Biopharmaceutical Process and Product Related Impurities Analysis
Understanding Process- and Product-Related Impurities in Biopharmaceuticals
Biopharmaceuticals, including monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, and vaccines, are complex biological molecules produced through the use of living cells. Unlike chemically synthesized small-molecule drugs, biopharmaceuticals involve intricate manufacturing processes that can introduce various impurities. These impurities must be thoroughly characterized and controlled to ensure product safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance.
Impurities associated with biopharmaceuticals are generally categorized into two types:
- Process-Related Impurities: These impurities originate from the manufacturing process itself and may include host cell proteins (HCPs), residual host cell DNA, media components, process reagents, solvents, and leachables from equipment. Such impurities represent unintended residual materials that can be introduced at different stages of production.
- Product-Related Impurities: These impurities are structurally or chemically related to the biopharmaceutical product but deviate from the desired molecular form. Examples include misfolded proteins, truncated variants, aggregates, chemically modified forms (e.g., deamidation or oxidation), and heterogeneity in post-translational modifications such as glycosylation.
Importance of Impurity Analysis
The rigorous analysis of both process- and product-related impurities is critical for multiple reasons:
- Safety: Certain impurities have the potential to elicit immunogenic responses or exhibit toxicity.
- Efficacy: Impurities can adversely affect the biological activity and stability of the biopharmaceutical product.
- Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory agencies, including the FDA and EMA, mandate comprehensive impurity profiling to ensure product quality.
- Process Optimization: Monitoring impurities facilitates improved process control and consistency in manufacturing.
At Creative BioMart, we offer comprehensive analysis services to identify, quantify, and characterize both process-related and product-related impurities across the full development cycle. Our advanced analytical platforms and experienced scientific team enable accurate profiling of molecular variants and contaminants. These services are essential for regulatory submissions, lot release testing, and long-term stability studies.
Our Impurity Analysis Services for Biopharmaceutical Process Development
1. Content, Purity, and Impurity Profiling
|
|
 Protein Content Determination |
 Purity Assessment |
|
Techniques |
Kjeldahl method, Lowry assay, Bradford assay, UV absorbance (A280/A230), HPLC, SDS-PAGE |
RP-HPLC, GF-HPLC (Size Exclusion), IEX-HPLC, HIC-HPLC, Capillary Electrophoresis (CE), SDS-PAGE |
|
Purpose |
To determine the overall protein concentration in the final product. |
To confirm the presence and percentage of the target product relative to total protein. |
2. Process-Related Impurity Analysis
Impurities introduced during upstream and downstream processing.
|
Impurity |
Methods |
|---|---|
|
Residual DNA |
qPCR, RT-PCR |
|
Host Cell Proteins (HCP) |
ELISA-based detection |
|
Mycoplasma |
PCR and culture-based detection systems |
|
Leachables and Extractables |
HPLC, gas chromatography |
|
Protein A Ligand |
Residual ELISA quantification |
|
Media Components |
ELISA for serum proteins, hormones, growth factors |
|
Other Residuals
|
Analyzed using tailored analytical techniques based on residue type. |
3. Product-Related Impurity Analysis
Molecular variants of the target biologic generated during production or storage.
|
Impurity |
Methods |
|---|---|
|
Aggregates, Subunits, and Fragments |
SE-HPLC, SDS-PAGE |
|
Oxidation/Deamidation |
RP-HPLC, Peptide Mapping, Test Kits |
|
N-terminal Cyclization & Modifications |
LC-MS, Edman Degradation, Peptide Mapping |
|
Truncation and Misfolding |
SDS-PAGE, Western Blot |
|
Phosphorylation, Sulfation |
IEF, IEX-HPLC, Peptide Mapping |
|
Glycosylation |
Lectin-binding, LC-MS, CE |
Why Our Analytical Expertise Ensures Reliable Impurity Profiling
- Regulatory-Ready Expertise: Our methods align with FDA, EMA, and ICH guidelines.
- Extensive Assay Portfolio: Broad coverage of physical, chemical, and biological impurities.
- Experienced Scientific Team: Skilled in identifying low-level impurities and complex PTMs.
- End-to-End Support: From early-stage characterization to lot-release and stability testing.
