Cytokines
🧪 CXCL10-08H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 22-98 aa
$311.50
$623
/ 50 µg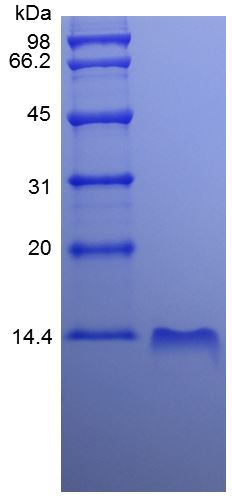
🧪 IFNA2-01H
Source: Yeast
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 165
$174.00
$348
/ 100μg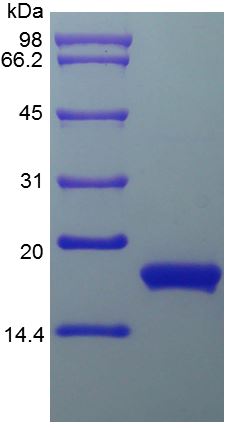
🧪 IFNA2-02H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
🧪 IFNA2-05H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:

🧪 IL10-16H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 160
$72.50
$145
/ 10μg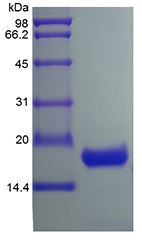
🧪 Il10-17M
Source: E.coli
Species: Mouse
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 160
$99.00
$198
/ 10μg$224.00
$448
/ 100μg$999.00
$1,998
/ 1mg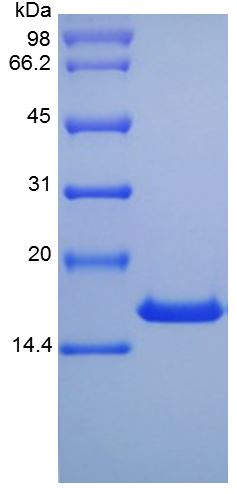

🧪 NGF-05H
Source: CHO
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Ser122-Arg239
🧪 TNFSF8-60H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Gln 63-Asp 234
🧪 IFNB1-14H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-187 a.a.
🧪 CCL1-19H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc
Conjugation:
Protein Length: Lys 24-Lys 96
🧪 CXCL14-25H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
🧪 CCL7-36H
Source: E.coli
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:

🧪 CCL7-46M
Source: E.coli
Species: Mouse
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
🧪 IFNGR1-22H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Fc
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-245 a.a.
🧪 IL3-120H
Source: HEK293
Species: Human
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:

SubCategories
Cytokines—Product Overview
Looking for cytokine products to enhance your research and therapeutic development with precision-engineered solutions? Our high-quality cytokines provide the accuracy and reliability you need to unravel complex immune mechanisms, make transformative discoveries, and develop innovative therapies—all while meeting stringent quality and safety standards.
Jump to Section
Cytokine Product Families
Browse our extensive range of cytokine proteins, grouped by family and function, with direct access to gene and receptor-specific products.
-
Chemokines & Receptor
-
Interferons & Receptor
-
Growth Factor & Receptor
-
Interleukins
-
Four-α-helix Bundle Family
-
IL-1 Family
-
Cystine Knot Cytokines
-
IL-17 Family
Background
Cytokines are small proteins that serve as key intercellular messengers in the immune system. Produced by immune cells, they play a critical role in immune communication and response. Cytokines regulate cellular processes in response to stimuli such as infection, injury, and tumor, driving the activation, proliferation, differentiation, and migration of immune cells. They also exert immunomodulatory effects by influencing the behavior and function of other cells to ensure a coordinated immune response.
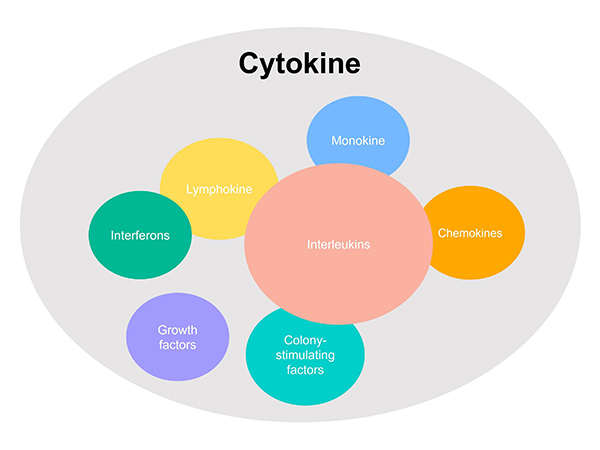
Cytokines are named based on their immune role, structural characteristics, or order of discovery, providing a systematic and consistent framework that highlights their key characteristics. Traditionally, they have been classified into groups such as lymphokines, interleukins, and chemokines. However, due to their redundancy (multiple cytokines performing similar functions) and pleiotropism (a single cytokine affecting multiple biological processes), this classification is now considered largely obsolete.
