Scavenger Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
- MRC1
- MRC2
- CD163
- CD36
- CD5
- CD5L
- CD6
- CD68
- COLEC11
- COLEC12
- CXCL16
- LDLR
- LRP1
- LRP11
- MARCO
- MSR1
- LOX-1
- SCARA5
- SCARB1
- LIMPII
- SCARF1
- SCARF2
- STAB1
Immunology Background
About Scavenger Receptors
Scavenger receptors (SRs) are a large family of cell-surface receptors that are diverse in their structure and biological function and are divided into different classes. SRs can bind to a range of ligands and enhance the elimination of altered-self or non-self targets. The functional mechanisms that lead to their clearance of harmful substances involve phagocytosis, endocytosis, adhesion, and signaling.
Structure and Classification:
Scavenger receptors are characterized by their structure, which typically includes extracellular domains responsible for ligand binding, a transmembrane domain, and cytoplasmic domains involved in signal transduction or endocytic processes. In a workshop that was organized by the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and included 15 experts in the SR field, a consensus was reached to categorize the metazoan SRs into 12 classes (Table 1 and Figure 1).
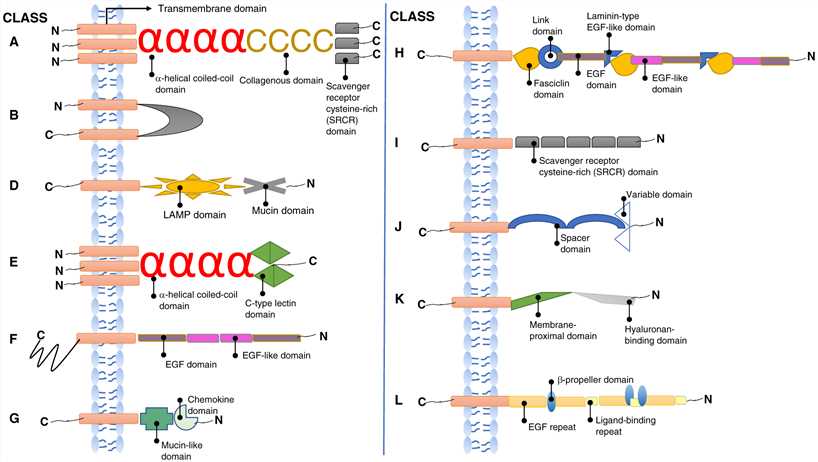 Fig. 1 Illustrative cartoons of the structures of the different classes of scavenger receptors. (Ali Alquraini, et al., 2020)
Fig. 1 Illustrative cartoons of the structures of the different classes of scavenger receptors. (Ali Alquraini, et al., 2020)
SRs are categorized into 12 classes that are all shown in this figure aside from class C, which is only found in Drosophila melanogaster. The char acteristic protein or carbohydrate domains of each class are indicated by the labels. Most SRs have single-span transmembrane domains except for those of class B, which have two transmembrane domains. All classes have short cytoplasmic tails, except for those of class F, which have long cytoplasmic tails.
Ligand Binding and Functions of Scavenger Receptors
Scavenger receptors exhibit broad ligand-binding capabilities and can recognize a diverse array of molecules, including modified lipoproteins, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), and apoptotic cells. By binding to these ligands, scavenger receptors participate in several important physiological functions:
Lipid Homeostasis: Scavenger receptors, such as SR-A and SR-B, are involved in the uptake and metabolism of lipids, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and oxidized LDL (ox-LDL). They contribute to the clearance of lipids and participate in lipid droplet formation and foam cell formation, which are associated with atherosclerosis.
Innate Immunity: Scavenger receptors recognize and internalize microbial components, such as bacterial cell wall components, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and viral particles. This allows immune cells to sense and respond to infections and initiate innate immune responses.
Clearance of Apoptotic Cells and Debris: Scavenger receptors, including CD36 and SR-A, are involved in the recognition and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cellular debris. This process is crucial for tissue homeostasis, resolution of inflammation, and prevention of autoimmunity.
Tissue Remodeling and Repair: Scavenger receptors participate in tissue remodeling and repair processes by mediating the clearance of extracellular matrix components, such as advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).
Pathogen Recognition and Host Defense: Scavenger receptors, such as LOX-1 and MARCO, recognize and internalize microbial pathogens, contributing to host defense mechanisms and immune responses against infections.
SRs are phagocytic and innate immune recognition receptors that play a crucial role as regulators of inflammatory signaling. These receptors are involved in multiple physiological and pathological processes, including interactions with TLRs and delivery of ligands to different cellular compartments. Additionally, the roles of these receptors in many degenerative and autoimmune diseases, as well as their potential as targets for therapeutic interventions to treat various disorders, warrant further study.
