Specially Designed Labeled Protein for Car-T Therapy
- Biotinylated Proteins
- R-PE Labeled Proteins
- APC-labeled Proteins
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD19 |
CD19-558H |
Recombinant
Human CD19, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
His |
| CD19-280H |
Recombinant
Human CD19, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-12H |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22 |
CD22-334H |
Recombinant Human CD22 Protein, Fc &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| CD22-532H |
Recombinant Human CD22 Protein
(Trp176-Arg687), His-tagged, Biotinylated |
Insect Cell |
Human |
His |
| CD22-560H |
Recombinant
Human CD22, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22-559H |
Recombinant
Human CD22, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
His |
| CD274 |
CD274-1283H |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Avi &
His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|His |
| CD274-1285M |
Recombinant Mouse CD274 protein, Avi &
Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Avi|Fc |
| CD274-1284H |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Avi &
Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| CD274-365H |
Recombinant Human CD274 Protein, His & Fc
& Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Fc|Avi |
| CD274-339H |
Recombinant Human CD274 Protein
(Met1-Thr239), HIgG1 Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| Cd274-721M |
Recombinant
Mouse Cd274, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Mouse |
Fc |
| CD274-785H |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, His-tagged,
biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| CD274-785M |
Recombinant Mouse CD274 Protein
(Met1-Thr238), His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
His |
| CD274-8229H |
Recombinant
Human CD274, Biotin-His-tagged |
HEK293 |
Human |
Biotin|His |
| CD274-8230H |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein,
His/Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Fc |
| CD274-256H |
Recombinant
Human CD274, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD276 |
CD276-1286H |
Recombinant Human CD276 protein, Avi &
His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|His |
| CD276-1287H |
Recombinant Human CD276 Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| CD276-502H |
Recombinant Human CD276 Protein (ECD)
(Met1-Thr461), HIgG1 Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| CD276-543H |
Recombinant
Human CD276, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| CD276-4893H |
Recombinant Human CD276 protein, His-tagged,
biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| CD33 |
CD33-1081C |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD33 Protein
(Met1-Gly248), His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
His |
| CD33-675H |
Recombinant
Human CD33, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| CD33-268H |
Recombinant Human CD33 Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| CD38 |
CD38-443H |
Recombinant Human CD38 Protein (Va43-Ile300),
His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| CD38-573H |
Recombinant
Human CD38, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| CD38-1822H |
Recombinant Human CD38 protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD44 |
CD44-578H |
Recombinant
Human CD44, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| CD70 |
CD70-892H |
Recombinant Human CD70 Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| EGFR |
EGFR-288H |
Recombinant Human EGFR Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| EGFR-341H |
Recombinant Human EGFRvIII Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| EGFR-285H |
Recombinant
Human EGFR, His&Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| EGFR-43H |
Recombinant Human EGFR(T790M/L858R) protein,
Flag-tagged, Biotinylated |
Insect Cell |
Human |
Flag |
| EGFR-284H |
Recombinant
Human EGFR, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| EGFR-602H |
Recombinant
Human EGFR, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-42H |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Flag-tagged,
Biotinylated |
Insect Cell |
Human |
Flag |
| EGFR-287H |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein,
Avi/His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CEACAM5 |
CEACAM5-495H |
Recombinant Human CEACAM5 Protein
(Met1-Ala685), His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| EPCAM |
EPCAM-572H |
Recombinant Human EPCAM Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| EPCAM-350H |
Recombinant Human EPCAM Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| EPCAM-7818H |
Recombinant Human EPCAM Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| EPCAM-571H |
Recombinant
Human EPCAM, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| EPCAM-418H |
Recombinant Human EPCAM Protein
(Met1-Lys265), HIgG1 Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Insect Cell |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| EPCAM-276H |
Recombinant
Human EPCAM, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| ERBB2 |
ERBB2-360H |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| ERBB2-183H |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| ERBB2-182H |
Recombinant
Human ERBB2, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| ERBB2-1110H |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 Protein
(Met1-Thr652), HlgG1 Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
HlgG1 Fc |
| FOLR1 |
FOLR1-031H |
Recombinant Human FOLR1 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| FOLR1-317M |
Recombinant Mouse FOLR1 Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
His|Avi |
| Folr1-0630M |
Recombinant Mouse Folr1 protein, His-tagged,
Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
His |
| GPC3 |
GPC3-2247H |
Recombinant Human GPC3 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| GPC3-619H |
Recombinant
Human GPC3, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| IL1RAP |
IL1RAP-628H |
Recombinant
Human IL1RAP, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR |
KDR-632H |
Recombinant Human KDR Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| KDR-630H |
Recombinant
Human KDR, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
His |
| KDR-631H |
Recombinant
Human KDR, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-6967H |
Recombinant Human KDR Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| KDR-58H |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Flag-tagged,
Biotinylated |
Insect Cell |
Human |
Flag |
| MET |
MET-195H |
Recombinant Human MET Protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| MET-64H |
Recombinant
Human MET protein, Flag-tagged, Biotinylated |
Insect Cell |
Human |
Flag |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| MS4A1 |
MS4A1-470H |
Recombinant Human MS4A1 Protein
(Ile141-Ser188), TrxA-tagged, Biotinylated |
E.coli |
Human |
TrxA |
| MS4A1-826H |
Recombinant
Human MS4A1, Biotin-Fc-tagged |
HEK293 |
Human |
Biotin|Fc |
| MSLN |
MSLN-303H |
Recombinant Human MSLN Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| MSLN-304H |
Recombinant Human MSLN Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| MSLN-266H |
Recombinant Human MSLN Protein, His-tagged,
Biotinylated |
HEK293 Cells |
Human |
His |
| MSLN-10623H |
Recombinant
Human MSLN protein, His-tagged, Biotin Labeled. |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| MSLN-642H |
Recombinant