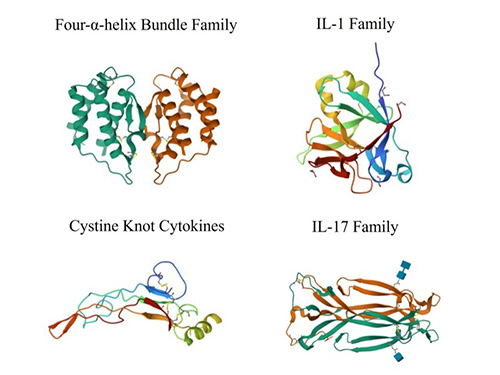
Cytokines are classified into families based on their structure and immune roles. The four-α-helix bundle family, the largest, includes interferons and IL-2. The IL-1 family, with a beta-sheet fold, regulates inflammation. Cysteine knot cytokines, such as TGF-β, have a conserved knot structure. The IL-17 family, with a signal peptide and chain region, includes pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17.
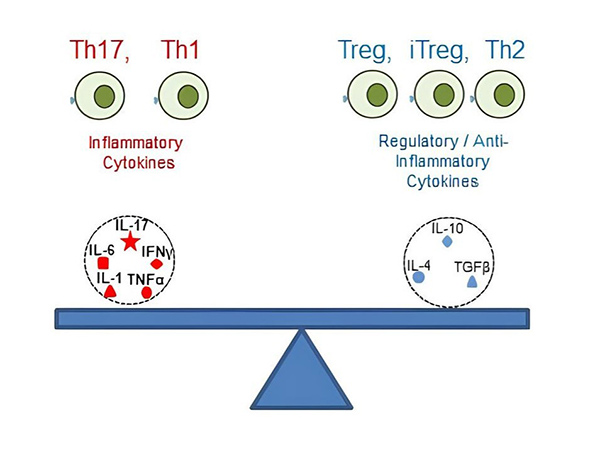
Cytokines regulate cellular responses to infection, inflammation, and cancer and play key roles in immune cell activation, differentiation, and hematopoiesis. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and TNF-α amplify inflammation, while anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β suppress immune activity and promote tissue repair. Balancing these cytokines is critical for immune regulation and recovery.
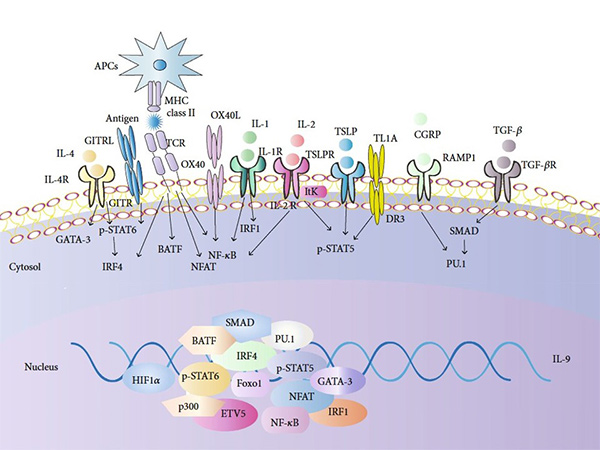
Cytokine signaling refers to the process by which cytokines bind to specific receptors on target cells and trigger intracellular signaling pathways. These pathways typically involve the activation of proteins such as JAKs (Janus kinases) and STATs (signal transducers and activators of transcription), leading to changes in gene expression that regulate immune responses, cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
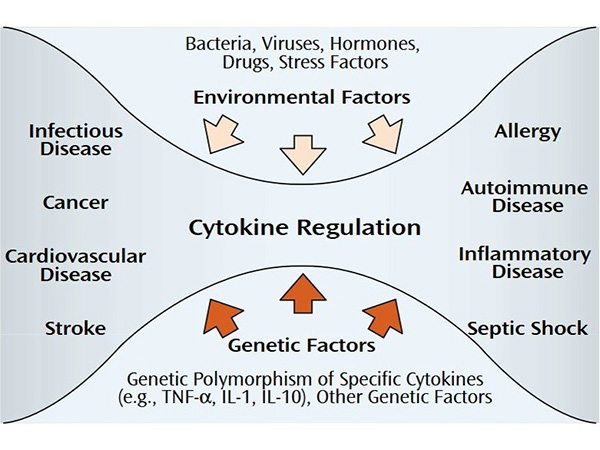
Cytokine regulation involves mechanisms that control the production, activity, and clearance of cytokines to maintain immune homeostasis. This regulation is critical to prevent overactivation (leading to inflammation or autoimmune disease) or underactivation (leading to infection or cancer). Regulatory mechanisms include feedback loops, receptor expression, and interactions with regulatory molecules such as cytokine inhibitors and regulatory T cells.
