Signal Pathway
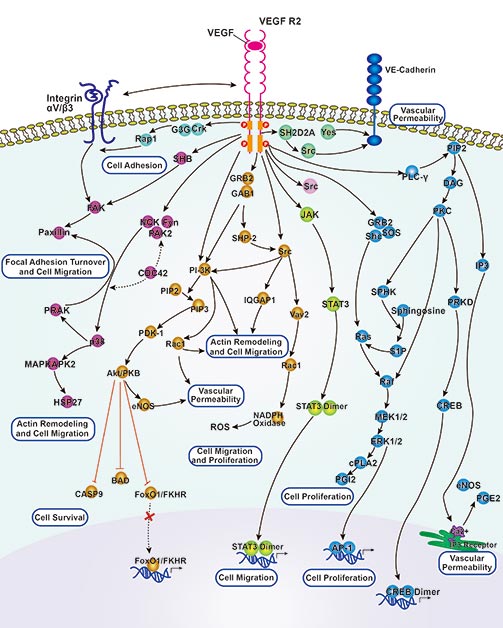
VEGF Signaling Pathway
Wnt Signal Pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signal pathway that regulates cell migration, cell polarity, and neural and organ formation during embryonic development.
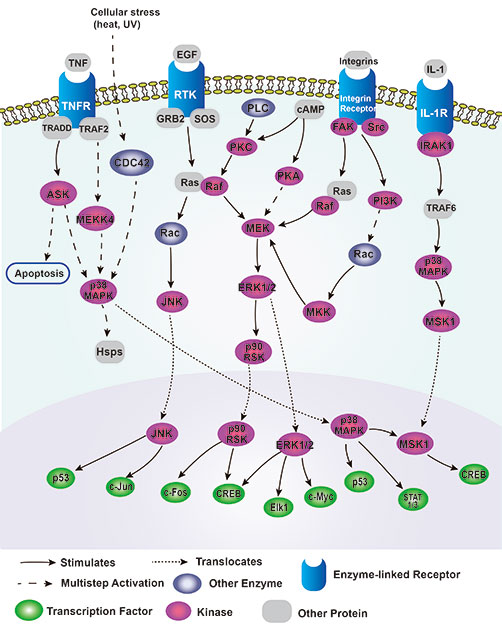
MAPK Signaling Pathway
MAPK Signaling Pathway is an important intracellular signaling pathway, which plays a key role in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, proliferation, survival and apoptosis.
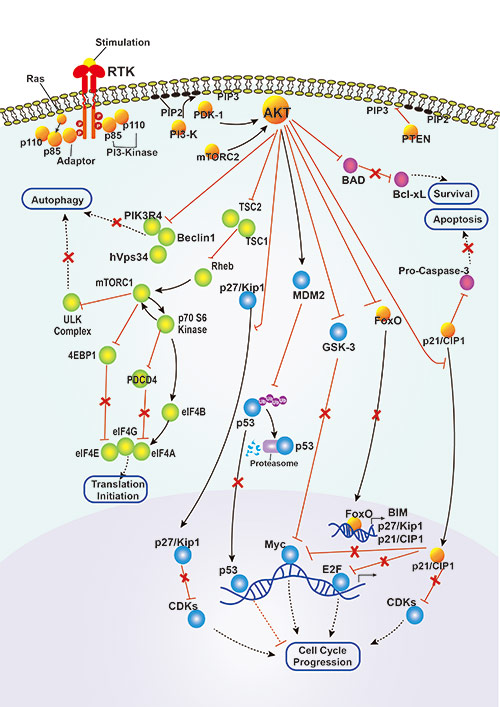
PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
Creative BioMart provides recombinant protein products associated with PI3K/Akt signaling pathways to help researchers gain insight into their roles in cell behavior.
