Cd36
-
Official Full Name
CD36 molecule (thrombospondin receptor)
-
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is the fourth major glycoprotein of the platelet surface and serves as a receptor for thrombospondin in platelets and various cell lines. Since thrombospondins are widely distributed proteins involved in a variety of adhesive processes, this protein may have important functions as a cell adhesion molecule. It binds to collagen, thrombospondin, anionic phospholipids and oxidized LDL. It directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes and it binds long chain fatty acids and may function in the transport and/or as a regulator of fatty acid transport. Mutations in this gene cause platelet glycoprotein deficiency. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014] -
Synonyms
CD36; CD36 molecule (thrombospondin receptor); FAT; GP4; GP3B; GPIV; CHDS7; PASIV; SCARB3; BDPLT10; platelet glycoprotein 4; GPIIIB; PAS IV; PAS-4 protein; glycoprotein IIIb; cluster determinant 36; fatty acid translocase; platelet glycoprotein IV; scavenger receptor class B, member 3; leukocyte differentiation antigen CD36; CD36 antigen (collagen type I receptor, thrombospondin receptor);
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Bos taurus (Bovine)
- Canine
- Chicken
- Cynomolgus
- Cynomolgus Monkey
- Homo sapiens (Human)
- Human
- Mesocricetus auratus (Golden hamster)
- Monkey
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Rhesus monkey
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- E.coli expression system
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Human Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- Avi
- His
- C
- hFc
- Fc
- Flag
- GST
- His (Fc)
- His|T7
- Myc
- DDK
- MYC
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- Other Resource
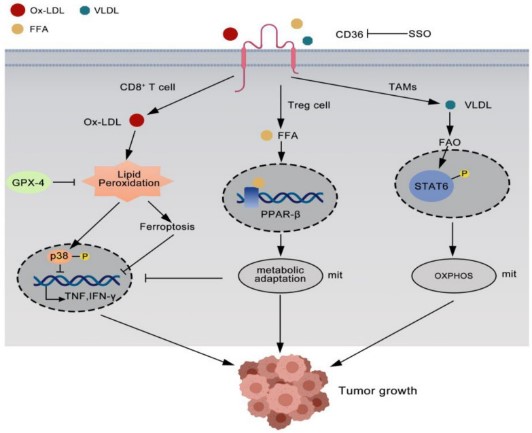
Fig1. CD36 plays a role in tumor immunity. (Xinzhi Liao, 2022)
What is CD36 protein?
CD36 (CD36 molecule) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7q21. The protein encoded by this gene is the fourth major glycoprotein of the platelet surface and serves as a receptor for thrombospondin in platelets and various cell lines. Since thrombospondins are widely distributed proteins involved in a variety of adhesive processes, this protein may have important functions as a cell adhesion molecule. It binds to collagen, thrombospondin, anionic phospholipids and oxidized LDL. It directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes and it binds long chain fatty acids and may function in the transport and/or as a regulator of fatty acid transport. The CD36 protein is consisted of 472 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 53.1 kDa.
What is the function of CD36 protein?
As a key receptor for fatty acid transmembrane transport, CD36 is involved in the uptake of long-chain fatty acids and is essential for maintaining energy balance and metabolic health. CD36 plays a role in regulating lipid metabolism, affecting the accumulation and breakdown of lipids within cells, and has been linked to the risk of obesity and cardiovascular disease. CD36 is involved in signaling during inflammation and promotes the release of inflammatory cytokines by binding ligands such as oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL). As a cell surface molecule, CD36 is involved in intercellular adhesion and plays an important role in the migration and localization of immune cells. CD36 is also involved in iron transport, influencing iron metabolism and utilization by binding to heme. CD36 is involved in the regulation of energy balance by regulating the intake and utilization of fatty acids and is associated with the development of metabolic syndrome.
CD36 Related Signaling Pathway
As a co-receptor of TLR4, CD36 recognizes pathogen-related molecular patterns, activates NF-κB signaling pathway, and regulates natural immune processes. CD36 promotes thrombosis by activating REDOX sensitive signaling molecules, such as ERK5, and interacts with the ox-LDL/CRP/β2GP1 complex to activate the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, inducing lipid accumulation and inflammatory response in macrophages. Cd36-induced signaling cascades lead to activation of specific Src kinase and activation of FAK, promoting foam cell formation and expansion, influencing actin polymerization and macrophage migration. CD36 is related to mTOR signaling pathway, regulating energy metabolism and lipid accumulation. Liquid fructose supplement can activate mTOR signaling pathway and improve CD36 translation efficiency, causing lipid accumulation. CD36 is involved in Fyn/LKB1/AMPK pathway through LKB1 mediated phosphorylation of AMPK, and influences the uptake and oxidation of fatty acids.