- Customized Reporting: Comprehensive data interpretation and documentation suitable for regulatory submissions.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Employing advanced tools for precise and efficient impurity detection.
Case Studies: Identifying and Mitigating Biopharmaceutical Impurities
* NOTE: We prioritize confidentiality to safeguard our clients’ technology and intellectual property. As an alternative, we present selected published research articles as representative case studies. For details on the assay services and products used in these studies, please refer to the relevant sections of the cited literature.
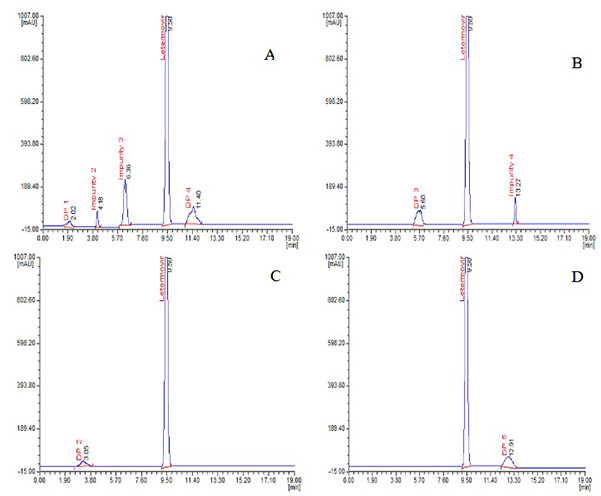
Case 1: HPLC analysis of letermovir impurities and LC-MS/MS characterization of degradants
Bhupatiraju et al., 2023. doi:10.25135/jcm.98.2311.2975
This study presents a simple, highly sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for evaluating letermovir and its process-related impurities, as well as the characterization of its stress-induced degradation. Using this method, letermovir and four impurities exhibited distinct retention times, demonstrating good sensitivity, linearity, and validation performance. Stress tests according to ICH Q1A(R2) revealed five degradation products that were characterized by LC-MS/MS. This method is suitable for the routine profiling of impurities and the analysis of letermovir degradation.
Case 2: Hydrophobic interaction chromatography in continuous flow-through mode for product-related variant removal
Wang et al., 2024. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465356
Product-related impurities in monoclonal antibody purification are difficult to remove due to their close similarity to the target molecule. Frontal chromatography using hydrophobic interaction resins can separate these impurities but often reduces product yield. This study introduces a two-column multicolumn continuous chromatography (MCC) process that uses frontal analysis to remove high levels of product-related impurities while minimizing yield loss. By connecting the columns during the product chase step, product wash losses are captured without in-process adjustments. This approach improved yield by 10% while maintaining 99% purity. A validated mechanistic model was developed to predict breakthrough behavior and optimize process performance.
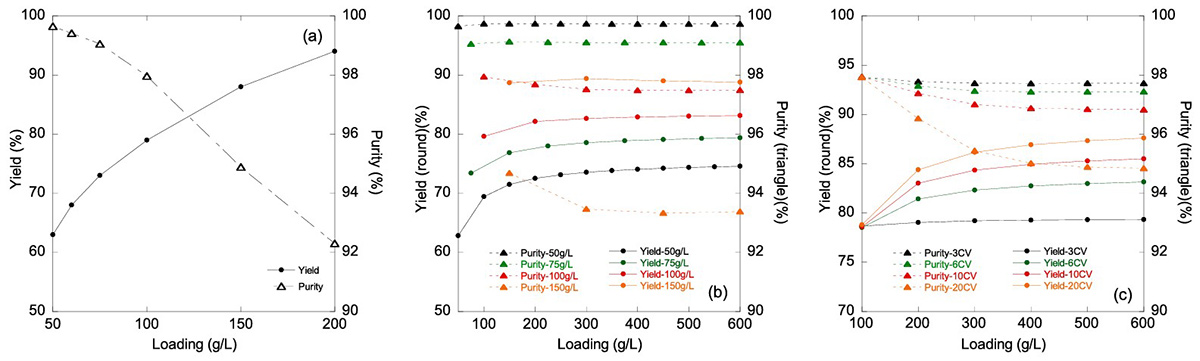
Figure 2. Yield and purity as a function of loading for (a) batch mode operation from 50 to 200 g/L resin loading (b) MCC mode operation at 50 g/L resin (black), 75 g/ L resin (green), 100 g/L resin (red) and 150 g/L resin (orange) loading with fixed 6 CV intermediate chase volume for each cycle. (c) MCC mode operation at 3 CV (black), 6 CV (green), 10 CV (red) and 20 CV (orange) chase volume at fixed 100 g/L resin loading for each cycle. (Wang et al., 2024)
Testimonials on Our Biopharmaceutical Impurity Analysis Services
“The impurity profiling services provided by Creative BioMart were instrumental in advancing our monoclonal antibody program. Their thorough characterization of low-level aggregates and oxidation variants enabled us to refine our purification process and improve stability. Their team’s detailed reports and proactive communication made regulatory submissions much smoother.”