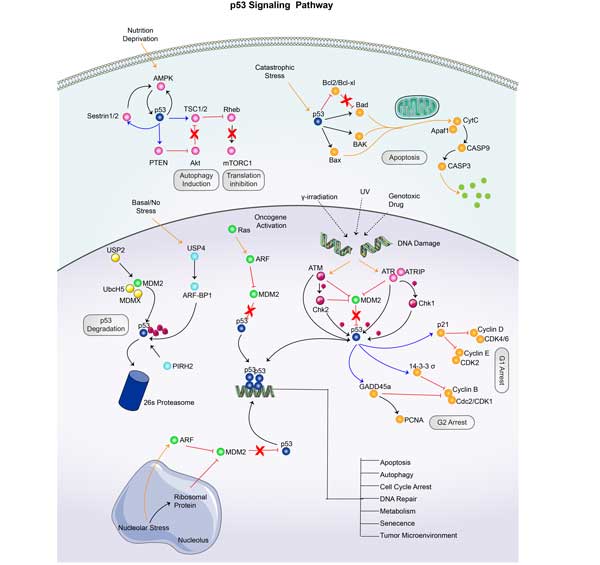
The p53 Pathway
The p53 signaling pathway is a complex biological signaling network, which plays a key role in cell response to DNA damage, cell cycle control, apoptosis, cell metabolism, and maintenance of genome stability.
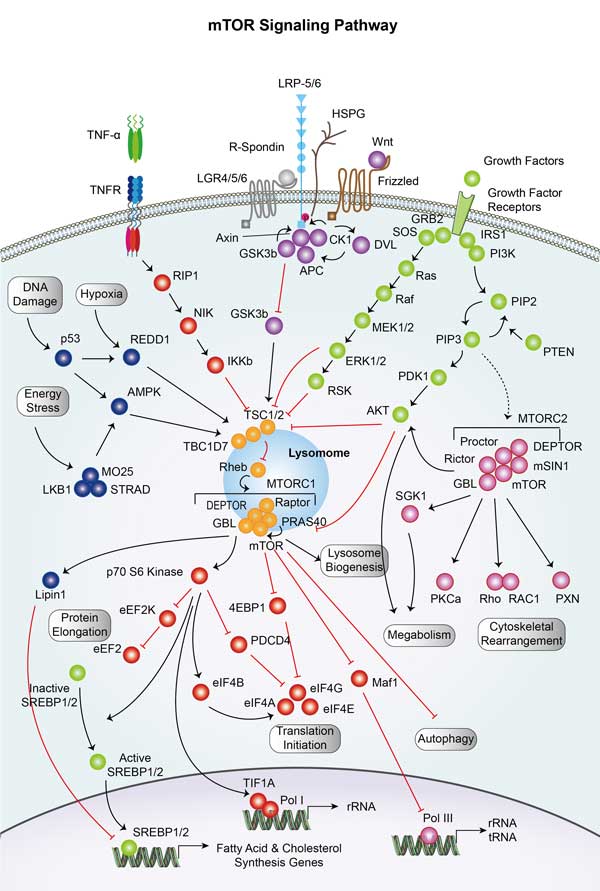
mTOR Signaling Pathway
mTOR Signaling Pathway is a critical intracellular signaling network that plays a pivotal role in regulating various cellular processes, including cell growth, metabolism, proliferation, and survival.
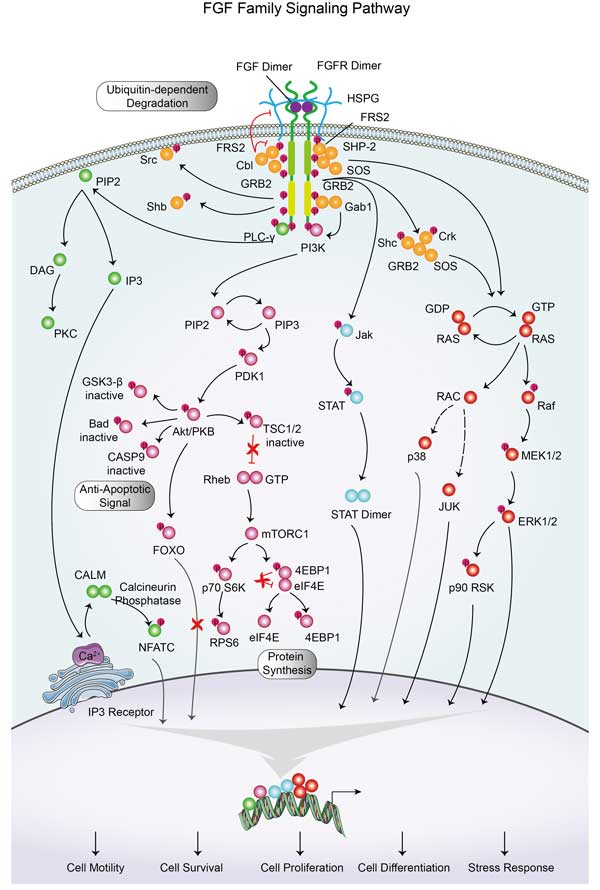
FGF Family Signaling Pathway
FGF Family Signaling Pathway is a complex and multifaceted system that plays a crucial role in a variety of biological processes, including development, tissue repair, and stem cell pluripotency.
