Protein Methylation Assay
Protein methylation is a key regulatory mechanism in cellular processes such as gene expression, signal transduction, and protein stability. As a leading biotechnology service provider, Creative BioMart offers advanced Protein Methylation Assay services, with particular expertise in histone methylation detection and site identification. Leveraging cutting-edge platform technologies, we deliver precise, reproducible, and high-throughput analysis for a wide range of sample types, including cultured cells and tissue specimens. Whether your research requires global profiling or site-specific methylation insights, our tailored solutions help uncover critical regulatory networks and accelerate discoveries in epigenetics, oncology, and developmental biology.
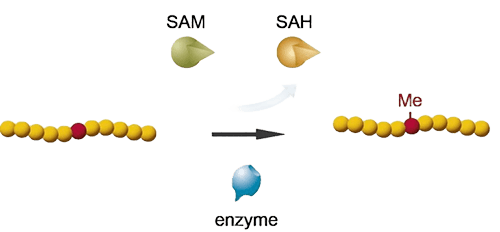
Introduction to Protein Methylation and Its Biological Significance
Protein methylation is a critical post-translational modification that regulates diverse biological processes, including transcription, signal transduction, and protein–protein interactions. It occurs primarily on lysine and arginine residues, catalyzed by specific methyltransferases, and directly influences cellular mechanisms central to health and disease.
Types of Methylation
- Lysine Methylation: This involves the addition of one, two, or three methyl groups to the ε-amino group of lysine residues. It is commonly found in histones and non-histone proteins and is involved in transcriptional regulation.
- Arginine Methylation: This involves the addition of one or two methyl groups to the guanidino group of arginine residues. It is catalyzed by protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) and is involved in RNA processing, signal transduction, and protein stability.
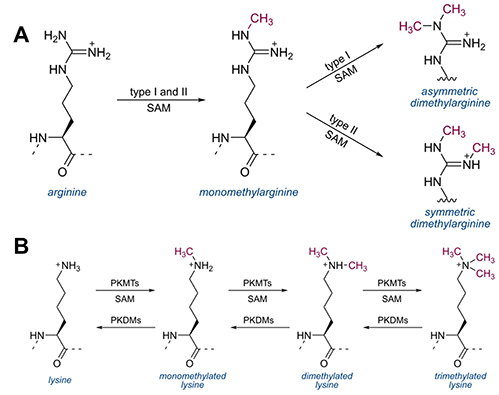
Figure 1. Types of methylation. A: Arginine methylation by type I and II PRMTs. B: Lysine methylation by PKMTs and demethylation by PKDMs.
Clinical and Research Importance
Histone methylation, in particular, is central to epigenetic regulation, influencing chromatin architecture and gene expression. Aberrant methylation patterns are strongly associated with cancer, neurological disorders, immune dysfunction, and developmental abnormalities. Accurate detection and quantification of these modifications are therefore essential for both basic research and therapeutic development.
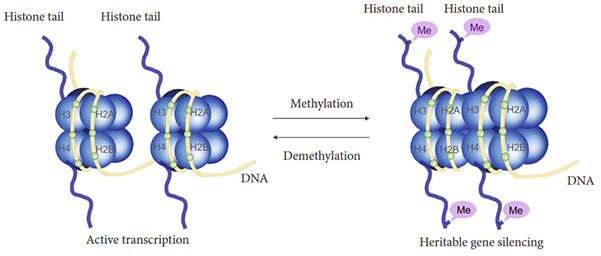
Figure 2. Schematic representation of histone methylation and demethylation . (Zhang et al., 2022)
Our Technological Advantage
Traditional methylation detection methods often require radioactive labeling, electrophoresis, or chromatography—techniques that are labor-intensive, hazardous, and time-consuming. Creative BioMart addresses these challenges with innovative, non-radioactive, high-throughput assay systems. Our platform ensures rapid, safe, and reliable methylation profiling across a wide range of biological contexts, empowering researchers with precise and reproducible results.
Comprehensive Protein Methylation Assay Solutions
Creative BioMart provides a comprehensive range of Protein Methylation Assay Services designed to meet the needs of academic, clinical, and pharmaceutical researchers.
-
In Situ Histone Methylation Measurement
Measure histone methylation directly in cultured adherent cells without preparing cell lysates.
-
Global Histone Methylation Quantification
Detect overall histone methylation levels across mammalian samples, including fresh/frozen tissues, suspension cultures, and cell lines.
-
Site-Specific Methylation Identification
Pinpoint methylation sites at specific residues to reveal functional insights into protein regulation.
Service Workflow

Service Details
|
Item |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Assay Platforms |
Non-radioactive, colorimetric microplate assays optimized for high-throughput screening. Formats are flexible and scalable, allowing for both small exploratory studies and large-scale projects. |
|
Sample Requirements |
Compatible with a wide range of mammalian materials, including fresh or frozen tissues, cultured adherent or suspension cells, and cell lines. Only minimal input is needed, preserving precious samples. |
|
Performance Highlights |
|
|
Applications |
Designed to support epigenetics, cancer research, developmental biology, neuroscience, and drug discovery. Particularly valuable for screening agents that regulate histone methylation. |
|
Customization & Support |
Creative BioMart offers tailored assay development, data analysis support, and consultation on experimental design to meet unique project requirements. |
Why Choose Us for Protein Methylation Analysis
- Quick and Efficient Procedures: Streamlined workflows minimize turnaround time without compromising accuracy.
- Innovative Non-Radioactive Assays: Safe and reliable colorimetric detection, eliminating the need for radioactivity, electrophoresis, or chromatography.
- Direct In Situ Measurement: Assays performed directly in cultured cells, avoiding the need for cell lysis or protein extraction.
- High-Throughput Compatibility: Microplate format enables efficient screening of agents that modulate methylation, ideal for large-scale studies.
- Reliable and Consistent Results: Standardized assay conditions ensure reproducibility and accuracy across experiments.
- Comprehensive Methylation Services: From global profiling to site-specific identification, we provide customized solutions for diverse research needs.
Case Studies: Applications of Protein Methylation Assays
Case 1: PRMT1-mediated methylation enhances antiviral immunity
Yang et al., 2021. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109731
TBK1 is a critical kinase in innate antiviral defense, yet its activation mechanisms remain incompletely understood. This study identifies PRMT1, a type I protein arginine methyltransferase, as a key regulator of TBK1. PRMT1 directly methylates TBK1 at residues R54, R134, and R228, enhancing its oligomerization, phosphorylation, and downstream type I interferon production. Functional studies revealed that myeloid-specific Prmt1 knockout mice are significantly more vulnerable to both DNA and RNA viral infections compared with controls. These findings highlight the pivotal role of PRMT1-mediated TBK1 methylation in innate immunity and provide new insights into antiviral signaling regulation.
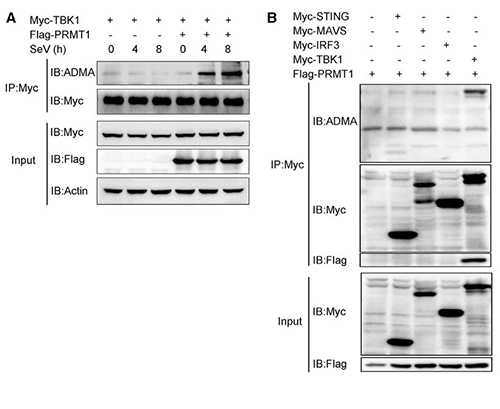
Figure 3. PRMT1 catalyzes the asymmetric methylation of TBK1 . (A) Co-IP analysis of TBK1 methylation in HEK293T cells transfected with Myc-TBK1 in the presence of control vector or FLAG-PRMT1, followed by infection with SeV for various times. (B) Co-IP analysis of asymmetric methylation in HEK293T cells transfected with Myc-STING, Myc-MAVS, Myc-IRF3, or Myc-TBK1 in the presence of FLAG-PRMT1. (Yang et al., 2021)
Case 2: Disrupted arginine methylation in Huntington’s Disease
Ratovitski et al., 2023. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddad125
Huntington’s disease (HD) arises from CAG repeat expansion in the huntingtin (HTT) gene, yet its cellular mechanisms remain unclear. This study highlights a novel role for HTT interactions with protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs), key enzymes in post-translational regulation. Normal HTT facilitates PRMT activity and arginine methylation complex formation, but these interactions are disrupted in mutant HTT. Quantitative proteomic analysis of striatal precursor neurons revealed altered arginine methylation, particularly in RNA-binding proteins critical for RNA processing and splicing. These findings suggest that disrupted HTT–PRMT interactions contribute to global RNA dysregulation in HD and point to arginine methylation as a potential therapeutic target.