— R&D Director | Global Pharmaceutical Company
“We required precise detection of host cell proteins and residual DNA for our gene therapy candidate. Creative BioMart’s sensitive assays and rapid turnaround times helped us maintain tight control over process-related impurities, ensuring product safety without delaying our timelines. The collaboration was seamless, and their expertise in complex biological matrices stood out.”
— Senior Scientist | Gene Therapy Biotech
“Our vaccine development benefited greatly from their extensive impurity analysis portfolio. The ability to differentiate closely related product variants and identify minor glycosylation changes was critical in optimizing our formulation. Their end-to-end support—from initial characterization to lot release testing—gave us confidence in every batch.”
— Analytical Development Manager | Vaccine Manufacturer
“We faced challenges detecting low-abundance truncated proteins in our recombinant enzyme product. Creative BioMart’s innovative use of mass spectrometry and capillary electrophoresis resolved these issues efficiently. Their customized reports provided clear interpretation, which helped our regulatory filings and internal decision-making.”
— Director of Analytical Sciences | Specialty Biopharmaceutical Company
FAQs on Process-Related Impurity Testing and Regulatory Compliance
-
Q: How do your impurity analysis methods comply with regulatory guidelines?
A: Our analytical methods are fully aligned with FDA, EMA, and ICH guidelines, ensuring that the data we generate is regulatory-ready. We design assays and reporting formats to meet stringent submission requirements, helping you streamline your approval process. -
Q: What types of impurities can your assays detect?
A: We offer a broad assay portfolio that covers physical impurities (e.g., aggregates), chemical variants (e.g., oxidized or deamidated forms), and biological impurities (e.g., host cell proteins and residual DNA). This comprehensive coverage supports thorough impurity profiling throughout product development. -
Q: What technology do you use for impurity detection?
A: We employ cutting-edge analytical platforms and data analytics tools to deliver high sensitivity, accuracy, and efficiency in impurity detection. This integration of advanced technology ensures reliable and reproducible results. -
Q: Can you handle low-level impurities and complex post-translational modifications (PTMs)?
A: Absolutely. Our experienced scientific team specializes in identifying and quantifying trace-level impurities and complex PTMs using advanced techniques such as mass spectrometry and capillary electrophoresis, ensuring precise characterization. -
Q: Do you provide support throughout the biopharmaceutical development lifecycle?
A: Yes, we offer end-to-end support ranging from early-stage product characterization to lot-release and stability testing. This continuity helps maintain impurity control and quality assurance at every critical stage. -
Q: How customizable are your reports and data interpretation?
A: We tailor our reporting to meet your specific regulatory and project needs, providing comprehensive data interpretation, clear documentation, and actionable insights suitable for regulatory submissions and internal decision-making.
Resources
Related Services
- Downstream Processing Development
- Pharmaceutical Product Release Testing
- Quality Control
- Protein Characterization
- Protein Analytical Service
- Protein Microarray Service
- Protein Quantitation Service
Related Products
References:
- Bhupatiraju RV, Kumar BS, Peddi P, Tangeti VS. An effective HPLC method for evaluation of process related impurities of Letermovir and LC-MS/MS characterization of forced degradation compounds. J Chem Metrol. 2023;(2):181-198. doi:10.25135/jcm.98.2311.2975
- Wang Y, Bhaskar U, Chennamsetty N, et al. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography in continuous flow-through mode for product-related variant removal. Journal of Chromatography A. 2024;1736:465356. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465356
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions