F8
-
Official Full Name
coagulation factor VIII, procoagulant component -
Overview
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the F8 gene. Defects in this gene results in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. Factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells outside of the liver throughout the body. This protein circulates in the bloodstream in an inactive form, bound to another molecule called von Willebrand factor, until an injury that damages blood vessels occurs. In response to injury, coagulation factor VIII is activated and separates from von Willebrand factor. The active protein (sometimes written as coagulation factor VIIIa) interacts with another coagulation factor called factor IX. This interaction sets off a chain of additional chemical reactions that form a blood clot. -
Synonyms
Factor VIII;FVIII;F8;coagulation factor VIII, procoagulant component;AHF;F8B;F8C;HEMA;FVIII;DXS1253E;coagulation factor VIII;factor VIII F8B;antihemophilic factor;coagulation factor VIIIc
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Dog
- Mouse
- Pig
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cattle
- Rabbit
- CHO
- Human Plasma
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- His
- GST
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F8-13HFL |
Recombinant Full Length Human F8 Protein
|
CHO | Human | Full L. 2322 amino acids | ||
| F8-3065H |
Human Factor-VIII

|
Human Plasma | Human | Non | ||
| F8-125H | Recombinant Human Coagulation Factor VIII, Procoagulant Component | CHO | Human | Non | ||
| F8-12626H | Recombinant Human F8, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | C-term-208a.a. | |
| F8-048H | Recombinant Human F8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. |
|
| F8-1920D | Recombinant Dog F8 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Dog | His | Met2191~Cys2337 |
|
| F8-1921M | Recombinant Mouse F8 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | His1854~Leu1988 linked by LASTYRLG |
|
| F8-1922P | Recombinant Pig F8 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Pig | His | Gly1669~Ala1824 |
|
| F8-2397H | Recombinant Human Coagulation Factor VIII, Procoagulant Component | E.coli | Human | Non | 2597-2791 a.a. |
|
| F8-6482HCL | Recombinant Human F8 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| F8-1452C | Recombinant Chicken F8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Chicken | His | Gln1766-Thr2075 |
|
| F8-1453M | Recombinant Mouse F8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Lys399-Cys730 |
|
| F8-1454H | Recombinant Human F8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Cys2040-Cys2345 |
|
| F8-2309H | Recombinant Human F8 Protein (Phe2253-Glu2346), N-GST tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | Phe2253-Glu2346 |
|
| F8-25H | Human Blood Coagulation Factor VIII Reference standard | Human | Non |
|
||
| F8-3215H | Recombinant Human F8 protein, His-GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST&His | 1-216aa |
|
| F8-3309R | Recombinant Rat F8 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | His1930~Glu2252 |
|
| F8-4417HF | Recombinant Full Length Human F8 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 216 amino acids |
|
| F8-912C | Recombinant Cattle F8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Cattle | His | Lys2010-Tyr2323 |
|
| F8-913R | Recombinant Rabbit F8 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Rabbit | His | Leu2005-Glu2331 |
|
| F8-P037H | Recombinant Human F8 therapeutic protein | CHO | Human | Non | 2332 aa |
|
Background
What is F8 protein?
F8 (coagulation factor VIII) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq28. Transcript variant 2 encodes a putative small protein, isoform b, which consists primarily of the phospholipid binding domain of factor VIIIc. This binding domain is essential for coagulant activity. F8 protein also known as factor VIII, contains the signal peptide at the N-terminal and the enzyme activity center at the C-terminal. The F8 protein is a giant protein found in the human body, consisted of 2351 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 267 kDa.
What is the function of F8 protein?
The function of the F8 protein, also known as coagulation factor VIII, is to play a critical role in the blood clotting process. It is a crucial factor in the intrinsic pathway of the clotting cascade. Specifically, F8 protein acts as a cofactor for the enzyme activated factor IX (FIXa) in the conversion of factor X (FX) to activated factor X (FXa). This conversion is essential for the subsequent formation of thrombin, which ultimately leads to the formation of a stable blood clot.
F8 related Signaling pathways
The main signaling pathway involving F8 is the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. This pathway is initiated when blood vessels are damaged, and it involves a series of enzymatic reactions that ultimately lead to the activation of factor X and the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
F8 Related Diseases
Defects in this gene results in hemophilia A, a common recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. According to the report, a large number of different mutations of the F8 gene have been found so far, including point mutations, gene deletion, insertion, nonsense mutations, splicing mutations, etc. These mutations often lead to the development of hemophilia A or B. Additionally, factor VIII is regulated by several other proteins and pathways, including von Willebrand factor (VWF). Patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) with VWF severely low or VWD Type 2N (VWD2N), a VWD subtype distinguished by defective VWF binding to F8, may have reduced F8 levels secondary to their VWD.
