CD79A
-
Official Full Name
CD79a molecule, immunoglobulin-associated alpha -
Overview
The B lymphocyte antigen receptor is a multimeric complex that includes the antigen-specific component, surface immunoglobulin (Ig). Surface Ig non-covalently associates with two other proteins, Ig-alpha and Ig-beta, which are necessary for expression and function of the B-cell antigen receptor. This gene encodes the Ig-alpha protein of the B-cell antigen component. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. -
Synonyms
CD79A;CD79a molecule, immunoglobulin-associated alpha;CD79A antigen (immunoglobulin associated alpha) , IGA;B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain;MB 1;ig-alpha;MB-1 membrane glycoprotein;surface IgM-associated protein;CD79
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cattle
- Cynomolgus
- Dog
- Bovine
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- Mouse
- GST
- rFc
- Fc
- His
- Non
- Flag
- T7
- Avi
- Cy5.5
- PerCP
Background
What is CD79A Protein?
CD79A gene (CD79a molecule) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. The B lymphocyte antigen receptor is a multimeric complex that includes the antigen-specific component, surface immunoglobulin (Ig). Surface Ig non-covalently associates with two other proteins, Ig-alpha and Ig-beta, which are necessary for expression and function of the B-cell antigen receptor. This gene encodes the Ig-alpha protein of the B-cell antigen component. The CD79A protein is consisted of 226 amino acids and CD79A molecular weight is approximately 25.0 kDa.
What is the Function of CD79A Protein?
The CD79A protein, also known as Igα, is a key component of the B cell receptor (BCR) complex and works together with Igβ (CD79B) to be essential for proper function and signaling of B cells. CD79A and CD79B form non-covalently bound heterodimers on the surface immunoglobulin (Ig) molecules of B cells that assist B cells in recognizing and binding antigens. Once BCR binds to the antigen, CD79A and CD79B trigger intracellular signaling processes through their immune receptor tyrosine activation motif (ITAM) domains. CD79A plays a critical role in the development and maturation of B cells and is involved in signal integration, survival, and antigen presentation of B cells. In addition, CD79A is also necessary for the expression of B cell receptors on the cell surface, which contributes to proper activation and function of B cells.
CD79A Related Signaling Pathway
In the signaling process, the intracellular domains of CD79A and CD79B contain the immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif (ITAM), which is directly involved in the mediation of BCR signaling through the phosphorylation of SRC-family kinases. At multiple stages of normal B cells, BCR signaling is critical to their performance, capable of inducing a wide range of cellular responses associated with B cell development and activation. In addition, post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and glycosylation of CD79A and CD79B define their own assembly, BCR expression, BCR endocytosis, strength of signal transduction, intracellular transport, and antigen processing and presentation.
CD79A Related Diseases
In B-cell malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL), CD79A mutations or changes in expression levels are closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of the disease. For example, in DLBCL, mutations in CD79A may enhance BCR signaling and promote tumor cell survival and proliferation. In addition, abnormalities in CD79A may also be associated with autoimmune diseases and immune deficiency states, but its specific role in these diseases needs further study.
Bioapplications of CD79A
Due to changes in the expression level or functional status of CD79A in a variety of B-cell-related diseases, it can be used as a biomarker to help diagnose diseases such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). In certain B-cell malignancies, abnormal activation or expression of CD79A is associated with the progression of the disease and, therefore, it is a potential therapeutic target. Based on the key role of CD79A in B-cell signaling, novel drugs that can specifically bind to CD79A and regulate its function are being developed, such as antibody-drug couplings (ADCs) and other small molecule inhibitors. Because the expression and functional status of CD79A may affect a patient's response to a specific treatment, it can be used to guide personalized medical strategies to select the most appropriate treatment for the patient.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kanutte Huse, 2022
Although the requirement of a CD79A/CD79B heterodimer for BCR complex assembly and surface expression is well established based on mice models, few studies have investigated this in human mature B cells. In this study, researchers found that human tonsillar B cells with high surface expression of IgM or IgG had potentiated BCR signaling compared with BCRlow cells. They explored the mechanism for IgM surface expression by CRISPR/Cas9-induced deletion of CD79A or CD79B in four B lymphoma cell lines. Deletion of either CD79 protein caused loss of surface IgM in all cell lines and reduced fitness in three. From two cell lines, we generated stable CD79A or CD79B knockout clones and demonstrated that loss of CD79A or CD79B caused a block in N-glycan maturation and accumulation of immature proteins, compatible with retention of BCR components in the endoplasmic reticulum. Rescue experiments with CD79B wild-type restored surface expression of CD79A and IgM with mature glycosylation, whereas a naturally occurring CD79B G137S mutant disrupting CD79A/CD79B heterodimerization did not.
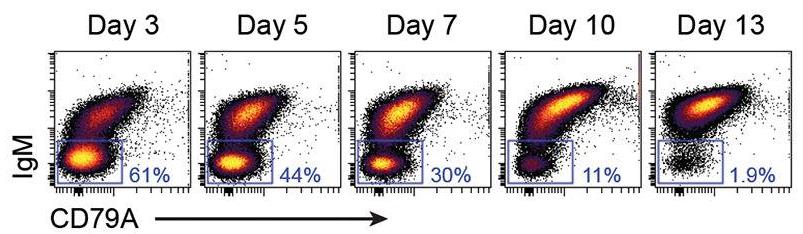
Fig1. CD79A-edited MINO cells analyzed at day 3–13 after transduction.