Figure 4. Protein arginine methylation is significantly altered in HD ISPNs. (Ratovitski et al., 2023)
Customer Voices: Methylation Assay Success
"We collaborated with Creative BioMart to measure histone methylation dynamics in patient-derived neural stem cells. Their colorimetric methylation assay provided clear, reproducible results without the need for radioactive labeling or complex chromatography. This not only saved our lab significant time but also allowed us to confidently identify key methylation changes associated with early neurodegeneration."
— Senior Scientist | Neuroscience Research Institute
"Our oncology pipeline required a scalable solution to assess the impact of small-molecule inhibitors on protein methylation. Creative BioMart’s microplate-based assay enabled us to screen hundreds of compounds efficiently, delivering reliable readouts with exceptional sensitivity. The workflow integrated seamlessly into our screening platform and helped us prioritize lead candidates with epigenetic activity."
— Director of Translational Research | Mid-Sized Pharmaceutical Company
"In a project focused on autoimmune disorders, we needed accurate quantification of arginine methylation in both frozen tissues and cultured suspension cells. Creative BioMart’s assays offered the flexibility and sensitivity we required, while their technical support team guided us in optimizing the workflow for our specific models. The data we obtained were instrumental in identifying novel disease-related pathways."
— Principal Investigator | Academic Medical Center
"For our preclinical studies on epigenetic therapies, we partnered with Creative BioMart to conduct global histone methylation profiling. The results not only exceeded our internal reproducibility standards but were also delivered in a format that aligned with regulatory reporting expectations. Their efficient and non-radioactive assay platform gave our team confidence to include the findings in IND-enabling studies."
— VP of R&D | Global Biopharmaceutical Company
FAQs About Protein Methylation Assay Services
-
Q: What types of protein methylation can you measure?
A: We provide comprehensive analysis of histone methylation (lysine and arginine residues), including global methylation levels and site-specific methylation, enabling precise functional studies. -
Q: What sample types are compatible with your assays?
A: Our platform supports a wide range of mammalian samples, including cultured adherent and suspension cells, fresh or frozen tissues, and even patient-derived samples, allowing versatile experimental designs. -
Q: Do your assays require radioactivity or complex procedures?
A: No. Our assays use an innovative colorimetric platform without radioactivity, electrophoresis, or chromatography, making them safer, faster, and more convenient than traditional methods. -
Q: Can you perform high-throughput methylation analysis?
A: Yes. The microplate format allows high-throughput screening of multiple samples or compounds, ideal for drug discovery or large-scale epigenetic studies. -
Q: How reliable and reproducible are your results?
A: We use standardized protocols and optimized assay conditions to ensure consistent, reproducible, and quantitative data, with optional expert consultation for interpretation. -
Q: Do you provide support for both basic research and translational studies?
A: Absolutely. Our assays are suitable for basic mechanistic studies, preclinical research, and therapeutic development, including regulatory-compliant preclinical workflows. -
Q: How quickly can we get results?
A: Our streamlined workflow and efficient in situ assay design enable rapid turnaround, helping accelerate research timelines without compromising accuracy. -
Q: Can you customize assays for specific research projects?
A: Yes. We offer tailored solutions, including site-specific methylation detection and assay optimization for unique sample types or experimental conditions.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References:
- Ratovitski T, Kamath SV, O’Meally RN, et al. Arginine methylation of RNA-binding proteins is impaired in Huntington’s disease. Human Molecular Genetics. 2023;32(20):3006-3025. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddad125
- Yan Z, Wu H, Liu H, et al. The protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 promotes TBK1 activation through asymmetric arginine methylation . Cell Reports. 2021;36(12):109731. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109731
- Zhang H, Fu H, Fang H, et al. Epigenetic regulation of methylation in determining the fate of dental mesenchymal stem cells. Deng R, ed. Stem Cells International. 2022;2022:1-19. doi:10.1155/2022/5015856
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

