CD3E
-
Official Full Name
CD3e molecule, epsilon (CD3-TCR complex) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is the CD3-epsilon polypeptide, which together with CD3-gamma, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. This complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. The genes encoding the epsilon, gamma and delta polypeptides are located in the same cluster on chromosome 11. The epsilon polypeptide plays an essential role in T-cell development. Defects in this gene cause immunodeficiency. This gene has also been linked to a susceptibility to type I diabetes in women. -
Synonyms
CD3E;CD3e molecule, epsilon (CD3-TCR complex);CD3e antigen, epsilon polypeptide (TiT3 complex);T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain;CD3-epsilon;T-cell surface antigen T3/Leu-4 epsilon chain;T-cell antigen receptor complex, epsilon subunit o;T3E;TCRE;IMD18;T-cell antigen receptor complex,
Recombinant Proteins
- Cynomolgus
- Human
- Mouse
- Canine
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Monkey
- Western lowland gorilla
- Pig
- Dog
- Sheep
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- CHO
- Yeast
- His
- Flag
- Fc
- GST
- Avi
- mFc
- Non
- lFc
- lIgG2b
- Myc
- DDK
- rFc
Background
What is CD3E protein?
CD3E gene (CD3 epsilon subunit of T-cell receptor complex) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q23. The protein encoded by this gene is the CD3-epsilon polypeptide, which together with CD3-gamma, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. This complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. The CD3E protein is consisted of 207 amino acids and CD3E molecular weight is approximately 23.1 kDa.
What is the function of CD3E protein?
MAdCAM-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule that controls lymphocyte migration to the intestinal mucosa. Although MAdCAM-1 is known to play a role in chronic intestinal inflammation, the regulatory mechanisms of its expression have been poorly studied. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) was found to induce MAdCAM-1 mRNA and protein expression in a dose - and time-dependent manner by activating tyrosine kinase, p42/44, p38 MAPK, and NF-κB/PARP signaling pathways. In addition, the distribution of MAdCAM-1 between endothelial cells is regulated by cytokines such as TNF-α, a process that involves the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB.
CD3E related signaling pathway
The CD3E protein is a key component of the T cell receptor (TCR) -CD3 complex, which, together with α/β or γ/δ heterodimers of TCR, is involved in antigen recognition and activates downstream signaling pathways. CD3E plays a critical role in T cell development, activation, and immune response. In the T cell receptor complex, the CD3E subunit is involved in signaling through immune receptor tyrosine motifs (ITams) within its cytoplasm, which are phosphorylated after TCR binds to the antigen, activating downstream signaling molecules including ZAP70, thus initiating the activation program of the T cell. In addition, CD3E is involved in regulating the development and function of T cells, and mutations in its genes can lead to immune deficiency diseases. In CAR-T cell therapy, the cytoplasmic domain of CD3E is used to construct chimeric antigen receptors to enhance the ability of T cells to kill tumor cells. The study suggests that specific sequence changes in CD3E can regulate cytokine release and persistence in CAR-T cells, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes.
CD3E related diseases
The CD3E protein is a key component of the T-cell surface receptor complex, which, together with the T-cell receptor (TCR), is involved in antigen recognition and triggers T cell activation. Genetic mutations in CD3E can lead to immune deficiencies such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and have been linked to the development of certain autoimmune diseases and cancer. In terms of clinical applications, CD3E is a target for a variety of therapeutic strategies, including bisspecific antibodies and CAR-T cell therapy. For example, CD3E-related bisspecific antibodies are able to recruit T cells to the vicinity of tumor cells, enhancing the immune response to the tumor. In addition, CD3E plays a role in regulating the activation, proliferation and differentiation of T cells, and plays an important role in clearing pathogens, resisting infection and maintaining immune balance. These functions of CD3E protein make it an important target for the treatment of hematoma and solid tumor, autoimmune diseases, and organ transplant rejection.
Bioapplications of CD3E
CD3E protein has been widely used in biomedicine field, especially in cancer immunotherapy. CD3E is part of the T cell surface receptor complex and is involved in antigen recognition and T cell activation by binding to the T cell receptor (TCR). In clinical use, CD3E becomes a key target for bisspecific antibody therapies that recruit T cells to the vicinity of tumor cells and enhance the immune response to the tumor. For example, Blinatumomab, a bispecific antibody targeting CD3E, has been approved to treat certain types of leukemia. In addition, CD3E also plays an important role in CAR-T cell therapy, and by modifying CD3E, the anti-tumor activity and persistence of CAR-T cells can be enhanced. The study also found that CD3E plays a role in regulating the activation, proliferation and differentiation of T cells, and plays an important role in clearing pathogens, resisting infection and maintaining immune balance. Therefore, CD3E has important therapeutic potential in the treatment of hematoma, solid tumor, autoimmune disease and organ transplant rejection.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nathan D Trinklein, 2019
Bispecific antibodies are able to recruit T cells to attack tumors, but may cause toxicity associated with cytokine release. By discovering novel anti-CD3 binding domains with better properties, bispecific antibodies with better efficacy can be developed. Researchers used a sequence-based discovery platform to screen novel anti-CD3 antibodies from humanized rats that bind to multiple epitopes and induce varying degrees of T cell activation. In the bisspecific antibody format, 12 different anti-CD3 domains were all able to induce the same level of tumor cell lysis in primary T cells, but with thousand-fold differences in potency. The major CD3 targeting domain effectively promotes tumor antigen-specific killing in vitro and in mouse xenotransplantation models with very low cytokine release. This novel CD3-targeting antibody provides a platform for the next generation of bisspecific antibodies that decouple potent cytotoxicity from low cytokine release, potentially broadening the therapeutic window in the clinic.