Human MSLN, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
His |
| MSLN-2967H |
Recombinant
Human MSLN, Fc Tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1 |
PDCD1-258H |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 Protein,
Fc-Avi-His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc|His |
| PDCD1-260H |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| PDCD1-259H |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| Pdcd1-206M |
Recombinant Mouse Pdcd1 Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Avi|Fc |
| PDCD1-384H |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 Protein
(Met1-Gln167), His-Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Fc |
| PDCD1-1003C |
Recombinant Cynomolgus PDCD1 Protein
(Met1-Gln167), AVI-Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Avi|Fc |
| PDCD1-370M |
Recombinant Mouse PDCD1 Protein, Fc &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Avi|Fc |
| Pdcd1-205M |
Recombinant
Mouse Pdcd1, Fc tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| PDCD1-257H |
Recombinant
Human PDCD1, His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| ROR1 |
ROR1-1810H |
Recombinant Human ROR1 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| ROR1-312H |
Recombinant Human ROR1 Protein (Gln 30 - Glu
403), Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi |
| ROR1-595H |
Recombinant Human ROR1 Protein (Met1-Glu403),
Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
N/A |
| ROR1-1811H |
Recombinant Human ROR1 protein, Fc &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| ROR1-666H |
Recombinant
Human ROR1, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| SLAMF7 |
SLAMF7-187H |
Recombinant Human SLAMF7 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| SLAMF7-688H |
Recombinant
Human SLAMF7, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| TNFRSF17 |
Tnfrsf17-882M |
Recombinant Mouse TNFRSF17 Protein,
Fc-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Avi|Fc |
| TNFRSF17-240H |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 Protein,
His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| TNFRSF17-409H |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 Protein
(Met1-Ala54), His-Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Fc |
| TNFRSF17-984R |
Recombinant Rhesus TNFRSF17 Protein
(Met1-Ala53), AVI-Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Avi|Fc |
| TNFRSF17-1827C |
Recombinant Cynomolgus TNFRSF17 protein, Fc
& Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Avi|Fc |
| TNFRSF17-552H |
Recombinant
Human TNFRSF17, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated |
Human Cell |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF17-238H |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 Protein, Fc &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
Avi|Fc |
| TNFRSF8 |
TNFRSF8-434H |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 Protein
(Met1-Lys379), His-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| TNFRSF8-1821H |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, His &
Avi-tagged, Biotinylated |
HEK293 |
Human |
His|Avi |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| TNFRSF17 |
TNFRSF17-1817HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF17-2348HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc/His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc/His |
| TNFRSF17-237HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Tnfrsf17-2266MP |
Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf17 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Tnfrsf17-661MP |
Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf17 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Tnfrsf17-881MP |
Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf17 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Tnfrsf17-7442RP |
Recombinant Rat Tnfrsf17 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| TNFRSF17-8829CP |
Recombinant Rhesus TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Fc |
| IL3RA |
IL3RA-121HP |
Recombinant Human IL3RA protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| IL3RA-29795THP |
Recombinant Human IL3RA protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| IL3RA-3248HP |
Recombinant Human IL3RA protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| Il3ra-5661MP |
Recombinant Mouse Il3ra protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Spodopterafrugiperda |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Il3ra-918MP |
Recombinant Mouse Il3ra protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| SDC1 |
Sdc1-8784RP |
Recombinant Rat Sdc1 protein, Fc-tagged, R-PE
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD19 |
CD19-3307HP |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-3308HP |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-408HP |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-159CP |
Recombinant Rhesus macaque CD19 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus macaque |
Fc |
| CD19-3309HP |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Human Cells |
Human |
His |
| MS4A1 |
MS4A1-17HP |
Recombinant Human MS4A1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22 |
CD22-482HP |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22-561HP |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22-562HP |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd22-1153RP |
Recombinant Rat Cd22 protein, Fc-tagged, R-PE
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD22-8854CP |
Recombinant Rhesus CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Fc |
| CD22-3947HP |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| CD226 |
CD226-634HP |
Recombinant Human CD226 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| CD226-635HP |
Recombinant Human CD226 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd226-635MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd226 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Cd226-8794RP |
Recombinant Rat Cd226 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD226-248CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD226 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| CD33 |
CD33-176HP |
Recombinant Human CD33 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| CD33-459HP |
Recombinant Human CD33 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD33-833HP |
Recombinant Human CD33 protein,
Fc/His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc/His |
| Cd33-6889MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd33 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| TNFRSF8 |
TNFRSF8-1594HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8-263HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8-641HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8-642HP |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| CD38 |
CD38-574HP |
Recombinant Human CD38 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd38-8742RP |
Recombinant Rat Cd38 protein, Fc-tagged, R-PE
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD38-1185CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD38 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| SPN |
Spn-7035MP |
Recombinant Mouse Spn protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| CD55 |
CD55-64HP |
Recombinant Human CD55 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD72 |
CD72-270HP |
Recombinant Human CD72 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD70 |
