Principle and Protocol of Pull-down Technology
Fusion protein pull-down technology is a method to study the interaction between two or more proteins in vitro. According to the different "bait" protein labels, pull-down is usually divided into GST pull-down analysis, MBP pull-down analysis and His pull-down analysis. Pulldown is usually used to verify whether the two proteins interact with each other. It is often used to further identify the protein interactions screened by other research methods, such as yeast two-hybrid, bacteriophage display and so on.
The experiment of identifying the interaction between two proteins through pull-down is usually called in vitro binding experiment. The "bait" protein can be obtained by prokaryotic expression, while the capture protein can be expressed by artificial protein expression system. In pull-down analysis, two controls are generally set, namely negative control and blank control. The negative control is mainly composed of pure affinity purification medium (without "bait" protein) and the capture protein sample, which is helpful to identify and eliminate the false positive caused by the non-specific binding of the capture sample to the affinity medium; The blank control is composed of a "secondary" affinity purification medium (containing "bait" protein, but not incubated with the captured protein sample) that is simply bound to the "bait" protein. It is helpful to identify and eliminate the false positive caused by the protein that is not specifically bound to the affinity purification medium during the purification of bait protein, At the same time, it can also be used as a positive control to verify that the affinity purification vector can functionally capture the tagged "bait" protein. In addition, some "bait" proteins are often labeled with proteins with relatively high molecular weight (such as MBP tags). At this time, the negative control needs to be formed by incubating the affinity carrier with simple label proteins (such as MBP) and the captured protein samples.
In pull-down analysis, elution and detection are also important links of protein. Identification of the interaction between "bait" protein and trap protein requires that the complex formed by the two can be dissociated (eluted) from the affinity carrier. SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) sample buffer or molecular eluent containing an affinity medium competitive with the "bait" protein tag can make the complete complex elute from the affinity carrier. The detection of bait and capture protein in the eluate can be completed by the methods of coomassie brilliant blue staining or silver nitrate staining SDS-PAGE gel, immunoblotting or 35S labeled radioisotope; The final determination of interaction often requires the separation of positive protein bands from polyacrylamide gel, and mass spectrometry identification after trypsin digestion.
This section mainly introduces the method of identifying protein-protein interaction by MBP pull-down technology.
The purpose of this experiment manual is to help scientific researchers learn the experimental principle of pull-down technology to identify protein interaction, and be familiar with the operation process and precautions of MBP pulldown technology.
Pull-down technology is an affinity chromatography technology, which provides a technical platform for sedimentation or co-purification of potential binding proteins. Pull-down technology is very similar to immunoprecipitation technology, but the difference is that the former uses "bait protein" and the latter use antibody. In the pull-down analysis, the tagged "bait" protein specifically combines with the ligand fixed in the affinity medium through the tag to build a "secondary affinity medium" that can capture and settle the protein interacting with the "bait" protein. The "secondary affinity medium" containing the fixed "bait" protein can be incubated with a variety of capture protein samples, such as cell lysates, tissue samples, or purified capture proteins. Then the bait capture protein complex is eluted, separated by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis, detected by immunoblotting or identified by mass spectrometry (Figure 4-5-1).
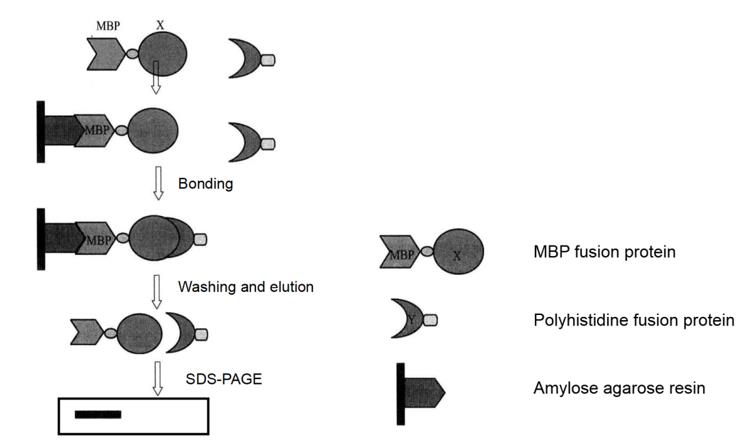 Figure 4-5-1 Pull-down Experiment Flow Chart
Figure 4-5-1 Pull-down Experiment Flow Chart
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Micropipette (20 μL, 200 μL, 1000μL), ice maker, chromatographic column, small desktop low-temperature centrifuge, 1.5mL centrifuge tube.