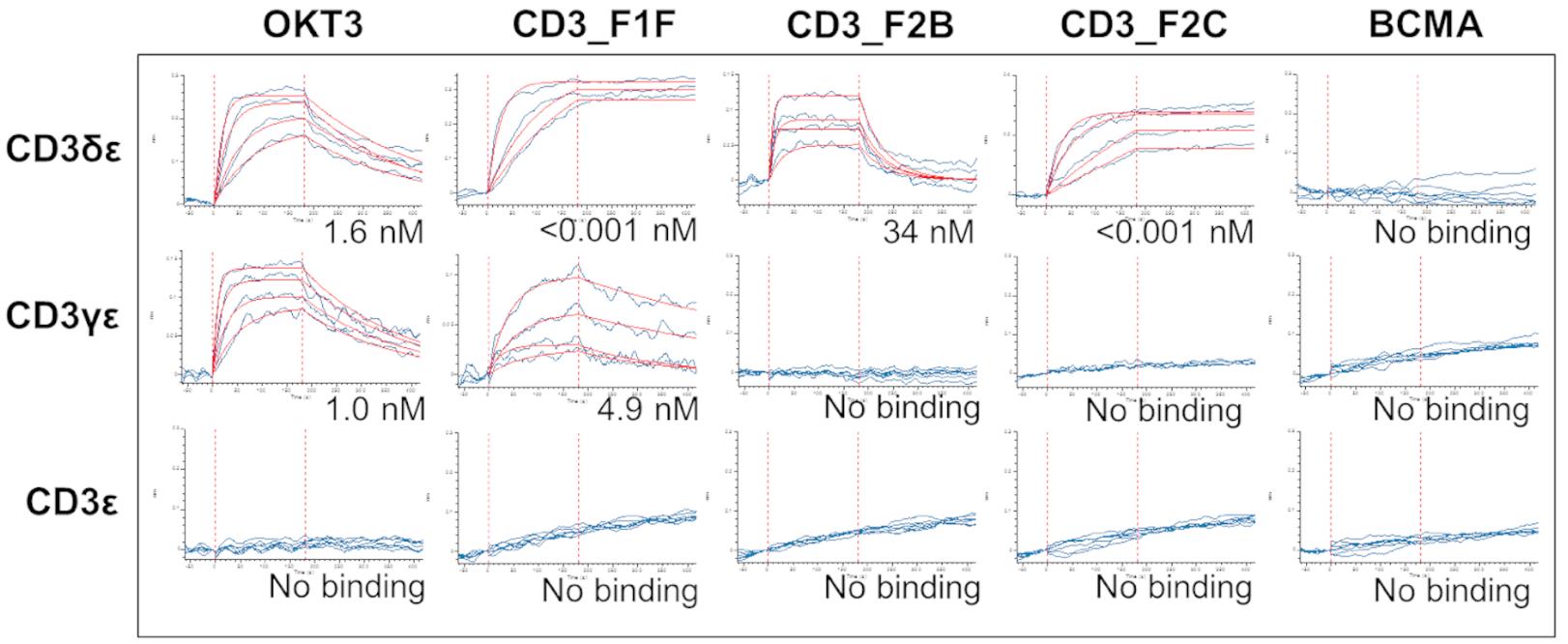
Fig1. Strong and roughly equivalent binding of OKT3 to CD3δε and CD3γε heterodimers.
Case Study 2: Wei Wu, 2020
TCR transmits antigen-stimulating signals through its associated CD3 subunits, but the specific role of these subunits is not fully understood. By quantitative mass spectrometry analysis of ITAM phosphorylation levels for all CD3 subunits after TCR activation, researchers found that a subpopulation of CD3ε ITAM was individually phosphorylated, which was attributed to the selectivity of Lck kinase and specifically recruited inhibitory Csk kinase to attenuate TCR signaling. In addition, the addition of CD3ε intracellular domains to second-generation CAR enhanced the antitumor activity of CAR-T cells. The mechanism of this effect is that ITAM of CD3ε reduces cytokine production in CAR-T cells, while its essential amino acid-rich sequence (BRS) promotes persistence of CAR-T cells by recruiting p85.
