Cellular Kits

🧪 Kit-0182
Source:
Species:
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
🧪 Kit-0181
Source:
Species:
Tag: Non
Conjugation:
Protein Length:
Background
Overview
Cellular kits are important tools in biomedical research, providing researchers with a fast, accurate and standardized way to assess and quantify the various biological properties and functions of cells. These kits typically include all necessary reagents, substrates, antibodies, dyes, standards, and controls, as well as detailed operating instructions, making the process easier and more efficient.
Classifications and Functions
Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assay Kits are used to assess the response of cells to specific compounds or conditions, such as drug screening, toxicology studies, etc. It usually includes substrates such as MTT, WST-1, XTT for cell proliferation determination, and LDH release for cytotoxicity detection.
Apoptosis Assay Kits are used to detect and quantify the extent of apoptosis, both early and late. Including Annexin V/PI staining, caspase activity detection, DNA break detection and other methods.
Cell Cycle Analysis Kits are used to analyze the various phases of the cell cycle, including G0/G1, S, and G2/M phases. Usually contains fluorescent dyes for DNA staining, such as propidium iodide (PI) or 7-AAD, as well as reagents for fixing and penetrating cells.
Cell Signaling Pathway Assay Kits are used to study the activation status of specific signaling pathways in cells, such as MAPK, PI3K/AKT, etc. This may include reagents and antibodies for ELISA, Western Blotting, immunofluorescence and other methods.
Cell Migration and Invasion Assay Kits are used to assess the migration and invasion potential of cells and are commonly used in cancer research. This typically includes Transwell or Boyden Chamber systems, as well as fluorescent dyes for cell labeling and quantification.
Development Course
With the deepening of biomedical research, the understanding of cell function and behavior is becoming more and more important. Cellular kits have emerged to meet the needs of researchers for high-throughput, standardized experimental methods. Technological advances in the fields of molecular biology, cell biology, and analytical chemistry have made the design and manufacture of kits possible. These techniques include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), fluorescent labeling, flow cytometry, Western Blot, etc.
The use of kits can significantly reduce experimental preparation time, streamline the experimental process, and allow investigators to focus on data analysis and interpretation. The use of kits reduces the variability of experimental operations and improves the repeatability and comparability of results. At the same time, pre-configured reagents and standards in the kit help standardize the experimental results.
Features of Kits
Easy and fast: Pre-configured reagents and detailed operating instructions make setting up an experiment easy and fast.
High sensitivity and specificity: The reagents and methods in the kit are often optimized to ensure high sensitivity and specificity for detection.
Reliable results: The inclusion of positive and negative controls helps to verify the accuracy of the experimental results.
Cost savings: Kits are often more cost effective than purchasing and preparing reagents separately.
Diverse selection: Various types of cell analysis kits are available on the market to meet the needs of different research fields and experimental purposes.
Applications
Cell analysis kits are important tools in biomedical research and clinical diagnosis, they provide a standardized and high-throughput method to evaluate the various biological properties and functions of cells. These kits usually contain all necessary reagents, substrates, antibodies, dyes, standards and controls, as well as detailed operating instructions. Here are some application areas for cell analysis kits:
Cell activities such as cell proliferation and toxicity detection, apoptosis detection, cell cycle analysis, cell signaling pathway analysis, cell migration and invasion detection, cell differentiation and stem cell analysis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Cathepsin D Activity Fluorometric Assay Kit (Kit-0182)
Proteasomes and lysosomes are responsible for homeostasis of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates within cells. Many reports have shown that the proteolytic pathway alters function during neurodegeneration and aging. Lewy body dementia (DLB) is one of the main forms of dementia, and the proteolytic changes of DLB have not been fully studied. This study shows that the components of proteasome and lysosome selectively alter gene expression and enzyme function. Specifically, PSMB8, an inducible proteasome beta subunit, showed elevated mRNA levels and protein levels in the DLB brain compared to age-matched controls. The caspase-like peptidase activity of DLB was significantly decreased by the test kit, and there was no statistical significance in trypsin-like/chemotactic trypsin-like activity. The mRNA levels of cathepsin B and D in the lysosomes of DLB were increased, but only the activity of cathepsin B was increased.
