ATPase/GTPase Assay
ATPase and GTPase enzymes play critical roles in regulating a wide range of cellular processes, from energy metabolism to intracellular signaling. Their activity is tightly controlled, and accurate measurement is essential for mechanistic studies, drug discovery, and therapeutic development. At Creative BioMart, we offer high-quality ATPase/GTPase Assay Services using multiple advanced technology platforms designed for rapid, quantitative, and large-scale analysis. Our assays achieve outstanding sensitivity and reproducibility by utilizing specially purified substrates and proprietary stabilizers, combined with phosphate-free nucleotide preparations to minimize background signal. These features ensure precise evaluation of enzyme activation, inhibition, and inhibitor screening at both research and industrial scales.
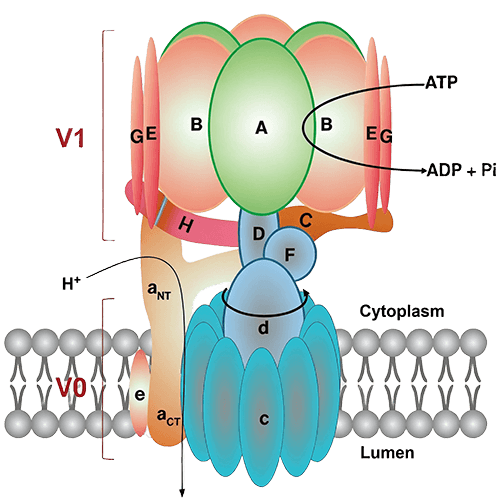
Introduction to ATPase and GTPase Assays
ATPases and GTPases are vital enzymes that regulate critical biological pathways, including energy transduction, transport mechanisms, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal dynamics. Dysregulation of their activity has been linked to various diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegeneration, making them important drug targets. Traditional assays for ATPase/GTPase activity often face limitations, including high background noise caused by contamination of nucleotides with inorganic phosphate, which interferes with accurate detection of liberated phosphate groups. To overcome these challenges, Creative BioMart employs highly purified nucleotide substrates and unique stabilizers, enabling sensitive detection and high-throughput screening of enzyme modulators.
ATPase/GTPase Assay Services & Capabilities
Our ATPase/GTPase Assay Services include:
-
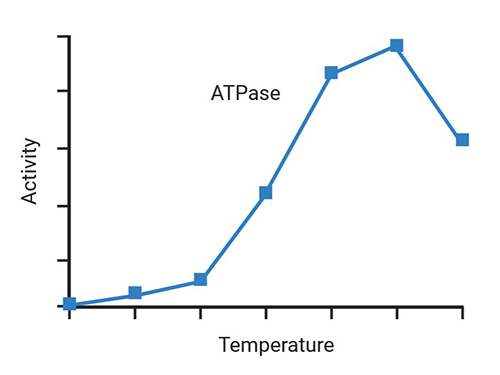
Quantitative Measurement
ATPase and GTPase activity by detecting liberated phosphate with extremely low background noise.
-
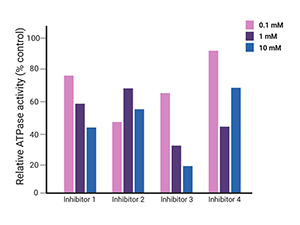
ATPase and GTPase inhibitors using robust platforms.
-
Allowing detailed analysis of both enzyme activation and inhibition.
-
Assay Customization
Tailored to specific enzymes, substrates, or conditions.
Service Workflow

Service Highlights
|
Features |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Ultra-low Background Signal |
Thanks to highly purified nucleotides free of inorganic phosphate and proprietary stabilizers, ensuring exceptional assay sensitivity. |
|
Scalable Platforms |
Capable of both small-scale mechanistic studies and high-throughput screening for drug discovery. |
|
Versatile Applications |
Suitable for ATPase, GTPase, and other phosphate-liberating enzyme assays. |
|
Dual Capability |
Comprehensive investigation of both enzyme activation and inhibition, including transporter-related studies. |
|
Custom-tailored Solutions |
Flexible assay design adapted to specific enzymes, substrates, and project requirements. |
|
Rapid Turnaround |
Advanced platforms and optimized protocols ensure efficient project completion without compromising accuracy. |
Why Partner with Us
- Cutting-edge Platforms: Multiple advanced technologies for rapid and large-scale analysis.