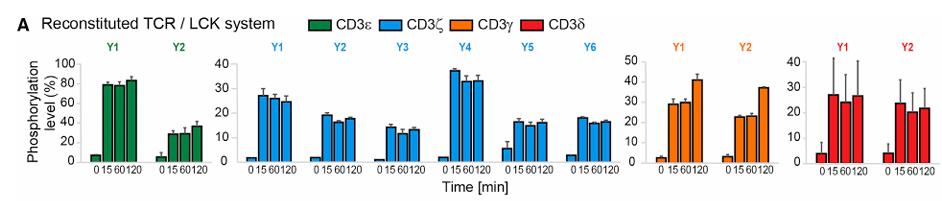
Fig3. Phosphorylation of all CD3 ITAMs measured.
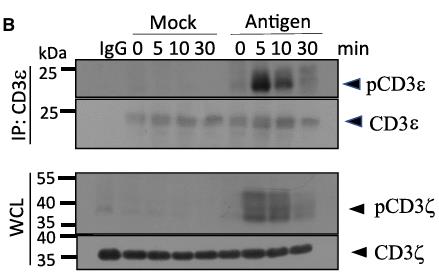
Fig4. CD3ε and CD3z phosphorylation with temporal resolution.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD3E&CD3G-342H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD3E&CD3D-377H)
Involved Pathway
CD3E involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD3E participated on our site, such as Hematopoietic cell lineage,T cell receptor signaling pathway,Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD3E were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Measles | cgr2b,IL13,IRF3,FAS,SH2D1A,BBC3,CCNE1,STAT1,IFNA17,STAT5A |
| Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | SMAD3,MAPK11,PLCB3,CD3D,AKT1,IL12A,IKBKB,CALR,PIK3R2,IL1B |
| nodeficiency | TAP1, Cd79b,AIRE,RAG2,CD40LG,PTPRC,CD4,IKBKG,BTK,DCLRE1C |
| Primary i | CD4,TAP1,IGLL1,IL2RG,AIRE,TNFRSF13B,RFXANK,ICOS,IL7R,ZAP70 |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | BCL10,FOS,IL5,MUC1,MAPK13,NFKB1,LCP2,LCK,CD8B1,IL4 |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | FLT3,IL11RA,CD1D2,CD9,CD24,FLT3LG,MS4A1,CD8A,CD1E,CSF3 |
| HTLV-I infection | VDAC1,PIK3CG,ICAM1,WNT7A,HLA-E,HLA-DRB4,SMAD4,CALR,EP300,PDGFRB |
Protein Function
CD3E has several biochemical functions, for example, SH3 domain binding,T cell receptor binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD3E itself. We selected most functions CD3E had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD3E. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase binding | GCSAM,SFN,PKD1,TBL2,PFKFB2,SOCS1,GRIN2A,CRY1,PPME1,TRIB3 |
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | P2RX5,OR4F29,Cd79a,SLC22A17,CD3D,SORL1,EGFR,NRXN2,KLRC3,FCGR2C |
| receptor signaling complex scaffold activity | GRIP2A,SPAG9A,MAGI2,G3BP2,CARD10,CD3G,SPAG9,MMS19,NCK2,NUP62 |
| protein binding | CRLF1,COA5,SELS,LANCL2,NAALADL2,ZNF232,RC3H2,GABARAP,BEND3,CXCL11 |
| receptor signaling protein activity | FCGR1A,PLCG1,DCLK1,KLK1B4,IL4R,BAG4,GNAZ,NCR1,FLRT3,FLRT1 |
| SH3 domain binding | SKAP1,SHANK1,ARHGAP1,DTX1,CNTNAP1,ENKUR,ZFP106,LANCL1,ADAM12,PDE4D |
| T cell receptor binding | EPS8L1,FYN,CD1d1,DOCK2,HLA-A,H2-Q10,CD3G |
| protein heterodimerization activity | NTSR1,SCUBE1,AGTR1,H3F3B,SNX5,ITGB1,TCF12,POU5F3,HIST3H2A,CEBPA |
Interacting Protein
CD3E has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD3E here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD3E.
EPS8L1;NCK1;SYK;ZAP70
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Dickson, MC; Ludbrook, VJ; et al. A model of skin inflammation in humans leads to a rapid and reproducible increase in the interferon response signature: a potential translational model for drug development. INFLAMMATION RESEARCH 64:171-183(2015).
- Chia, LY; Walsh, NC; et al. Isolation and gene expression of haematopoietic-cell-free preparations of highly purified murine osteocytes. BONE 72:34-42(2015).