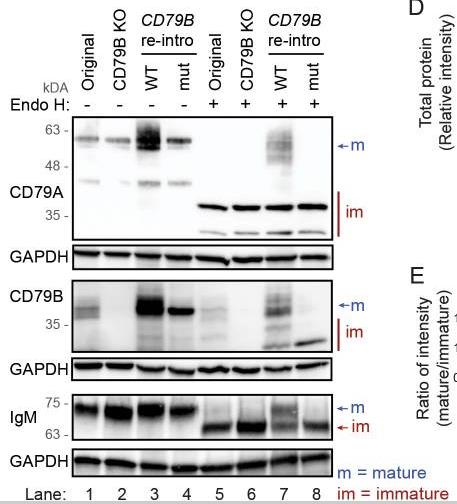
Fig2. Protein lysates were left untreated or treated with Endo H for 1 hour before western blot analysis.
Case Study 2: Linh Tran Nguyen Truc, 2023
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a common genetic disorder arising from developmental and postnatal processes. Defects in primary cilia and their signaling (eg, mTOR) underlie the pathogenesis. However, how mTOR regulates tubular integrity remains unclear. The paucity of faithful models has limited our understanding of pathogenesis and, therefore, the refinement of therapeutic targets. To understand the role of mTOR in early cystogenesis, we studied an in-house mouse model, Cd79a-Cre;Tsc1ff. (Cd79a-Tsc1 KO hereafter), recapitulating human autosomal-dominant PKD histology. Cre-mediated Tsc1 depletion driven by the promoter for Cd79a, a known B-cell receptor, activated mTORC1 exclusively along the distal nephron from embryonic day 16 onward. mTORC1 was activated in a portion of cyst-lining cells and occasionally even when Tsc1 was not depleted, implying a non-autonomous mechanism.
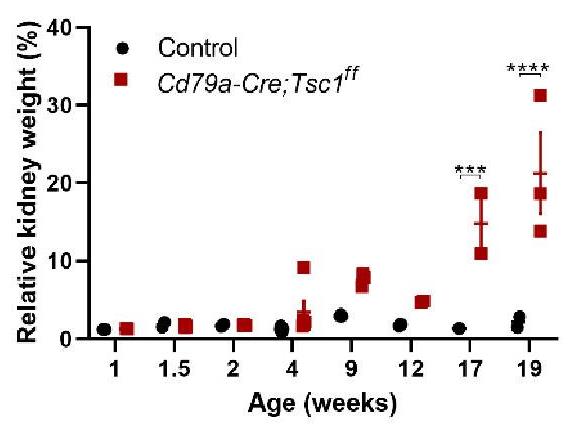
Fig3. Progressive enlargement of Cd79a-Tsc1 KO kidneys.
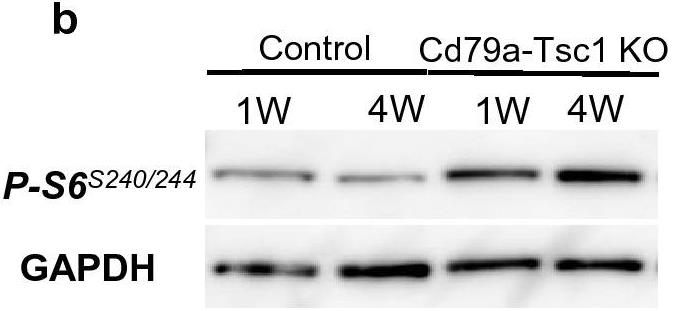
Fig4. Analysis of whole kidney lysates indicates that p-S6 expression is enriched in Cd79a-Tsc1 KO kidneys.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD79A-6887H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD79A-1444H)
Involved Pathway
CD79A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD79A participated on our site, such as B cell receptor signaling pathway,Primary i,nodeficiency, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD79A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| nodeficiency | Cd79b,PTPRC,ICOS,ORAI1,ZAP70,CD40LG,TNFRSF13B,CD3D,Cd79a,IL2RG |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | PIK3AP1,MAPK3,CARD11,CD19,BANK1,PTPN6,NRAS,GSK3AB,AKT2,GRB2 |
| Primary i | RFXAP,IGLL1,TAP2,DCLRE1C,CD40LG,RAG2,AICDA,ZAP70,PTPRC,Cd79a |
Protein Function
CD79A has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,transmembrane signaling receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD79A itself. We selected most functions CD79A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD79A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | CLDN3,Cd79a,OR2A4,GP6,IL1R1,TNFRSF10C,THBD,OR4D2,BAI2,P2RX6 |
| protein binding | ATP6V0C,WASF2,SLC25A18,TOR1A,PDCD5,ZW10,LSM4,ZNF329,CA8,PTPLAD1 |
Interacting Protein
CD79A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD79A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD79A.
FATE1;FN1
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chang, CH; Wang, Y; et al. Extensive crosslinking of CD22 by epratuzumab triggers BCR signaling and caspase-dependent apoptosis in human lymphoma cells. MABS 7:199-211(2015).
- Chung, TH; Kim, HJ; et al. Multicentric epitheliotropic T-cell lymphoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). VETERINARY CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 43:601-604(2014).