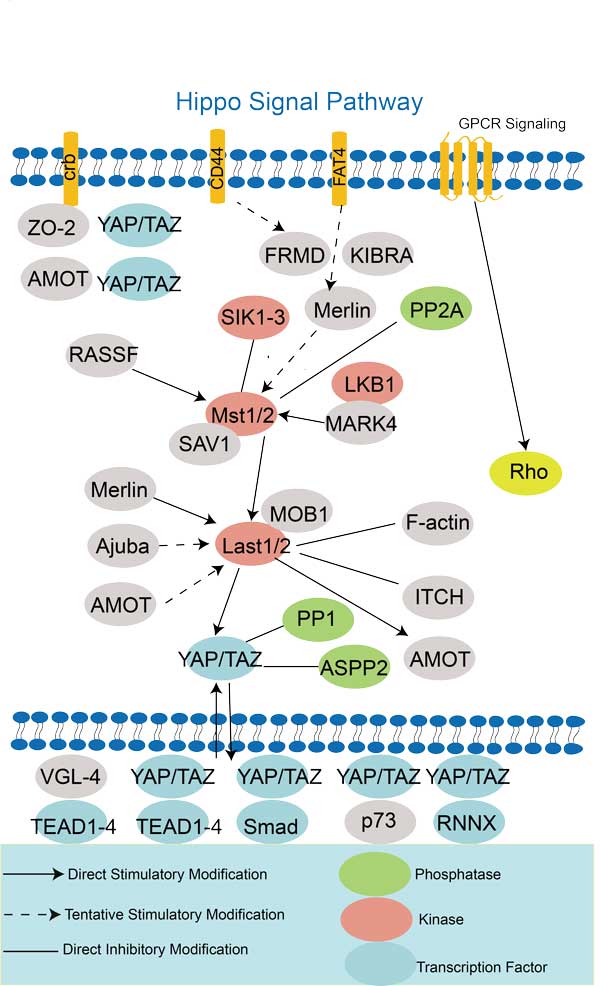
Hippo Signal Pathway
The Hippo signaling pathway is a conserved regulator of proliferation and cell survival in metazoans.
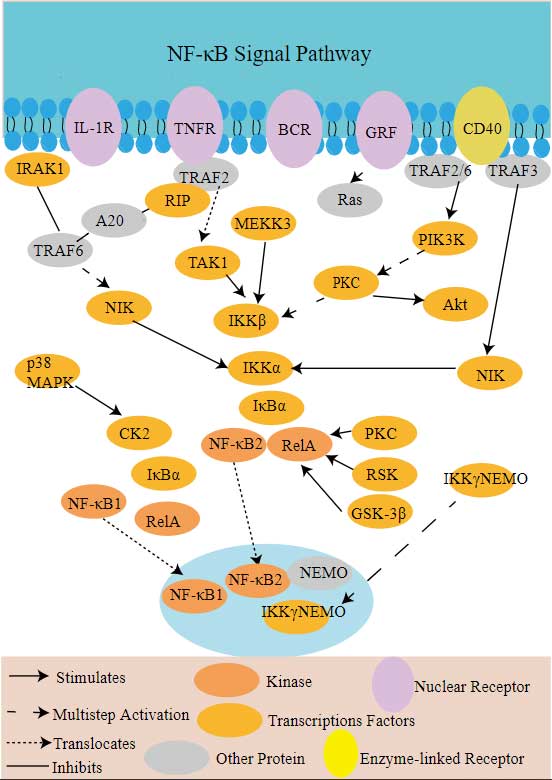
NF-κB Signal Pathway
Notch Signal Pathway is an evolutionarily highly conserved cellular communication mechanism, found in both non-vertebrates and vertebrates.