CD36 Related Diseases
CD36 is involved in lipid metabolism, and its abnormal expression is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), atherosclerosis (AS), and obesity. CD36 plays a role in atherosclerosis and is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. CD36 is expressed in a variety of tumors, including breast, brain, and ovarian cancers, and its expression levels are associated with poor tumor progression and prognosis. CD36 is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and is associated with inflammatory diseases such as metabolic inflammatory syndrome (MIS). As a pattern recognition receptor, CD36 participates in natural immune processes and is associated with the occurrence and development of some infectious diseases. CD36 plays a role in age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR). CD36 may play a role in the development of chronic kidney disease by mediating lipid deposition and inflammatory responses in the kidneys.
Bioapplications of CD36
Because of its role in a variety of diseases, CD36 is an important research target, helping to shed light on the pathogenesis of metabolic diseases, cardiovascular diseases, tumors, and neurodegenerative diseases. As a potential target for drug development, CD36 is being investigated for the development of small molecule inhibitors and antibody drugs targeting this protein for the treatment of the above-mentioned related diseases.
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD36-2954H)
High Bioactivity
.jpg)
Fig2. Activity Data (CD36-2954H)
Case Study 1: Shruti Gururaj Gadagkar, 2023
Innate immune response in neonatal brain is associated with a robust microglial activation and induction of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs). To date, the role of the scavenger receptor CD36 in TLRs modulation, particularly TLR2 signaling, has been well established in adult brain. However, the crosstalk between TLR4, TLR2 and CD36 and its immunogenic influence in the neonatal brain remains unclear. In this study, using a CD36 blocking antibody (anti-CD36) at post-natal day 8, the researchers evaluated the response of neonates to systemic endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide; LPS) challenge. They visualized the TLR2 response by bioluminescence imaging using the transgenic mouse model bearing the dual reporter system luciferase/green fluorescent protein under transcriptional control of a murine TLR2 promoter. The anti-CD36 treatment modified the LPS induced inflammatory profile in neonatal brains, causing a significant decrease in inflammatory cytokine levels and the TLR2 and TLR3 mediated signalling.The interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) pathway remained unaffected. Treatment of the LPS-challenged human immature microglia with anti-CD36 induced a marked decrease in TLR2/TLR3 expression levels while TLR4 and IRF3 expression was not affected, suggesting the shared CD36 regulatory mechanisms in human and mouse microglia.
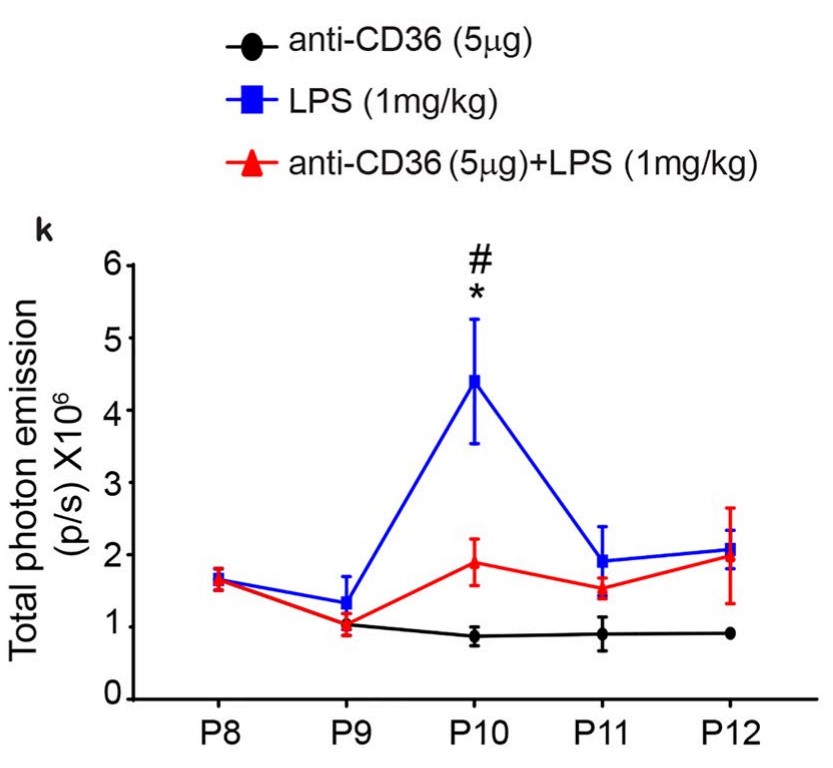
Fig1. Quantification of the in vivo bioluminescence data from P8–P12 (in photons per second, p/s).