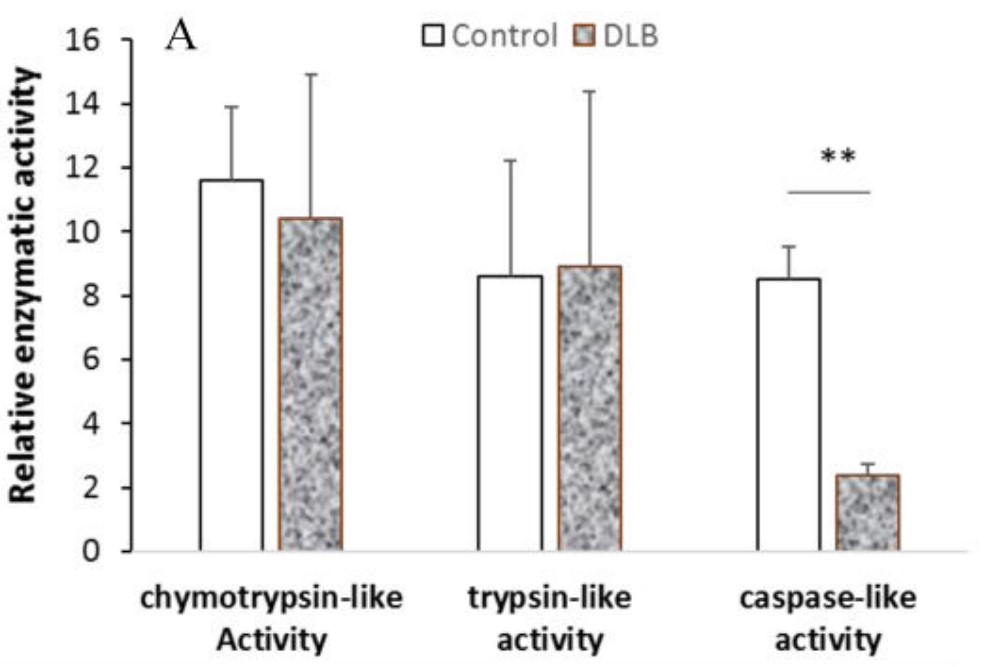
(Qunxing Ding, 2018)
Fig1. Cell lysate was isolated from the SMTG tissue of each subject and the activity of each enzyme was analyzed.
Case Study 2: Cell Proliferation Assay Kit
Conventional proliferation assays mainly quantify cell number based on a calibration curve of a homogeneous cell population, and therefore are not applicable for the analysis of cocultured cells. Moreover, these assays measure cell proliferation indirectly, based on cellular metabolic activity or DNA content. To overcome these shortcomings, a dye dilution assay employing fluorescent cell tracking dyes that are retained within cells was applied and was diluted proportionally by subsequent cell divisions. Here, it was demonstrated that this assay could be implemented to quantitatively analyze the cell proliferation of different types of cell lines, and to concurrently analyze the proliferation of two types of cell lines in coculture by utilizing cell tracking dyes with different spectral characteristics. The mean division time estimated by the dye dilution assay is compared with the population doubling time obtained from conventional methods and values from literature. Additionally, dye transfer between cocultured cells was investigated and it was found that it is a characteristic of the cells rather than a characteristic of the dye.