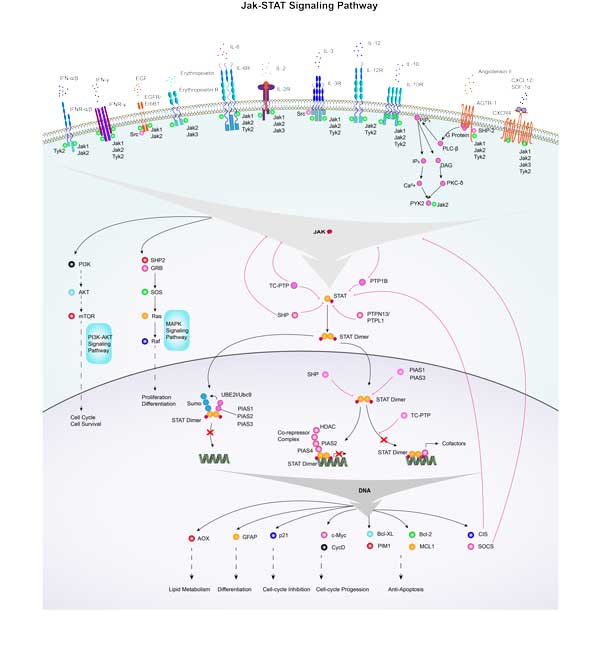
JAK-STAT Signal Pathway
JAK-STAT signal pathway is a cytokine-stimulated signal transduction pathway which consists of three major components: RTK, JAK, and STAT.
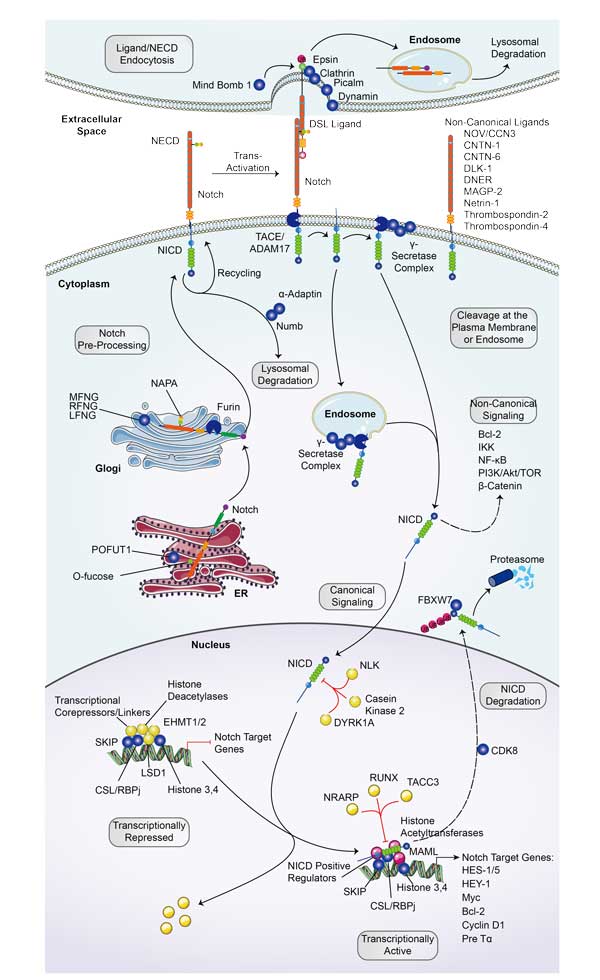
Notch Signal Pathway
Notch Signal Pathway is an evolutionarily highly conserved cellular communication mechanism, found in both non-vertebrates and vertebrates.
Wnt Signal Pathway
Wnt Signal Pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signal pathway that regulates cell migration, cell polarity, and neural and organ formation during embryonic development.