- Lowest Background Signal: Proprietary stabilizers and phosphate-free substrates ensure exceptional assay sensitivity.
- Comprehensive Capabilities: Quantitative assays, activation/inhibition studies, and high-throughput inhibitor screening.
- Customizable Workflows: Assay conditions optimized for your specific research needs.
- High Reproducibility: Rigorous quality controls for consistent and reliable results.
- Experienced Scientific Team: Strong expertise in enzyme kinetics, assay design, and drug discovery support.
Case Studies: Applications of ATPase and GTPase Assays
Case 1: High-throughput dual screening method for Ras activities and inhibitors
Kopra et al., 2017. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04904
Ras GTPases function as molecular switches, cycling between inactive GDP-bound and active GTP-bound states, and Ras-driven cancers remain largely untreatable despite decades of research. Traditional drug discovery has been hindered by limited screening methods and poorly defined binding sites. To address this, a homogeneous quenching resonance energy transfer (QRET)-based screening strategy was developed to identify Ras interfacial and competitive inhibitors. By using a GTP-specific antibody fragment to monitor GTPase cycling in the presence of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), this approach enables efficient high-throughput screening. Compared to conventional assays, it identifies both overlapping and unique potential inhibitors.
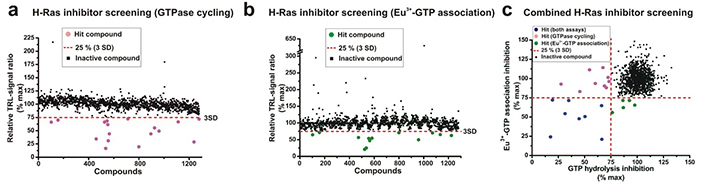
Figure 1. 2A4 GTP Fab fragment-based GTPase cycling assay and Eu3+-GTP association assay identified eight congruent inhibitors. (a) A 1280 small molecule library was screened for potential H-Ras inhibitors using the GTPase cycling assay. In panel (b), the same compounds were screened for potential H-Ras inhibitors using the Eu3+-GTP association assay. (c) The results of the GTPase cycling and Eu3+-GTP association assays were compared, showing eight congruent inhibitor hits (blue), nine exclusively GTPase cycling inhibitor hits (pink), and five exclusive Eu3+-GTP association inhibitor hits (green). (Kopra et al., 2017)
Case 2: P-glycoprotein substrate transport and ATPase activity
Nervi et al., 2010. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.11.022
This study compared P-glycoprotein (P-gp) ATPase activity in inside–out plasma membrane vesicles and living NIH-MDR1-G185 cells to evaluate substrate transport using six compounds with differing passive membrane influx. In cells, substrates must diffuse through the lipid bilayer to reach P-gp’s cytosolic binding site, whereas in vesicles, this site is directly accessible. Compounds with rapid passive influx relative to active P-gp efflux showed similar ATPase activity in both systems, while compounds with balanced influx and efflux exhibited lower cytosolic concentrations in cells, resulting in differing ATPase profiles. Overall, P-gp transported all compounds proportionally to ATP hydrolysis, limiting cytosolic entry only when passive influx matched active efflux.
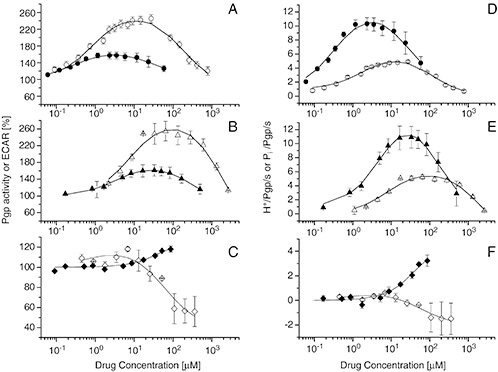
Figure 2. (A–F) Pgp ATPase activity in NIH-MDR1-G185 cells (filled symbols) and inside–out plasma membrane vesicles (open symbols) induced by three drugs. (A–C) Pgp ATPase activity expressed as percent of the basal value in the absence of drugs. (D–F) Pgp ATPase activity expressed as protons (i.e. lactic acid) or phosphate released per Pgp per second. (A, D) Verapamil; (B, E) diltiazem, and (C, F) daunorubicin. (Nervi et al., 2010)
Researcher Feedback on Our ATPase/GTPase Services
"Creative BioMart supported our oncology drug discovery program by running a high-throughput screen of over 10,000 small molecules targeting GTPase inhibition. Their proprietary assay platform delivered outstanding signal-to-noise ratios, allowing us to confidently identify several first-in-class inhibitor candidates. The rapid turnaround and data quality were critical in moving our hits into lead optimization much faster than anticipated."