CD70-639P |
Recombinant Human CD70 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD70-891HP |
Recombinant Human CD70 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd70-972MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd70 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Cd70-8730RP |
Recombinant Rat Cd70 protein, Fc-tagged, R-PE
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| ULBP1 |
ULBP1-3249HP |
Recombinant Human ULBP1 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| IL1RAP |
IL1RAP-175HP |
Recombinant Human IL1RAP protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| IL1RAP-627HP |
Recombinant Human IL1RAP protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MET |
MET-1624HP |
Recombinant Human MET protein, Fc-His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc-His |
| MET-196HP |
Recombinant Human MET protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Met-31HP |
Recombinant Human Met protein, Fc-His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| Met-1744MP |
Recombinant Mouse Met protein, Fc-His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Sf 21 Insect Cells |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Met-4061MP |
Recombinant Mouse Met protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Met-730MP |
Recombinant Mouse Met protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Murine myeloma cellline, NS0-derived. |
Mouse |
Fc |
| MET-382RP |
Recombinant Rat MET protein, Fc-tagged, R-PE
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| MET-183CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus MET protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| ULBP2 |
ULBP2-449HP |
Recombinant Human ULBP2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EPCAM |
EPCAM-475HP |
Recombinant Human EPCAM protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| EPCAM-81HP |
Recombinant Human EPCAM protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Epcam-191MP |
Recombinant Mouse Epcam protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Epcam-7481RP |
Recombinant Rat Epcam protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| EPCAM-186CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus EPCAM protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| EGFR |
EGFR-024HP |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-28395THP |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-464HP |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-629HP |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-692HP |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-102MP |
Recombinant Mouse EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| EGFR-1226RP |
Recombinant Rhesus EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| EPHA2 |
Epha2-197MP |
Recombinant Mouse Epha2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| ERBB2 |
ERBB2-033HP |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| ERBB2-40HP |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| ERBB2-41HP |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| ERBB2-552HP |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| Erbb2-2514MP |
Recombinant Mouse Erbb2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Erbb2-4097RP |
Recombinant Rat Erbb2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| ERBB2-1216CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus ERBB2 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| GPC3 |
GPC3-620HP |
Recombinant Human GPC3 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Gpc3-120MP |
Recombinant Mouse Gpc3 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| GPC3-50CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus GPC3 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| GPC3-2246HP |
Recombinant Human GPC3 protein, His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Human Cells |
Human |
His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CEACAM5 |
CEACAM5-665HP |
Recombinant Human CEACAM5 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| MSLN |
MSLN-10625HP |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-185HP |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-340HP |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-528HP |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-7350HP |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-8558HP |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CA9 |
CA9-1544CP |
Recombinant Canine CA9 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Canine |
Fc |
| CA9-890HP |
Recombinant Human CA9 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| MUC1 |
MUC1-342HP |
Recombinant Human MUC1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MUC1-3952HP |
Recombinant Human MUC1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1 |
PDCD1-031HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
MIgG2a Fc |
| PDCD1-032HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, HIgG1
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| PDCD1-034HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, mutant HIgG1
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
mutant HIgG1 Fc-tagged |
| PDCD1-188HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1-189HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1-191HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1-3244HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| PDCD1-821HP |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD40 |
CD40-108HP |
Recombinant Human CD40 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD79a |
Cd79a-904MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd79a protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| CD79b |
CD79B-239HP |
Recombinant Human CD79B protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274 |
CD274-002HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
MIgG2a Fc |
| CD274-010HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, mutant HIgG1
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
mutant HIgG1 Fc |
| CD274-020HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, HIgG1
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| CD274-175HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274-178HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274-2142HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Mammalian Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274-2146HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, mouse
IgG1-Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
mouse IgG1-Fc |
| CD274-2330HP |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd274-1707MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| CD274-188MP |
Recombinant Mouse CD274 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Mouse |
MIgG2a Fc |
| CD274-189MP |
Recombinant Mouse CD274 protein, mutant
MIgG2a Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Mouse |
mutant MIgG2a Fc |
| Cd274-359MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein, mouse IgG2a
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
mouse IgG2a Fc |
| Cd274-593MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Cd274-821MP |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Cd274-561RP |
Recombinant Rat Cd274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD274-130CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD274 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| CD274-167CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD274 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| CD274-199CP |
Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD274 protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus Monkey |
Fc |
| CD274-1058CP |
Recombinant Canine CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Canine |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| KDR |
KDR-5442HP |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Insect Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-1697HP |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc-His |
| KDR-236HP |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-31716THP |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
Insect Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-643HP |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-645HP |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-83HP |
Recombinant Human KDR 7 Domains protein,
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
Insect Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| Kdr-1786MP |
Recombinant Mouse Kdr protein, Fc-His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Kdr-7413MP |
Recombinant Mouse Kdr protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Kdr-8115MP |
Recombinant Mouse Kdr protein, mFc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
mFc |
| KDR-8718RP |
Recombinant Rat KDR protein, Fc-tagged, R-PE
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| ROR1 |
ROR1-198HP |
Recombinant Human ROR1 protein, His-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| ROR2 |
ROR2-183HP |
Recombinant Human ROR2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| IL13RA2 |
IL13RA2-618HP |
Recombinant Human IL13RA2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| IL13RA2-765HP |
Recombinant Human IL13RA2 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| IL13RA2-766HP |
Recombinant Human IL13RA2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Il13ra2-1056MP |
Recombinant Mouse Il13ra2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Il13ra2-764MP |
Recombinant Mouse Il13ra2 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Il13ra2-8738RP |
Recombinant Rat Il13ra2 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| FOLR1 |
FOLR1-1146RP |
Recombinant Rat FOLR1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| FOLR1-1062CP |
Recombinant Canine FOLR1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Canine |
Fc |
| MMP2 |
MMP2-8392HP |
Recombinant Human MMP2 protein, GST-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
E.coli Cells |
Human |
GST |
| L1CAM |
L1CAM-485HP |
Recombinant Human L1CAM protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| L1CAM-526HP |
Recombinant Human L1CAM protein,
His/Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
His/Fc |
| L1CAM-628HP |
Recombinant Human L1CAM protein,
Fc-His-tagged, R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| VCAM1 |
VCAM1-1794MP |
Recombinant Human VCAM1 protein, HIgG1
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| VCAM1-71HP |
Recombinant Human VCAM1 protein, Fc-tagged,
R-PE labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| VCAM1-1793MP |
Recombinant Mouse VCAM1 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, R-PE labeled |
CHO |
Mouse |
MIgG2a Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| TNFRSF17 |
TNFRSF17-1817HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF17-2348HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc/His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc/His |
| TNFRSF17-237HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Tnfrsf17-2266MA |
Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf17 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Tnfrsf17-661MA |
Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf17 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Tnfrsf17-881MA |
Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf17 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Tnfrsf17-7442RA |
Recombinant Rat Tnfrsf17 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| TNFRSF17-8829CA |
Recombinant Rhesus TNFRSF17 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Fc |
| SDC1 |
Sdc1-8784RA |
Recombinant Rat Sdc1 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD19 |
CD19-3307HA |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-3308HA |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-408HA |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD19-159CA |
Recombinant Rhesus macaque CD19 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus macaque |
Fc |
| CD19-3309HA |
Recombinant Human CD19 protein, His-tagged,
APC labeled |
Human Cells |
Human |
His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| IL3RA |
IL3RA-121HA |
Recombinant Human IL3RA protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| IL3RA-29795THA |
Recombinant Human IL3RA protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| IL3RA-3248HA |
Recombinant Human IL3RA protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| Il3ra-5661MA |
Recombinant Mouse Il3ra protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
Spodopterafrugiperda |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Il3ra-918MA |
Recombinant Mouse Il3ra protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| MS4A1 |
MS4A1-17HA |
Recombinant Human MS4A1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22 |
CD22-482HA |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22-561HA |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD22-562HA |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd22-1153RA |
Recombinant Rat Cd22 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD22-8854CA |
Recombinant Rhesus CD22 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Fc |
| CD22-3947HA |
Recombinant Human CD22 protein, His-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD226 |
CD226-634HA |
Recombinant Human CD226 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| CD226-635HA |
Recombinant Human CD226 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd226-635MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd226 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Cd226-8794RA |
Recombinant Rat Cd226 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD226-248CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD226 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8 |
TNFRSF8-1594HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8-263HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8-641HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| TNFRSF8-642HA |
Recombinant Human TNFRSF8 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| SPN |
Spn-7035MA |
Recombinant Mouse Spn protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD33 |
CD33-176HA |
Recombinant Human CD33 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| CD33-459HA |
Recombinant Human CD33 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD33-833HA |
Recombinant Human CD33 protein,
Fc/His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc/His |
| Cd33-6889MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd33 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| CD38 |
CD38-574HA |
Recombinant Human CD38 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd38-8742RA |
Recombinant Rat Cd38 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD38-1185CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD38 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| MET |