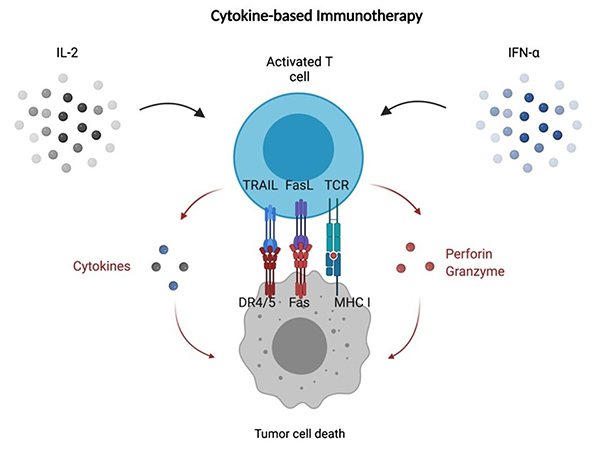
Cytokine therapy involves the use of cytokines or cytokine-modulating agents to treat disease. This may include the administration of cytokines to stimulate immune responses (e.g., interferons for viral infections or cancer) or the use of cytokine inhibitors to reduce excessive immune activity (e.g., TNF inhibitors for autoimmune diseases). Cytokine therapy holds great promise for the treatment of a wide range of immune-related diseases.
Applications of Our Cytokines Products
Medical Therapy
Cytokines enhance immune responses in diseases such as cancer, HIV, and hepatitis, and modulate immunity in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Certain cytokines, like IL-10, help reduce inflammation in conditions like psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Vaccine Development
Used to amplify immune responses, cytokines improve vaccine efficacy.
Cell Growth & Regeneration
As growth factors, cytokines regulate cell proliferation and are used in cancer and regenerative medicine therapies.
Wound Healing & Tissue Repair
Essential for tissue regeneration, cytokines accelerate the healing of injuries and post-surgical recovery.
Bone Growth & Repair
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) promote bone formation and are used in orthopedic treatments.
Disease Diagnosis & Monitoring
Cytokine levels serve as biomarkers for disease detection and monitoring.
Stem Cell Differentiation
Crucial in regenerative medicine, cytokines drive stem cell specialization for targeted therapies.
Fertility Treatment
Regulate key reproductive processes like ovulation, fertilization, and embryo implantation.
Product Features
-
Broad Species Compatibility : Available for multiple species, including human, mouse, rabbit, rat, porcine, canine, bovine, cynomolgus, chicken, dog, Rhesus macaque , guinea pig, and cattle—ideal for cross-species experiments.
-
Diverse Expression Systems : Produced from human cells, E. coli , yeast, and in vitro cell-free systems to suit different research needs.
-
Flexible Labeling Options : Tagged with His, Fc, GST, or Flag for enhanced detection and purification flexibility.
-
High Purity & Structural Integrity : Verified by SDS-PAGE to ensure superior homogeneity.
-
Exceptional Bioactivity : Detection of receptor or antibody binding by ELISA, SPR, BLI and cell-based assays.
-
Stringent Quality Control : ELISA-based QC testing ensures high batch-to-batch consistency.
Case Study
Case 1: Serum Cytokine Pattern
Ou et al ., 2023. Serum cytokine pattern in children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
This study aimed to compare the serum levels of 34 cytokines of children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and explored the specific cytokine pattern of HLH subtypes and the relationship between cytokine levels and prognosis. Various cytokines play important roles in HLH. Different subtypes of HLH have their specific cytokines pattern, and the ratio of cytokines may be more significant in differentiating HLH subtypes than the single one. Elevated GM-CSF and MCP-1 could be useful biomarkers for a poor prognosis for patients with HLH.