2. Material
MBP-X fusion protein, polyhistidine-Y fusion protein.
3. Main Reagents
(1) Bonding buffer
| Tris-HCl | 20 mmol/L |
| NaCl | 200 mmol/L |
| EDTA | 1 mmol/L |
| DTT | 5 mmol/L |
| PMSF | 2 mmol/L |
| Triton X-100 | 1% (Volume fraction) |
(2) 1 X SDS Loading buffer
Experimental Methods
1. Preparation of Fusion Expression Proteins
(1) The cDNA sequences of the coding region of the target genes X and Y were respectively constructed into the prokaryotic expression vector for prokaryotic expression of the protein.
(2) The MBP-X and 6×His-Y fusion proteins were purified separately.
(3) The concentrations of the purified fusion proteins were determined.
2. Pull-down Experiment
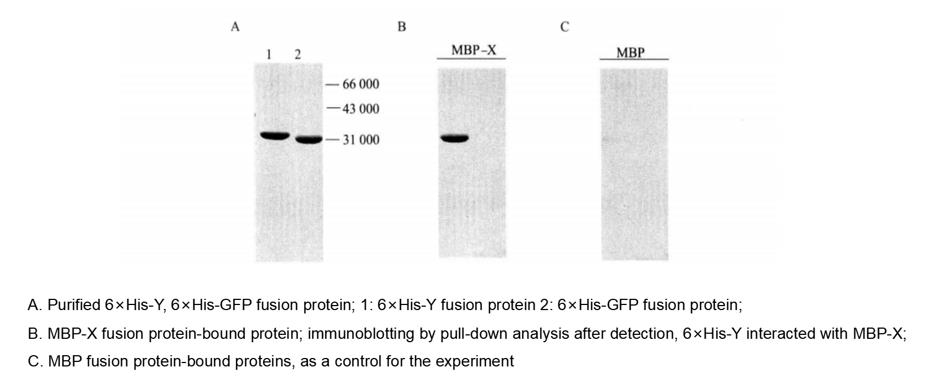 Figure 4-5-2 Pull-down Analysis of the Interaction of MBP-X with 6×His-Y protein
Figure 4-5-2 Pull-down Analysis of the Interaction of MBP-X with 6×His-Y protein
(1) Add 2μg of MBP-X and 6×His-Y fusion protein to 1 mL of binding buffer, respectively.
(2) Bind with shaking at room temperature for 2h.
(3) Add straight-chain starch-agarose resin*1, and shake for 2h at room temperature.
(4) Centrifuge at 3000g for 5min at room temperature and discard the supernatant.
(5) Resuspend the precipitate with 1mL of binding buffer and leave it at room temperature for 5min.
(6) Centrifuge at 3000g for 5min at room temperature and discard the supernatant.
(7) Repeat steps (5) and (6) 2 times each*2.
(8) Add an appropriate amount of 1×SDS loading buffer to the precipitation solution.
(9) The samples were heated at 100°C for 5 min, and the results were detected by Komas Brilliant Blue staining of SDS-PAGE gel or by immunoblotting (Figure 4-5-2).
1. There may be a weak or transient combination between the "bait" protein and the captured protein, so it is a good strategy to adjust the number of times of washing or reduce the strength of the washing liquid.
2. If the concentration of "bait" protein and the concentration of captured protein samples are low, different strategies need to be used for different protein sample sources to improve the protein concentration, such as concentration of samples.
3. Consider whether to add appropriate auxiliary factors, because some protein interactions require the assistance of auxiliary factors, which requires the laboratory personnel to have a clear understanding of the "bait" protein.
4. The experimental solutions used in different types of pull-down experiments, especially the sample lysates or reaction solutions, will be different. Even the same type of pull-down experiments can also use different "bait" proteins or different capture proteins, which requires the laboratory personnel to refer to relevant literature and optimize the experimental conditions.
*1 The amount of straight-chain starch-agarose resin added should be sufficient to bind the MBP-X fusion protein.
*2 Typically, the buffer is used to wash 3 times.


