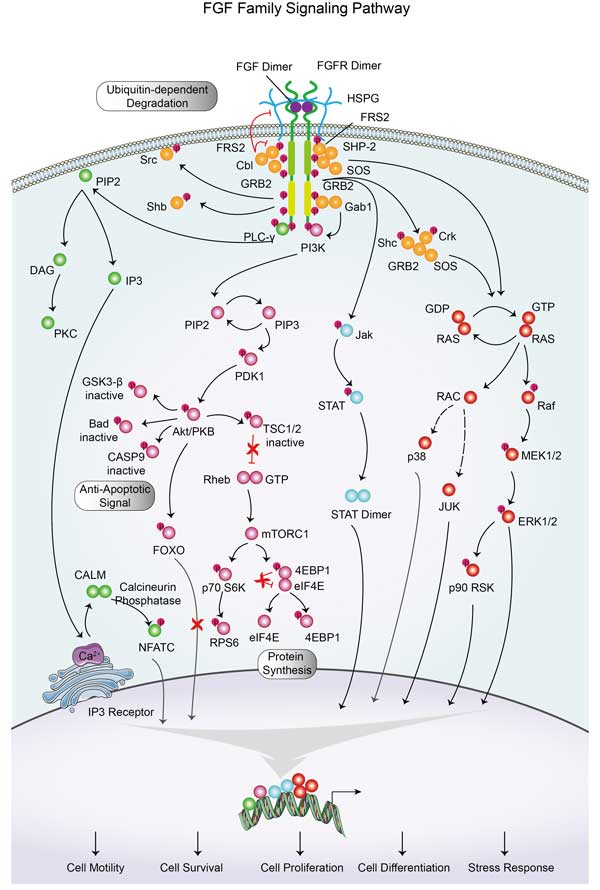
After binding to FGFR, FGF2 can activate RAS proteins, which in turn activate RAF-1, MEK, and ERK kinases, and this cascade reaction ultimately leads to changes in gene transcription, affecting cell proliferation and differentiation. FGF2 can also activate phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), and then activate AKT protein, which is involved in the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and metabolism. Fgf2-activated FGFR can induce hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol diphosphate (PIP2) to produce inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), which are second messengers that further activate protein kinase C (PKC) and other signaling molecules. FGF2 may also regulate gene expression by activating Janus kinase (JAK) and signal transducers and transcriptional activators (STAT).
FGF2 Related Diseases
FGF2 is implicated in a variety of physiological and pathological processes. It plays a crucial role in embryonic development, tissue repair, wound healing, and cell proliferation. However, dysregulation of FGF2 signaling has been associated with several diseases, including various types of cancer. Furthermore, FGF2 has been linked to Hodgkin lymphoma, where it causes aberrant signaling activities in neoplastic cells. In the context of solid tumors, FGF2 contributes to cancer progression by acting directly on tumor cells, promoting angiogenesis, and modulating the tumor microenvironment. High levels of FGF2 have also been correlated with reduced survival in cancer patients and are associated with relapse and recurrence in various cancers.
Bioapplications of FGF2
It is extensively studied for its potential in regenerative medicine, where it can stimulate the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and the healing of wounds. FGF2's ability to promote tissue regeneration makes it a candidate for therapeutic use in chronic wounds, burns, and ulcers. Additionally, its neurotrophic properties suggest applications in neurology, potentially aiding in the recovery from injuries or neurodegenerative diseases by supporting neuronal survival and growth. In the field of oncology, while FGF2's role in tumor growth is a concern, understanding its mechanisms also helps in developing targeted therapies against cancer. Moreover, FGF2's involvement in embryonic development and tissue homeostasis has made it a subject of interest in stem cell research, where it can be utilized to enhance stem cell proliferation and differentiation.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Rucha V Joshi, 2013