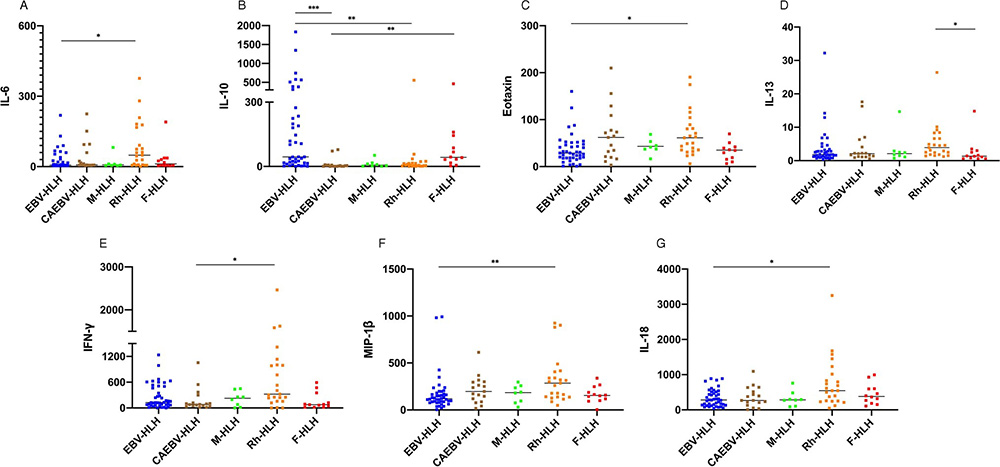
Figure 1. Different levels of IL-6, IL-10, Eotaxin, IL-13, IFN-γ, MIP-1β, and IL-18 in HLH subtypes.
Case 2: Engineered Cytokine
VanDyke et al ., 2022. Engineered human cytokine/antibody fusion proteins expand regulatory T cells and confer autoimmune disease protection.
Low-dose human interleukin-2 (hIL-2) treatment is clinically used to treat autoimmune diseases due to the cytokine's preferential expansion of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, off-target immune cell activation and a short serum half-life limit the clinical potential of IL-2 treatment. Recent work has shown that complexes of hIL-2 and the anti-hIL-2 antibody F5111 overcome these limitations by preferentially stimulating Tregs over immune effector cells. The results of this article provide a roadmap for IC design and establish a Treg-biased immunotherapy that could be clinically translated for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
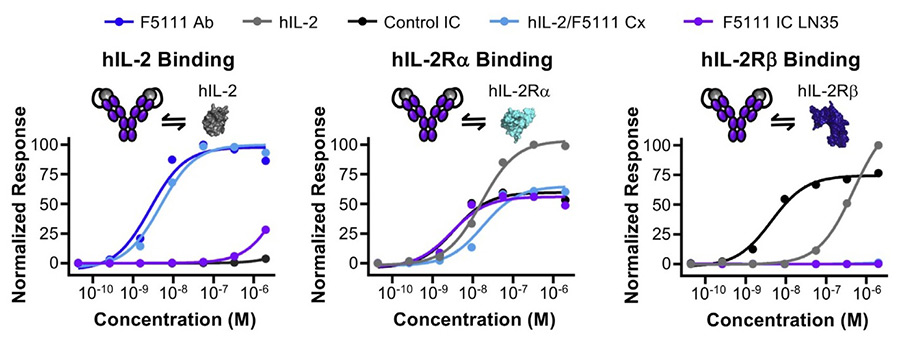
Figure 2. F5111 Figure 2. IC blocks IL-2 binding to IL-2Rβ and biases toward Treg activation. Equilibrium biolayer interferometry-based titrations of F5111 antibody (Ab), hIL-2, control IC, hIL-2/F5111 complex (Cx, 1:1 molar ratio), and F5111 IC LN35 binding to hIL-2 (left), hIL-2Rα (middle), or hIL-2Rβ (right).
Case 3: Cytokine in LVV
Abe et al. , 2022. Cytokine and chemokine multiplex analysis-based exploration for potential treatment and prognostic prediction in large-vessel vasculitis: A preliminary observational study.
Large-vessel vasculitis (LVV) is subclassified into two phenotypes; Takayasu arteritis and giant cell arteritis. Although the pathogenesis of LVV is not fully established, IL-6-IL-17 axis and IL-12-IFN-γ axis play critical roles in the disease development. This article aimed to clarify the association between the disease state and cytokine/chemokine levels, to assess disease course as prognosis and to predict regulators in patients with LVV using the blood profiles of multiple cytokines/chemokines.