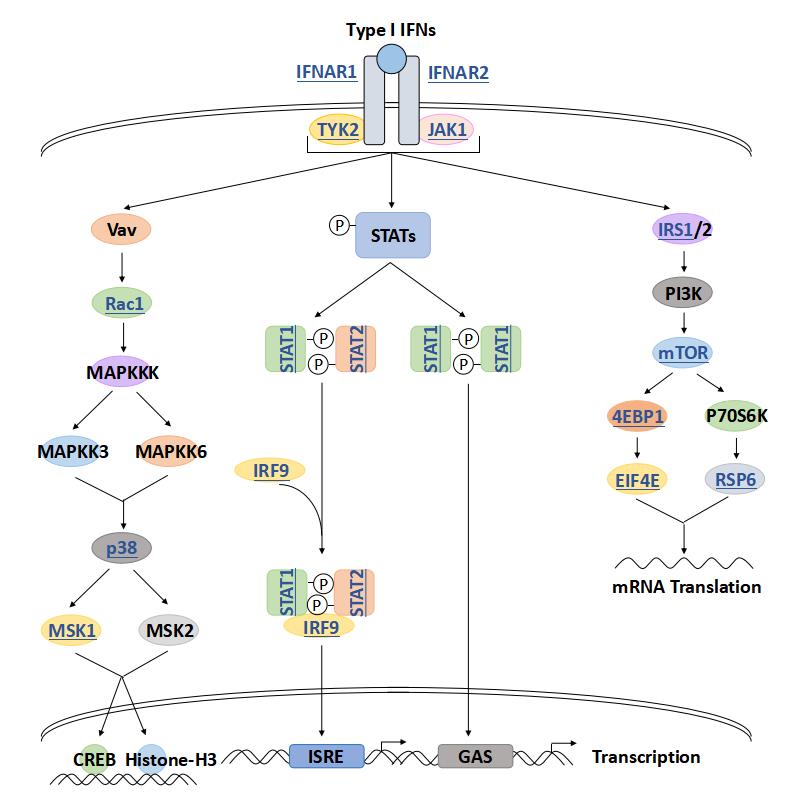
Type I Interferon Signal Pathway
VEGF Signaling Pathway is a key signaling network in cell biology, which plays a crucial role in angiogenesis.
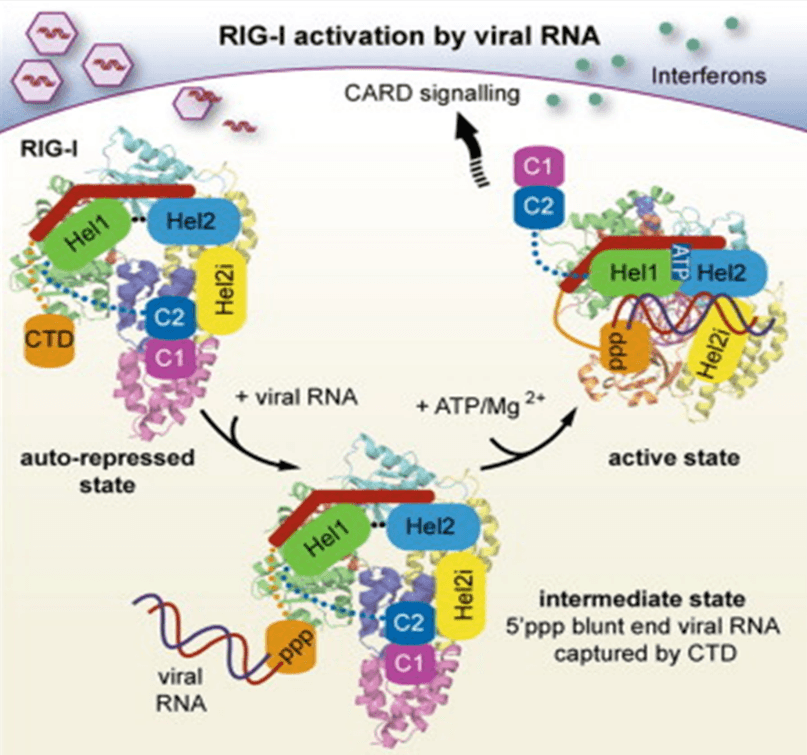
RNA Viruses Triggered Signal Pathway
The p53 signaling pathway is a complex biological signaling network, which plays a key role in cell response to DNA damage, cell cycle control, apoptosis, cell metabolism, and maintenance of genome stability.