Using fibroblast growth factor 2, injectable "smart" microspheres that are sensitive to both temperature and pH have been fabricated and tested for controlled delivery of therapeutic proteins to ischemic skeletal muscle. At 37°C and pH representative of ischemic muscle (i.e. pH 5.2-7.2), these microspheres produced sustained, diffusion-controlled release, and at normal, physiological pH (i.e. pH 7.4), they underwent dissolution and rapid clearance. Delivery of fibroblast growth factor 2 was used to confirm that protein bioactivity was retained following microsphere encapsulation/release based on a dose-dependent increase in NIH3T3 fibroblast proliferation in vitro. Microsphere-loaded or free Cy5.5-labeled albumin was injected into ischemic and control gastrocnemii of mice following unilateral induction of hind limb ischemia to model peripheral arterial disease. In the ischemic limb at days 3.5 and 7, there was higher local retention of the protein delivered via microspheres relative to injected free protein (p<0.05). Finally, histological analysis of the gastrocnemius revealed that the polymeric microspheres did not produce any microscopic signs of toxicity near the injection site.
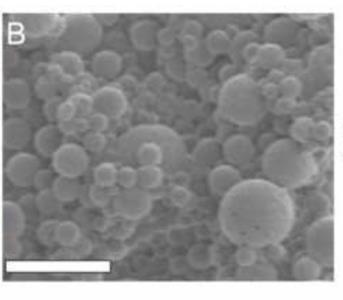
Fig1. SEM of microspheres shows the size distribution and morphology of microspheres.
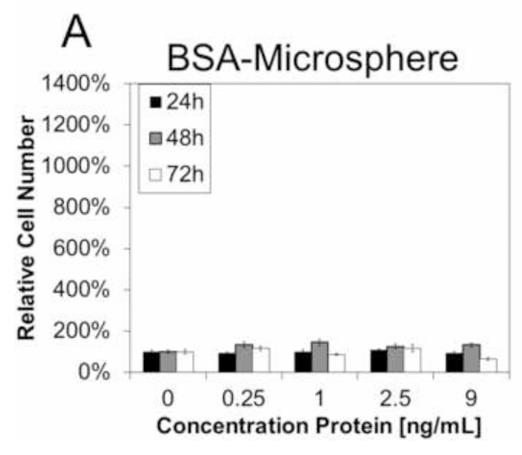
Fig2. BSA-loaded P6 microspheres showed little toxicity to LR3T3s with a small but significant reduction at 72 h at the highest dose.
Case Study 2: James S Farrelly, 2019
Researchers sought to develop a minimally invasive intra-amniotic therapy for prenatal treatment of myelomeningocele (MMC) in an established rat model. Time-dated pregnant rats were gavage-fed retinoic acid to induce MMC. Groups received intraamniotic injections at E17.5 with alginate particles loaded with fluorescent dye, basic fibroblast growth factor (Alg-HSA-bFGF), fluorescently tagged albumin (Alginate-BSA-TR), free bFGF, blank alginate particles (Alg-Blank), or PBS. Groups were analyzed at 3 h for specific particle binding or at term (E21) to determine MMC coverage. The results showed that 18 of 61 (30%) treated with Alg-HSA-bFGF showed evidence of soft tissue coverage compared to 0 of 24 noninjected (P = 0.0021), 0 of 13 PBS (P = 0.0297), and 0 of 42 free bFGF (P = P < 0.0001). Thus, injection of microparticles loaded with bFGF resulted in significant soft tissue coverage of the MMC defect compared to controls.
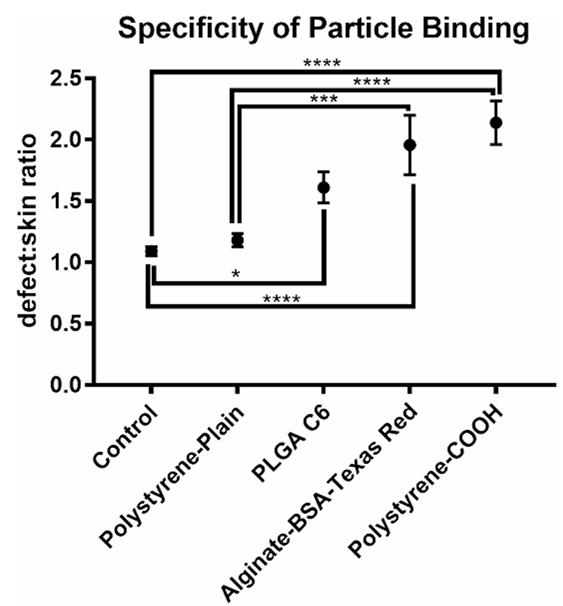
Fig3. Binding specificity of fluorescent particles to the MMC defect compared to adjacent skin.
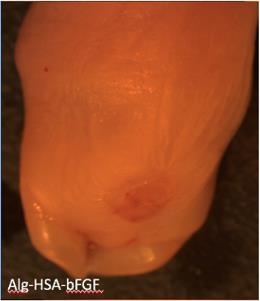
Fig4. Gross light images of specimens treated with Alg-HSA-bFGF.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
FGF2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FGF2 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FGF2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Melanoma | PIK3CD,IGF1,FGFR1,PDGFD,NRAS,RB1,FGF4,FGF8,HGF,PIK3R3 |