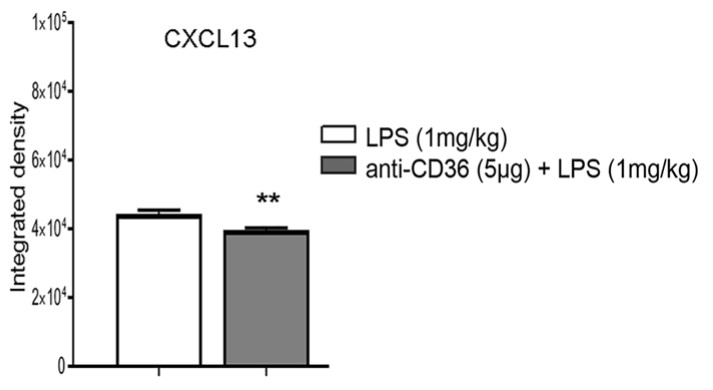
Fig2. CXCL13 when the pups are treated with anti-CD36 before LPS.
Case Study 2: Jun Zhang, 2022
This study aimed to elucidate the roles of miR-1254 in cervical cancer progression and to explore the underlying mechanisms. The binding sites between CD36 and miR-1254 were determined using luciferase reporter assays. The correlation of CD36 and miR-1254 with cervical cancer development was re-confirmed by co-transfection of miR-1254 mimic and CD36 overexpression using CCK-8, colony formation, transwell and western blot assays. The luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that CD36 messenger RNA and miR-1254 bound to one another. CD36 overexpression reversed the inhibitory effects of upregulated miR-1254 in the cervical cancer cells, suggesting that miR-1254 regulates cervical cancer progression by modulating CD36.
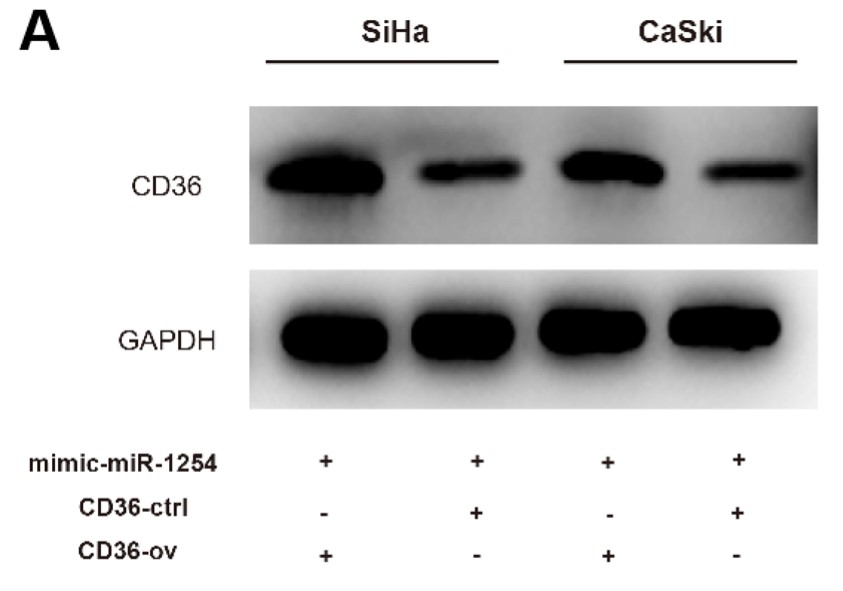
Fig3. CD36 overexpression rescued the effects of miR-1254 on the cervical cancer cells.