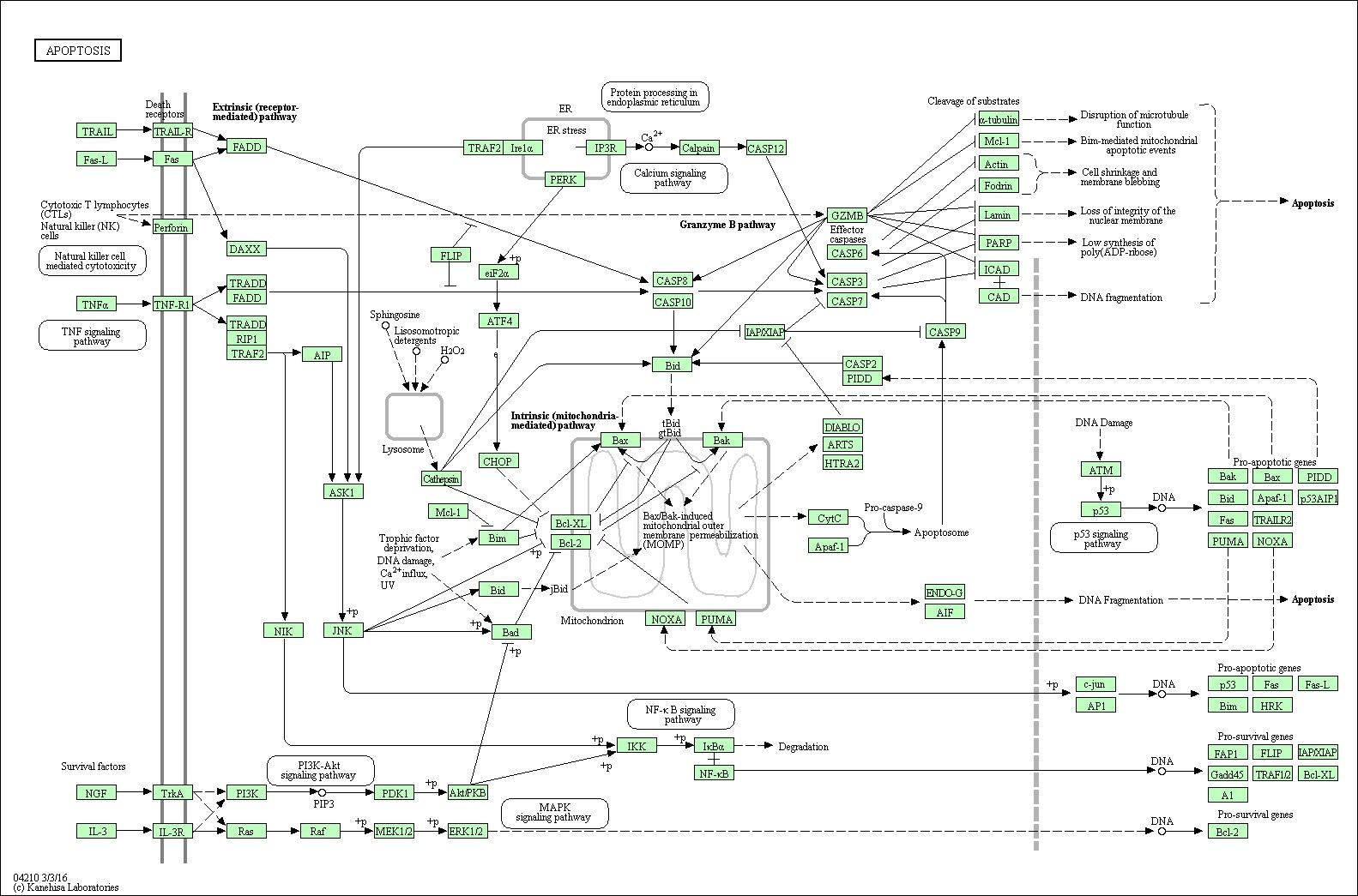
Apoptosis Signal Pathway Overview
Apoptosis Signal Pathway plays an important role in the development, maintenance of tissue homeostasis and immune defense of multicellular organisms.