— Director of Discovery Biology | Global Pharmaceutical Company
"We required precise ATPase activity measurements to study transporter protein function in a rare disease project. Creative BioMart’s team customized the assay conditions for our membrane protein of interest and used their phosphate-free ATP preparation to eliminate background interference. The resulting kinetic data gave us clear insight into activation and inhibition profiles, which directly shaped our drug design strategy."
— Head of Protein Sciences | Mid-Sized Biotech Firm
"Our academic lab collaborated with Creative BioMart to investigate GTPase activity in a cardiovascular signaling pathway. Their experts designed a tailored assay that combined quantitative detection with robust reproducibility across replicates. The high-quality data were instrumental in validating our hypothesis, and the professionalism and scientific input from their team were invaluable."
— Principal Investigator | University Research Center
"We engaged Creative BioMart to profile ATPase inhibition for a panel of transporter proteins in our toxicology studies. Their assays provided highly reproducible dose–response curves and reliable IC50 values across multiple compounds. Importantly, their detailed reports included expert commentary that helped our scientists interpret subtle activity shifts."
— Senior Scientist, Preclinical Development | Biotechnology Startup
FAQs About ATPase and GTPase Assay
-
Q: What makes your ATPase/GTPase assay platform different from others?
A: Our platform uses highly purified ATP and GTP substrates completely free of inorganic phosphate, combined with proprietary stabilizers. This ensures the lowest possible background signal, delivering highly sensitive and accurate measurement of enzyme activity. -
Q: Can you perform both activation and inhibition studies?
A: Yes. Our assay systems are designed to investigate both activation and inhibition of ATPases and GTPases, including transporter-related studies. This dual capability makes our service ideal for mechanistic research as well as drug discovery. -
Q: Do you offer high-throughput screening for inhibitors?
A: Absolutely. We provide large-scale, high-throughput inhibitor screening with robust assay performance and excellent reproducibility. This service supports pharmaceutical and biotech clients looking to accelerate their hit-to-lead processes. -
Q: Are your services customizable for specific enzymes or projects?
A: Yes. Each project begins with a consultation to design a tailored workflow. We can optimize assay conditions for your enzyme of interest, adapt to unique substrates, and provide detailed kinetic analyses according to your research needs. -
Q: How do you ensure the reliability and reproducibility of results?
A: Our assays are backed by rigorous quality control, advanced detection technologies, and highly reproducible workflows. Clients consistently report that our results are both robust and publication-ready. -
Q: What kind of organizations typically use your ATPase/GTPase assay services?
A: We serve a wide range of clients, including global pharmaceutical companies, mid-sized biotechs, and academic research institutes. Projects range from high-throughput drug screening to customized mechanistic studies and transporter analysis.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References:
- Chen F, Kang R, Liu J, Tang D. The V-ATPases in cancer and cell death. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022;29(11):1529-1541. doi:10.1038/s41417-022-00477-y
- Kopra K, Van Adrichem AJ, Salo-Ahen OMH, Peltonen J, Wennerberg K, Härmä H. High-throughput dual screening method for Ras activities and inhibitors. Anal Chem. 2017;89(8):4508-4516. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04904
- Nervi P, Li-Blatter X, Äänismaa P, Seelig A. P-glycoprotein substrate transport assessed by comparing cellular and vesicular ATPase activity . Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 2010;1798(3):515-525. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.11.022
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