MET-1624HA |
Recombinant Human MET protein, Fc-His-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc-His |
| MET-196HA |
Recombinant Human MET protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Met-31HA |
Recombinant Human Met protein, Fc-His-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| Met-1744MA |
Recombinant Mouse Met protein, Fc-His-tagged,
APC labeled |
Sf 21 Insect Cells |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Met-4061MA |
Recombinant Mouse Met protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Met-730MA |
Recombinant Mouse Met protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
Murine myeloma cellline, NS0-derived. |
Mouse |
Fc |
| MET-382RA |
Recombinant Rat MET protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| MET-183CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus MET protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD55 |
CD55-64HA |
Recombinant Human CD55 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD72 |
CD72-270HA |
Recombinant Human CD72 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274 |
CD274-002HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
MIgG2a Fc |
| CD274-010HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, mutant HIgG1
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
mutant HIgG1 Fc |
| CD274-020HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, HIgG1
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| CD274-175HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274-178HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274-2142HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
Mammalian Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| CD274-2146HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, mouse
IgG1-Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
mouse IgG1-Fc |
| CD274-2330HA |
Recombinant Human CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd274-1707MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| CD274-188MA |
Recombinant Mouse CD274 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Mouse |
MIgG2a Fc |
| CD274-189MA |
Recombinant Mouse CD274 protein, mutant
MIgG2a Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Mouse |
mutant MIgG2a Fc |
| Cd274-359MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein, mouse IgG2a
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
mouse IgG2a Fc |
| Cd274-593MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Cd274-821MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Cd274-561RA |
Recombinant Rat Cd274 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD274-130CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD274 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| CD274-167CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus CD274 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| CD274-199CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey CD274 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus Monkey |
Fc |
| CD274-1058CA |
Recombinant Canine CD274 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Canine |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CD70 |
CD70-639A |
Recombinant Human CD70 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD70-891HA |
Recombinant Human CD70 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd70-972MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd70 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Cd70-8730RA |
Recombinant Rat Cd70 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| ULBP1 |
ULBP1-3249HA |
Recombinant Human ULBP1 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| EGFR |
EGFR-024HA |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-28395THA |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-464HA |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-629HA |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-692HA |
Recombinant Human EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EGFR-102MA |
Recombinant Mouse EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| EGFR-1226RA |
Recombinant Rhesus EGFR protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Rhesus |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| ULBP2 |
ULBP2-449HA |
Recombinant Human ULBP2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| IL1RAP |
IL1RAP-175HA |
Recombinant Human IL1RAP protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| IL1RAP-627HA |
Recombinant Human IL1RAP protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| EPCAM |
EPCAM-475HA |
Recombinant Human EPCAM protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| EPCAM-81HA |
Recombinant Human EPCAM protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Epcam-191MA |
Recombinant Mouse Epcam protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Epcam-7481RA |
Recombinant Rat Epcam protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| EPCAM-186CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus EPCAM protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| CEACAM5 |
CEACAM5-665HA |
Recombinant Human CEACAM5 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| KDR |
KDR-5442HA |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
Insect Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-1697HA |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-His-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc-His |
| KDR-236HA |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-31716THA |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
Insect Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-643HA |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-645HA |
Recombinant Human KDR protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| KDR-83HA |
Recombinant Human KDR 7 Domains protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
Insect Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| Kdr-1786MA |
Recombinant Mouse Kdr protein, Fc-His-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Kdr-7413MA |
Recombinant Mouse Kdr protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Kdr-8115MA |
Recombinant Mouse Kdr protein, mFc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
mFc |
| KDR-8718RA |
Recombinant Rat KDR protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| EPHA2 |
Epha2-197MA |
Recombinant Mouse Epha2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| ERBB2 |
ERBB2-033HA |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| ERBB2-40HA |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| ERBB2-41HA |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| ERBB2-552HA |
Recombinant Human ERBB2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| Erbb2-2514MA |
Recombinant Mouse Erbb2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Erbb2-4097RA |
Recombinant Rat Erbb2 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| ERBB2-1216CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus ERBB2 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| MSLN |
MSLN-10625HA |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-185HA |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-340HA |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-528HA |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-7350HA |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MSLN-8558HA |
Recombinant Human MSLN protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| GPC3 |