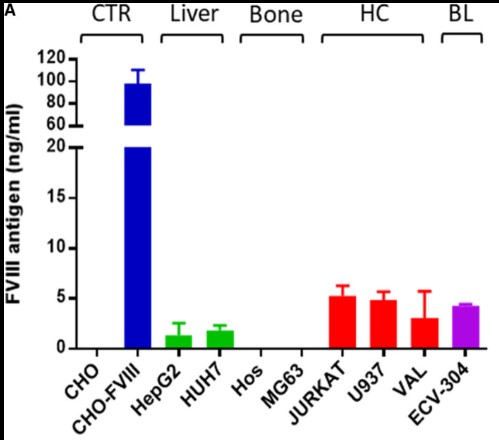
Fig1. Secreted factor VIII protein from cancer cell lines is bioactive. Graphical representation of the measurement of FVIII antigen.
Bioapplications of F8
In hemophilia studies using AAV (adeno-associated virus) for treatment, it has been found that AAV vectors carrying F8 or F9 genes can produce functional FIX or F8 proteins under the control of liver promoters. Or using gene-editing technology to repair mutations in the F8 gene could also treat hemophilia A.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Maitreyee Sharma, 2016
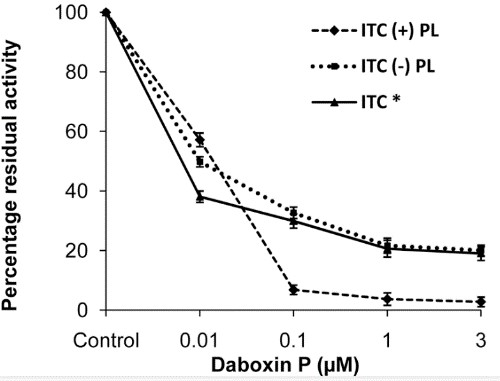
Fig1. Intrinsic tenase complex (ITC), in the presence or absence of phospholipid and alkylated daboxin P (indicated by *).
Case Study 2: Victor Tse, 2024
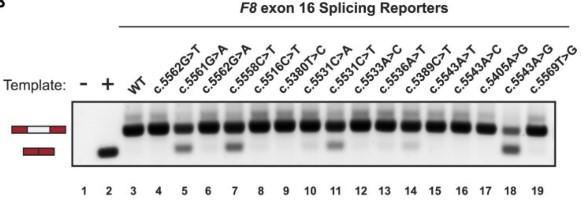
Fig2. A representative agarose RNA gel showing the effects on splicing by various HA-causing variants in a panel of F8 exon-16 splicing reporters.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F8-3624H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
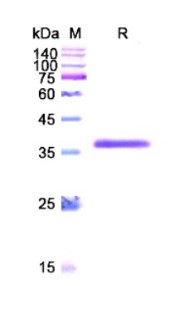
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F8-2309H)
Involved Pathway
F8 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways F8 participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with F8 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | PLAU,C6,F2,C3AR1,F13B,CPB2,C5AR1,CR1L,C1QC,PLAUR |
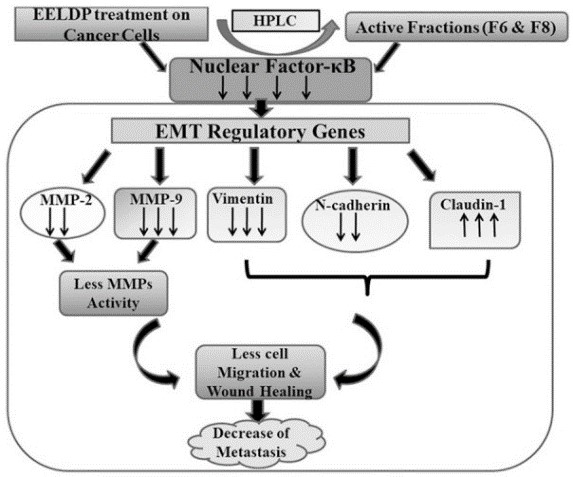
Pictorial diagram showing the inhibition of in vitro metastasis by ethanolic extracts of leaves of D. pentagyna (EELDP) and active fractions (F6 and F8) treatment.
Protein Function
F8 has several biochemical functions, for example, copper ion binding,oxidoreductase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by F8 itself. We selected most functions F8 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with F8. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | NXF1,ETF1,RRAGA,GPM6A,ASNS,ZFYVE19,GRM6,CD160,RPS16,CCDC24 |
| oxidoreductase activity | ALOX8,TXNRD3,ADOB,CYP2P6,CYP2K18,HADHAB,NDOR1,CYP3C1,TYRP1B,LDHBA |
| copper ion binding | COX11,MOXD1L,LOXL2,HAMP,PAM,MT1,SOD3A,LOXL3B,LOXL3,IL1A |
Interacting Protein
F8 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with F8 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of F8.
kv312_human;EIF1B;CALR;GGA1;UBQLN1;MAP1LC3A
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Anderson, DR; Cameron, AC; et al. WASP-20b and WASP-28b: a hot Saturn and a hot Jupiter in near-aligned orbits around solar-type stars. ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS 575:-(2015).
- Hashemi, SM; Fischer, K; et al. Improved prediction of inhibitor development in previously untreated patients with severe haemophilia A. HAEMOPHILIA 21:227-233(2015).