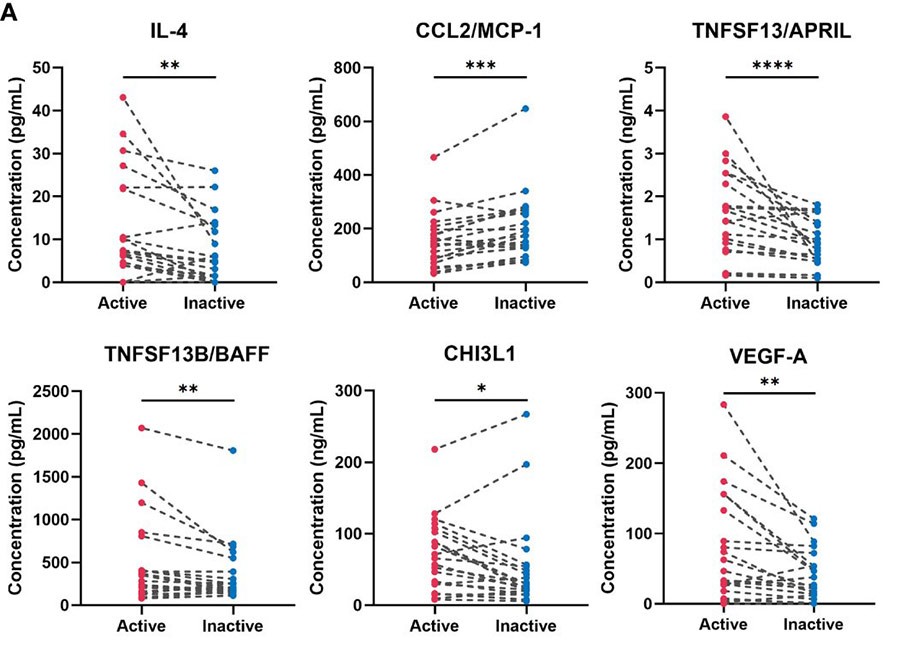
Figure 3. Multiplex blood cytokine/chemokine analysis results in the untreated and treated patients with large-vessel vasculitis (LVV). Twenty-one blood samples from 21 patients with LVV in active or inactive state were examined using multiplex cytokines/chemokines analysis. A dot plot with a line shows individual cases.
FAQs
-
Q: What cytokine and receptor protein products do you offer?
A: We offer a wide range of recombinant cytokines and receptors, including interleukins (ILs), interferons (IFNs), tumor necrosis factors (TNFs), chemokines, colony stimulating factors (CSFs), and growth factors, along with their respective receptors. These proteins are available in multiple species including human, mouse, rat, rabbit, swine, canine, bovine, and more. -
Q: What are the main applications of cytokine and receptor proteins?
A: Our cytokine and receptor proteins are widely used in:
- Medical research (e.g., immunotherapy, cancer, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases)
- Drug discovery and screening
- Cell culture and differentiation studies
- Vaccine development
- Functional assays, including ELISA, SPR, BLI, and cell-based assays
-
Q: What is the purity of your recombinant cytokine proteins?
A: Our cytokine proteins are of high purity, typically exceeding 95% as verified by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analysis. This ensures minimal contamination and high structural homogeneity.
-
Q: How is the bioactivity of your cytokine proteins validated?
A: We validate bioactivity through functional ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) and cell-based assays, assessing receptor-binding activity and downstream signaling. -
Q: What expression systems do you use to produce cytokines and receptors?
A: We use a variety of expression systems tailored to different research needs, including:
- Mammalian cell expression (HEK293, CHO cells): for proper glycosylation and high bioactivity
- E. coli : for cost-effective, high-yield production
- Yeast: for functional expression of secreted cytokines
- In vitro cell-free systems: for rapid production with high purity
-
Q: Do your cytokine proteins contain any purification tags?
A: Yes, we offer proteins with His, Fc, GST, and Flag tags, depending on the application. Tag-free versions are also available upon request.
-
Q: How should I store cytokine and receptor proteins?
A: For specific product information, please visit the product detail page or contact our experts.
-
Q: Do you offer bulk orders or custom protein production?
A: Yes, we do! We offer bulk quantities and custom recombinant protein production services, including:
- Custom species selection
- Expression system selection (mammalian, bacterial, yeast, cell-free)
- Specific purification tags or tag removal
- Special buffer formulations
-
Q: What quality control measures do you implement?
A: We ensure high batch-to-batch consistency through strict quality control (QC) testing, including:
- Purity assessment by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
- Endotoxin testing
- Bioactivity verification using ELISA, SPR, BLI, and functional assays