GPC3-620HA |
Recombinant Human GPC3 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Gpc3-120MA |
Recombinant Mouse Gpc3 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| GPC3-50CA |
Recombinant Cynomolgus GPC3 protein,
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Cynomolgus |
Fc |
| GPC3-2246HA |
Recombinant Human GPC3 protein, His-tagged,
APC labeled |
Human Cells |
Human |
His |
| MUC1 |
MUC1-342HA |
Recombinant Human MUC1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MUC1-3952HA |
Recombinant Human MUC1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CA9 |
CA9-1544CA |
Recombinant Canine CA9 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Canine |
Fc |
| CA9-890HA |
Recombinant Human CA9 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| PDCD1 |
PDCD1-031HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
MIgG2a Fc |
| PDCD1-032HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, HIgG1
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| PDCD1-034HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, mutant HIgG1
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
mutant HIgG1 Fc-tagged |
| PDCD1-188HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1-189HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1-191HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| PDCD1-3244HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| PDCD1-821HA |
Recombinant Human PDCD1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| CD40 |
CD40-108HA |
Recombinant Human CD40 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
Fc |
| Cd79a |
Cd79a-904MA |
Recombinant Mouse Cd79a protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| IL13RA2 |
IL13RA2-618HA |
Recombinant Human IL13RA2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| IL13RA2-765HA |
Recombinant Human IL13RA2 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| IL13RA2-766HA |
Recombinant Human IL13RA2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| Il13ra2-1056MA |
Recombinant Mouse Il13ra2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Mouse |
Fc |
| Il13ra2-764MA |
Recombinant Mouse Il13ra2 protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Mouse |
Fc-His |
| Il13ra2-8738RA |
Recombinant Rat Il13ra2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| CD79B |
CD79B-239HA |
Recombinant Human CD79B protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| MMP2 |
MMP2-8392HA |
Recombinant Human MMP2 protein, GST-tagged,
APC labeled |
E.coli Cells |
Human |
GST |
| Gene |
Cat.No. |
Products Name |
Source |
Species |
Tag |
| FOLR1 |
FOLR1-1146RA |
Recombinant Rat FOLR1 protein, Fc-tagged, APC
labeled |
HEK293 |
Rat |
Fc |
| FOLR1-1062CA |
Recombinant Canine FOLR1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Canine |
Fc |
| L1CAM |
L1CAM-485HA |
Recombinant Human L1CAM protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
Fc |
| L1CAM-526HA |
Recombinant Human L1CAM protein,
His/Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
NS0 Cells |
Human |
His/Fc |
| L1CAM-628HA |
Recombinant Human L1CAM protein,
Fc-His-tagged, APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc-His |
| VCAM1 |
VCAM1-1794MA |
Recombinant Human VCAM1 protein, HIgG1
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Human |
HIgG1 Fc |
| VCAM1-71HA |
Recombinant Human VCAM1 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
| VCAM1-1793MA |
Recombinant Mouse VCAM1 protein, MIgG2a
Fc-tagged, APC labeled |
CHO |
Mouse |
MIgG2a Fc |
| ROR1 |
ROR1-198HA |
Recombinant Human ROR1 protein, His-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
His |
| ROR2 |
ROR2-183HA |
Recombinant Human ROR2 protein, Fc-tagged,
APC labeled |
HEK293 |
Human |
Fc |
Background
Overview
The principle of CAR-T therapy is to use genetic engineering technology to extract a patient's own T cells and modify
them to express a protein called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). This CAR protein recognizes and binds to antigens
on the surface of tumor cells, activating T cells to attack tumor cells. Specifically, CAR-T therapy involves the
following steps:
Collection of T cells: First, the doctor will collect a certain amount of T
cells from the patient.
Genetic modification: In the lab, doctors introduce a gene called a
chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) into T cells to make them express the CAR protein. This process is usually
implemented using viral vectors.
Culture CAR-T cells: After genetic modification, doctors will
grow T cells for several days to increase their numbers.
Injection of CAR-T cells: Finally,
the doctor will re-inject the cultured CAR-T cells into the patient. These CAR-T cells enter the patient's
circulatory system and begin attacking tumor cells. Because CAR-T cells only recognize and attack tumor cells
without causing harm to normal cells, the therapy has a higher therapeutic effect and fewer side effects.
Research Progress
CAR-T therapy was first proposed by American scientists in the 1980s. At that time, researchers discovered that
introducing a protein called a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) into T cells through genetic engineering could enable
T cells to attack cancer cells without harming normal cells. After making some progress in the laboratory, CAR-T
therapy entered the clinical trial phase. Early clinical trials were mainly conducted on patients with hematologic
tumors, and certain curative effects were achieved. In 2017, the US FDA approved Kymriah, the first CAR-T therapy
drug, for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children and young adults. Since then, a number of CAR-T
therapy drugs have been approved by the FDA. With the continuous advancement of technology, the scope of application
of CAR-T therapy is also expanding. At present, the therapy has been used in the treatment of many types of cancer,
such as lymphoma, myeloma, lung cancer and so on.
Advantages of CAR-T Therapy
Highly targeted: CAR-T therapy is an individualized treatment method that uses the patient's own T
cells to treat, avoiding the problems of rejection and immunosuppression that exist in allotransplantation. At the
same time, CAR-T cells only attack tumor cells without causing harm to normal cells, so they have a higher
therapeutic effect and fewer side effects.
Long-lasting therapeutic effect: CAR-T cells can
exist in the patient's body for a long time, so their therapeutic effect is relatively long-lasting. Some
FDA-approved CAR-T therapy drugs, such as Kymriah and Yescarta, have therapeutic effects that can last for months or
even years.
Wide range of applications: The application of CAR-T therapy is constantly
expanding. At present, it has been used in the treatment of many types of cancer, including blood tumors and solid
tumors. With the continuous advancement of technology, CAR-T therapy is expected to become an important cancer
treatment.
New treatment means: CAR-T therapy is a new cancer treatment method, and its
appearance has brought new hope for cancer treatment. Compared with traditional radiotherapy, chemotherapy and other
treatment methods, CAR-T therapy has higher therapeutic effect and fewer side effects, and is expected to become one
of the main means of cancer treatment in the future.

Evaluation Means
Creative BioMart offers a variety of pre-fluorescent-conjugated (R-PE Labeled Proteins and APC-labeled Proteins) and
pre-biotinylated recombinant proteins, which are convenient for cell separation.