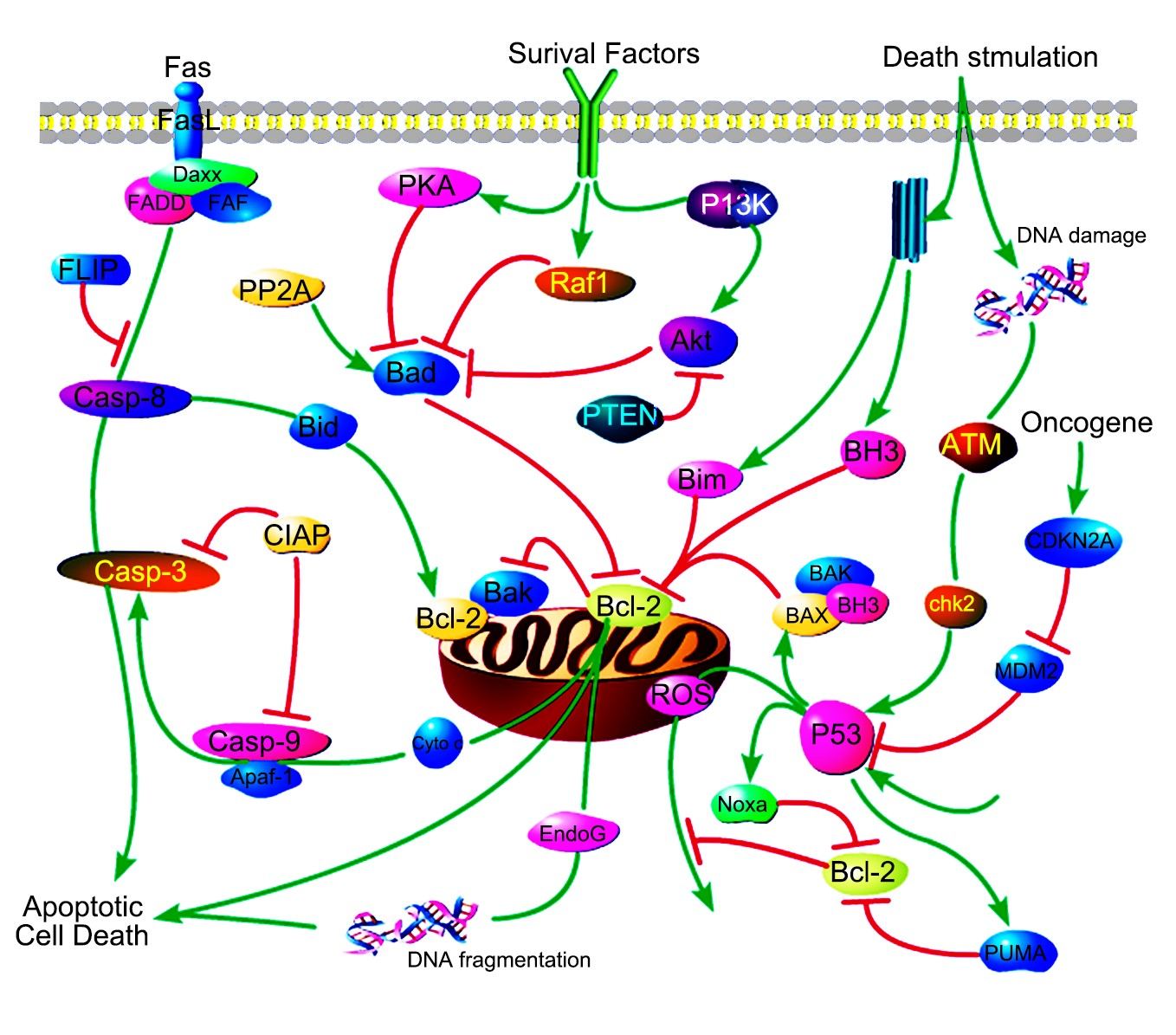
Mitochondrial Control of Apoptosis
Mitochondrial Control of Apoptosis, also called theintrinsic pathway, is the most common mechanism of apoptosis in vertebrates.