| Pathways in cancer | HSP90B1,FZD6,TRAF6,AXIN1,LAMB3,MAPK3,CTNNA3,RELA,WNT3,BDKRB1 |
| Ras signaling pathway | INS,SHC2,GNG13,MLLT4,PLA2G2E,FGF12,FOXO4,SHOC2,RAP1A,PAK1 |
| Rap signaling pathway | RALGDS,LPAR4,F2R,MAPK11,GNAO1,MAPK1,GRIN1,GNAS,FGF4,PLCB4 |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | KITLG,TSC2,IL6R,THBS3,LAMB3,IGF1R,FLT4,TCL1B,MAPK1,CREB3L2 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | WNT3A,CTTN,SDC2,ITGA2,VAV2,PPP1CA,CBLC,RPS6,GPC1,HPSE |
| MAPK signaling pathway | HSPA1A,RAC3B,MECOM,STK4,PDGFRA,NFATC1,PPP3R2,PPP3CA,EGFRA,FGF1B |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | WASL,INS,PIP5KL1,RAC2,ITGB8,GNA12A,ITGB6,PIP5K2,ITGA5,RAF1 |
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | WNT2B,MAPK1,ESRRB,ISL1,BMPR1A,IGF1,BMPR2,IGF1R,GSK3B,PIK3R1 |
Protein Function
FGF2 has several biochemical functions, for example, chemoattractant activity,cytokine activity,fibroblast growth factor receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FGF2 itself. We selected most functions FGF2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FGF2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | USP20,BCL2L14,NUDT4,DDX23,BLMH,TFPT,DLAT,FANCI,HOOK1,HIP1 |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor binding | FGF8,FGF20A,FGF21,FGF1,FGF3,FRS2,FGF1A,FGF4,FGF18B,FGF6A |
| chemoattractant activity | CXCL12,VHL,CCL15,FGF10,CXCL12A,HMGB1,FIGF,CCL16,VEGFB,VEGFA |
| heparin binding | SELP,CECR1,HDGF,NRP1A,APLP2,LPA,APOB,LPL,SOST,FGFBP3 |
| growth factor activity | NENF,FGF6,LFT2,HBEGF,MANF,Artn,IL5,GDF11,CTGF,PRL2C3 |
| cytokine activity | Ccl9,EDN1,OSM,SECTM1,IFNG,IL1B,IFNA16,Ifnl2,IFNB1,IL31 |
| ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity | PRKCB,BUD31,TSG101,ZMIZ2,ACTN4,PPARGC1B,DCAF6,NCOA2,MED4,CCAR1 |
Interacting Protein
FGF2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FGF2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FGF2.
FGFR1;FGFR2;FGFBP1;chondroitin sulfate;ssr;DCN;FGFR1;FGFR2;q6dtl8_bovin;ANOS1
FGF2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
-

High Quality FGF2 Protein for Your Research-20% Off
-

FGF2 Proteins An Invaluable Resource for Cell Culture and Research
-

FGF2 Proteins: An Invaluable Resource for Cell Culture and Research
-

Specialized Cytokines for Organoid Culture — Robust Liver Organoid Culture Solutions
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Correa, D; Somoza, RA; et al. Sequential exposure to fibroblast growth factors (FGF) 2, 9 and 18 enhances hMSC chondrogenic differentiation. OSTEOARTHRITIS AND CARTILAGE 23:443-453(2015).
- Bohnsack, RN; Warejcka, DJ; et al. Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 Receptor in Corneal Keratocytes During Differentiation and in Response to Wound Healing. INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY & VISUAL SCIENCE 55:7697-7708(2014).



.jpg)
.jpg)