- Fluorescently linked recombinant proteins can be used to track the distribution and behavior of
CAR-T cells in the body. By binding fluorescent proteins to specific proteins or receptors on the surface of CAR
T cells, visualization of CAR T cells can be achieved. This helps doctors and researchers monitor the status of
CAR T cells in the body in real time, including their number, activity and distribution. In addition, the use of
fluorescence-linked recombinant proteins can also evaluate the therapeutic effect of CAR T cells, for example by
detecting the degree of infiltration of CAR T cells in tumor tissue.
- Prebiotinized recombinant proteins can be used to optimize the therapeutic efficacy of CAR-T
cells. Prebiotin is a protein that can bind to biotin, and it can be used to bind CAR T cells to biotin-labeled
molecules or antibodies. In this way, positive or negative regulation of CAR T cells can be achieved to optimize
their therapeutic effect. For example, CAR-T cells can be bound to specific antigens on the surface of tumor
cells through biotin-avidin interaction, thereby enhancing the ability of CAR-T cells to attack tumor cells;
Alternatively, CAR T cells can be bound to inhibitory molecules through biotin-avidin interactions, thereby
inhibiting their ability to attack tumor cells.

Applications
Specific applications of fluorescentially linked and prebiotinized recombinant proteins in CAR-T therapy include:
- Monitoring the status and behavior of CAR-T cells: Visualization of CAR-T cells can be achieved
by binding fluorescent proteins to specific proteins or receptors on the surface of CAR-T cells. This helps
doctors and researchers monitor the status of CAR T cells in the body in real time, including their number,
activity and distribution. For example, fluorescently labeled anti-CD3 antibodies can be used to monitor the
activity and function of CAR T cells.
- Evaluating the efficacy of CAR-T cells: The efficacy of CAR-T cells can be evaluated by binding
fluorescent proteins to specific antigens on the surface of tumor cells. For example, fluorescently labeled
anti-PD-L1 antibodies can be used to evaluate the killing effect of CAR T cells on tumor cells.
- Optimization of therapeutic strategies for CAR-T cells: By binding pre-biotinized molecules or
antibodies to CAR-T cells, positive or negative regulation of CAR-T cells can be achieved to optimize their
therapeutic efficacy. For example, biotin-avidin interactions can be used to bind CAR-T cells to specific
antigens on the surface of tumor cells, thereby enhancing the ability of CAR-T cells to attack tumor cells; Or
biotin-avidin interactions could be used to bind CAR-T cells to inhibitory molecules, thereby inhibiting their
ability to attack tumor cells.
- Study the biological characteristics of CAR-T cells: By combining fluorescent proteins or
prebiotinized molecules with CAR-T cells, the biological characteristics of CAR-T cells can be studied, such as
their activation, proliferation, apoptosis and other processes. This contributes to a deeper understanding of
the mechanism of action of CAR T cells and provides a theoretical basis for optimizing CAR T cell therapy.

Case Study
Case Study 1: Active Recombinant Human CD19
T cells expressing anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) have activity against chronic lymphocytic leukemia
(CLL), but complete response rates range from 18% to 29%, so improvement is needed. Peripheral blood mononuclear
cells (PBMCs) of CLL patients often contain high levels of CLL cells that can interfere with CAR T cell production,
and T cells from CLL patients are prone to exhaustion and other functional defects. The researchers previously
developed an anti-CD19 CAR designated Hu19-CD828Z. Hu19-CD828Z has a binding domain derived from a fully human
antibody and a CD28 costimulatory domain. They aimed to develop an optimized process for producing
Hu19-CD828Z-expressing T cells (Hu19-CAR T) from PBMC of CLL patients. They determined that supplementing Hu19-CAR-T
cultures with interleukin (IL)-7 + IL-15 had advantages over using IL-2, including greater accumulation of Hu19-CAR
T cells during in vitro proliferation assays. They determined that positive selection with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8
magnetic beads was the optimal method of T cell purification because this method resulted in high T cell purity.
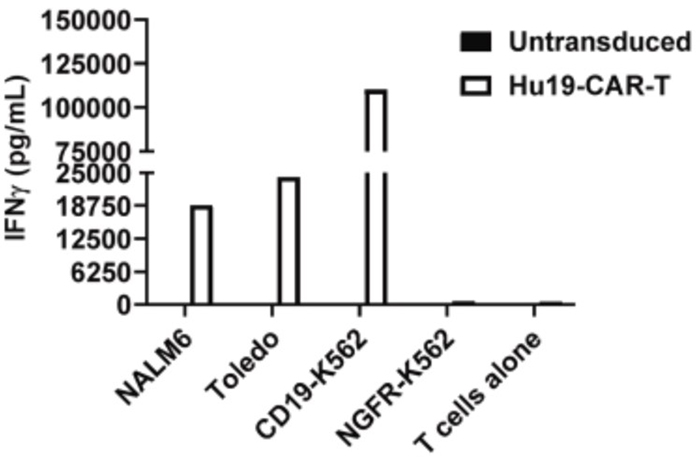
(Christina Amatya, 2024)
Fig1. On day 7 of clinical manufacturing, Hu19-CAR T derived from CLL PBMC
were cultured alone or co-cultured with CD19-positive (NALM6, Toledo, CD19-K562) or CD19-negative (NGFR-K562)
target cells.