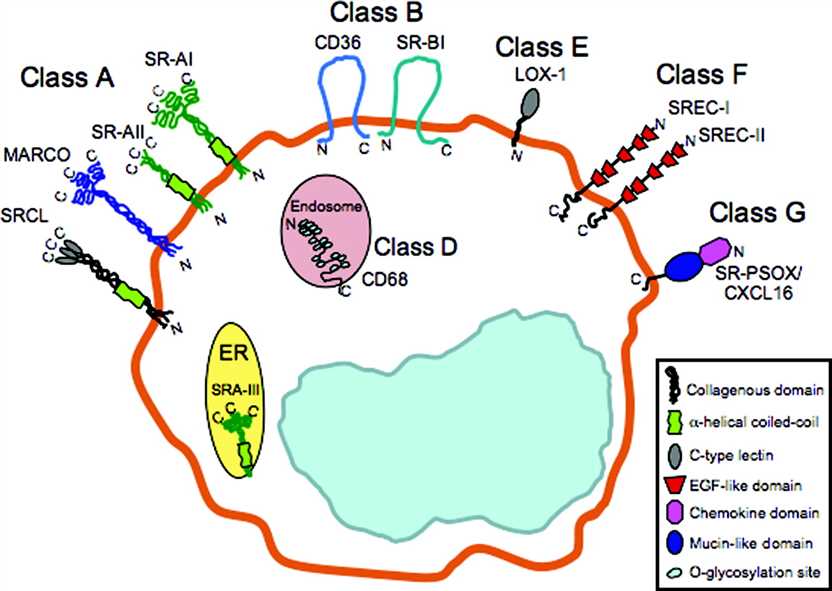 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of scavenger receptor family members with proposed roles in atherosclerosis. (Moore K J, et al., 2006)
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of scavenger receptor family members with proposed roles in atherosclerosis. (Moore K J, et al., 2006)
Application Areas of Scavenger Receptors
Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease: Scavenger receptors' involvement in lipid metabolism and foam cell formation has made them important targets for studying atherosclerosis and developing therapeutic interventions to reduce plaque formation and progression.
Infectious Diseases: Understanding the role of scavenger receptors in microbial recognition and immune responses provides insights into infectious diseases. Targeting scavenger receptors can potentially modulate immune responses and improve host defense against pathogens.
Autoimmune Disorders: Scavenger receptors' involvement in the clearance of apoptotic cells and prevention of autoimmunity makes them potential targets for studying and managing autoimmune disorders.
Drug Delivery: Scavenger receptors are being explored for drug delivery purposes. By utilizing their targeting capabilities, scavenger receptors can be targeted to deliver therapeutic agents to specific cell types or tissues.
Research on scavenger receptors continues to expand our understanding of their roles in various physiological and pathological conditions. The versatile ligand-binding abilities of scavenger receptors make them attractive targets for therapeutic interventions and the development of novel diagnostic tools in several areas of medicine.
Available Resources for Scavenger Receptors
Creative BioMart is a company dedicated to providing scientific researchers with a wide range of products and customized services to support areas such as scavenger receptor research. Their product line includes recombinant proteins and more to meet the needs of researchers in scavenger receptor research.
In addition to product offerings, Creative BioMart provides a wealth of resources covering involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and related topics. These resources can help researchers gain more information and deepen their understanding of scavenger receptors and their related fields.
If you have a specific need for scavenger receptor research or other related areas, you can contact Creative BioMart, which offers customized services and can provide personalized solutions based on your needs.
Our Featured Products
- Recombinant Human CD163, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Cd36, Fc-His tagged
- Recombinant Human CD5, His tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Cd5 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human LIMPII, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human LIMPII protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human CD5L, His tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Cd5l, His tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Cd6, His tagged
- Recombinant Human CD68, Fc-His tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Cd68 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human COLEC11, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human CXCL16, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Cxcl16, His tagged
- Recombinant Cynomolgus CXCL16 Protein
- Recombinant Human LDLR protein, His-tagged
- Active Recombinant Human LDLR Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated
- Recombinant Mouse Ldlr, His tagged
- Recombinant Human LRP1, None tagged
- Recombinant Human MARCO, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human MSR1 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human SCARA5 Protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human SCARB1 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Rat Scarb1 Protein, His/GST-tagged
Should you have any questions, specific requirements, or intentions for collaboration, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We eagerly anticipate the opportunity to collaborate with you and assist in achieving your research and commercial goals.
References:
- Alquraini A, El Khoury J. Scavenger receptors. Curr Biol. 2020;30(14): R790-R795. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.051.
- Taban Q, Mumtaz P T, Masoodi K Z, et al. Scavenger receptors in host defense: from functional aspects to mode of action[J]. Cell Communication and Signaling, 2022, 20: 1-17.
- Zani IA, Stephen SL, Mughal NA, et al. Scavenger receptor structure and function in health and disease. Cells. 2015;4(2):178-201. Published 2015 May 22. doi:10.3390/cells4020178
- Moore K J, Freeman M W. Scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis: beyond lipid uptake[J]. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 2006, 26(8): 1702-1711.