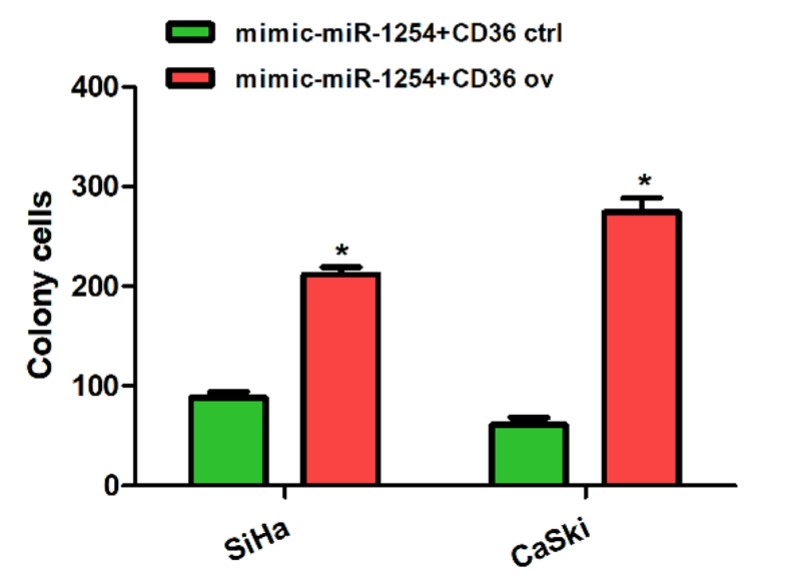
Fig4. The transwell assays showed that CD36 overexpression enhanced the invasive ability of the SiHa cells transfected with miR-1254 mimic.
Cd36 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Cd36 participated on our site, such as PPAR signaling pathway, Phagosome, AMPK signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Cd36 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| PPAR signaling pathway | PLTP;RXRG;SLC27A2;RXRAA;PDPK1;CD36;CYP4A12A;RXRA;ACADL |
| Phagosome | SEC22BA;ATP6V0E2;FCAR;RAB7A;NCF4;FCGR4;H2-AB1;SFTPD;TUBA3B |
| AMPK signaling pathway | ULK1;CD36;PIK3R2;CPT1A;PFKFB3;HMGCR;RPS6KB1;G6PC;PPARG |
| ECM-receptor interaction | LAMA2;COL27A1A;GP1BA;COL1A1B;COL6A3;TNW;Reln;LAMB3;COMP |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | IL6;IL2RA;CD1A;CD3D;CD3E; CD3D;CD1E;IL1R2;ITGA3;HLA-DRB4 |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | PPARAB;G6PC2;IKBKG;PRKAA2;MTOR;TRAF2;ADIPOR2;ADIPOR1;ACSL4A |
| Insulin resistance | PIK3R3A;G6PCA.1;PTENB;PRKCBB;PRKCE;PRKCQ;PIK3R3B;MAPK8B;PTPN11 |
| Fat digestion and absorption | APOB;FABP1;MOGAT2;PPAP2C;APOA1;PPAP2A;AGPAT1;PLA2G1B;PNLIPRP1 |
| Malaria | HBB-B1;TGFB1;THBS3;ITGB2L;TLR9;KLRB1;THBS2;IL-8;IL18 |
Cd36 has several biochemical functions, for example, MAP-kinase scaffold activity, kinesin binding, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Cd36 itself. We selected most functions Cd36 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Cd36. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MAP-kinase scaffold activity | CD36;JIP1;MAPK8IP3;SPAG9;SPAG9A;DUSP19;KSR1;MAPK8IP2 |
| kinesin binding | CD36;SPAG9;SNCA;CLSTN1;NUP62;FAM83D;IFT88;ACTB;JAKMIP1 |
| protein binding | PDE2A;OXA1L;WBP11;LIMS3L;ZZZ3;ZNF317;ALKBH3;GRAP;SMO |
| protein kinase binding | PARN;DOK7;CCNL1;SQSTM1;MAP3K12;NCS1;FOXO3;AP2A2;CDKN2A |
| protein kinase inhibitor activity | PRKRIP1;WNK1;SH3BP5B;SH3BP5L;SH3BP5LA;CHP;SOCS3A;CD36;MBIP |
Cd36 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Cd36 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Cd36.
dacD; cutA; q7ciq1_yerpe; yapE; icc; CHRD; cona_canen
Research Area
Related articles
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (7)
Ask a questionCD36 is involved in inflammation and immune responses, potentially exacerbating chronic inflammatory conditions.
Variations in CD36 function can influence the risk of obesity and associated health issues like metabolic syndrome.
CD36 modulates cell signaling related to energy utilization and storage, impacting metabolic health.
CD36 affects the development of metabolic disorders by influencing lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
CD36 aids in taste perception, particularly in detecting and responding to dietary fats.
CD36 is implicated in cardiovascular diseases, contributing to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
CD36 facilitates the uptake and metabolism of fatty acids in cells, playing a critical role in lipid processing.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewDependable protein purification, consistently high-quality results.
Great antibody validation, enhances our immunoprecipitation experiments.
Swift protein expression optimization, invaluable for our research efficiency.
Ask a Question for All Cd36 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Cd36 Products
Required fields are marked with *