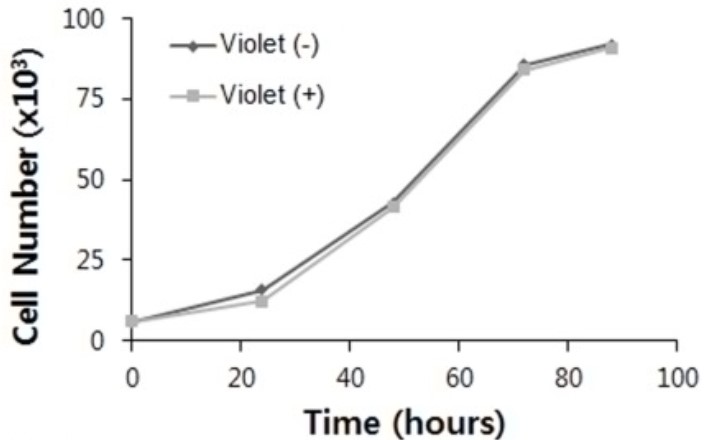
(Soobin Chung, 2017)
Fig2. Hepatoprotective effects of GLM (500 mg/kg/day) on serum levels of AST in CP-induced liver injury in rats.
Case Study 3: Cell Transformation Assay Kit
Bhas 42 cell transformation assay (CTA) has been used to estimate the carcinogenic potential of chemicals by exposing Bhas 42 cells to carcinogenic stimuli to form colonies, referred to as transformed foci, on the confluent monolayer. Transformed foci are classified and quantified by trained experts using morphological criteria, this classification process is laborious, time consuming, and subjective. The researchers propose using deep neural network to classify foci more rapidly and objectively. To obtain datasets, Bhas 42 CTA was conducted with a potent tumor promotor, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, and focus images were classified by experts (1405 images in total). The labeled focus images were augmented with random image processing and used to train a convolutional neural network (CNN). The trained CNN exhibited an area under the curve score of 0.95 on a test dataset significantly outperforming conventional classifiers by beginners of focus judgment. The generalization performance of unknown chemicals was assessed by applying CNN to other tumor promotors exhibiting an area under the curve score of 0.87.
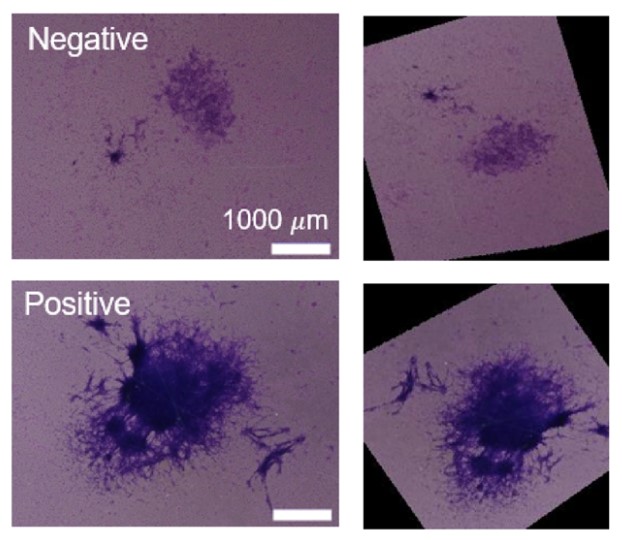
(Minami Masumoto, 2021)
Fig3. Representative images of transformed foci induced by exposure to TPA. Two experts classified the images into positive and negative foci.
Advantages
- Technical specialization. The cellular kits we offer cover a wide range of biological research areas, and our R&D team is dedicated to developing all kinds of test kits.
- Product diversity. Our extensive product line includes activity detection kits for different biological applications to detect a variety of biological processes such as cell proliferation, cell apoptosis, cell migration, cell viability and so on.
- Customized service. We not only provide standardized test kits, but also provide customized test kits according to customer needs. The flexibility of this service can better meet specific research needs and provide customers with more personalized solutions.
Creative BioMart contains various cellular detection kits to provide a standardized and high-throughput method to evaluate the various biological properties and functions of cells. You can also let us know if you have any customized requirements. Please contact us for more product details.
References
- Ding Q, Zhu H. Upregulation of PSMB8 and cathepsins in the human brains of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett. 2018;678:131-137.
- Chung S.; et al. Quantitative analysis of cell proliferation by a dye dilution assay: Application to cell lines and cocultures. Cytometry A. 2017;91(7):704-712.
- Masumoto M.; et al. Deep neural network for the determination of transformed foci in Bhas 42 cell transformation assay. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):23344.