Case Study 2: Active Recombinant Human EGFR Protein
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC), and in some somatic cells at a limited level, rendering it an attractive antitumor target. In this study,
the researchers engineered chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells using the piggyBac transposon system, autologous
artificial antigen-presenting cells, and natural ligands of EGFR. The researchers showed that this approach yielded
CAR-T cells with favorable phenotypes and CAR positivity. They exhibited potent antitumor activity against NSCLC
both in vitro and in vivo. When administered to tumor-bearing mice and non-tumor-bearing cynomolgus macaques, they
did not elicit toxicity despite their cross-reactivity to both murine and simian EGFRs. In total they tested three
ligands and found that the CAR candidate with the highest affinity consistently displayed greater potency without
adverse events.
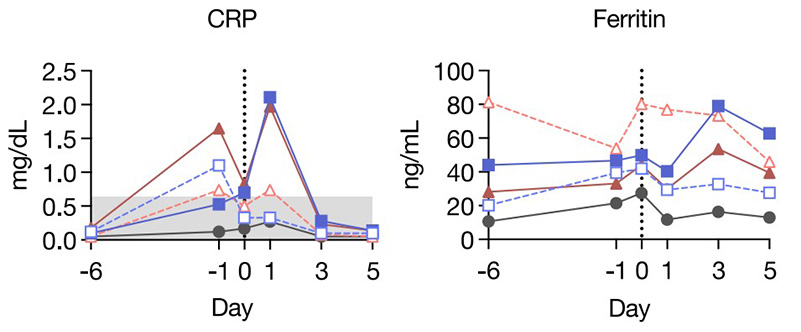
(Thanyavi Chinsuwan, 2023)
Fig2. Anti-EGFR CAR administration was safe in lymphodepleted cynomolgus
macaques at clinically relevant doses. The amount of C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, and selected
pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Case Study 3: Active Recombinant Human CD33
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a malignant disorder derived from neoplastic myeloid progenitor cells characterized
by abnormal proliferation and differentiation. Although novel therapeutics have recently been introduced, AML
remains a therapeutic challenge with insufficient cure rates. In the last years, immune-directed therapies such as
chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells were introduced, which showed outstanding clinical activity against B-cell
malignancies including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). However, the application of CAR-T cells appears to be
challenging due to the enormous molecular heterogeneity of the disease and potential long-term suppression of
hematopoiesis. Here the researchers report on the generation of CD33-targeted CAR-modified natural killer (NK) cells
by transduction of blood-derived primary NK cells using baboon envelope pseudotyped lentiviral vectors (BaEV-LVs).
Transduced cells displayed stable CAR-expression, unimpeded proliferation, and increased cytotoxic activity against
CD33-positive OCI-AML2 and primary AML cells in vitro. Furthermore, CD33-CAR-NK cells strongly reduced leukemic
burden and prevented bone marrow engraftment of leukemic cells in OCI-AML2 xenograft mouse models without observable
side effects.
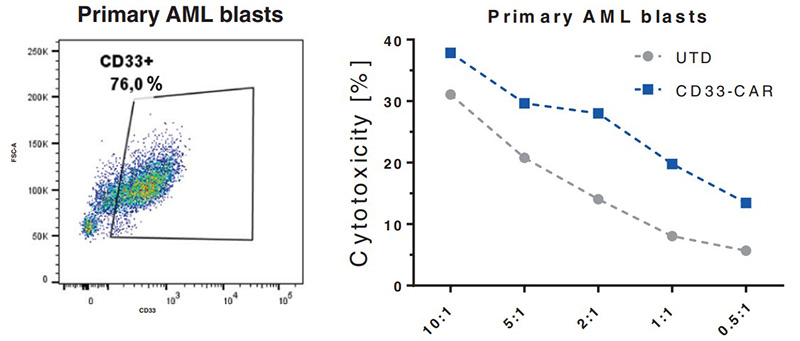
(Nawid Albinger, 2022)
Fig3. NK cells equipped with a CD33-CAR become highly cytotoxic against
CD33-positive primary AML cells.
Case Study 4: Recombinant Human GPC3 protein
Available evidence regarding the most suitable treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with inferior
vena cava tumor thrombus (IVCTT) is extremely limited, and the median overall survival time for these patients after
liver resection is only 17.76 months. Other local or systemic treatments for HCC with IVCTT result in a median
overall survival time ranging from 5.88 to 15.36 months. Thus, new therapeutic strategies are urgently needed to
improve the survival of HCC patients with IVCTT. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T‐cell therapy has seen success in
treating B‐cell neoplasms with impressive outcomes. However, this therapy alone has shown limited efficacy on solid
tumors, such as HCC. In this study, the researchers put forward a proof‐of‐concept treatment strategy that local
therapy plus CAR‐glypican‐3 (CAR‐GPC3) T‐cell therapy might be effective for advanced HCC patients and reported the
application of this combination in two GPC3‐positive HCC patients with rapidly progressing IVCTT. In brief, both
patients received local therapy to treat liver lesions and IVCTT, followed by sequential infusions of CAR‐GPC3
T‐cells, and achieved more than 5‐year disease‐free survival and more than 8‐year overall survival.
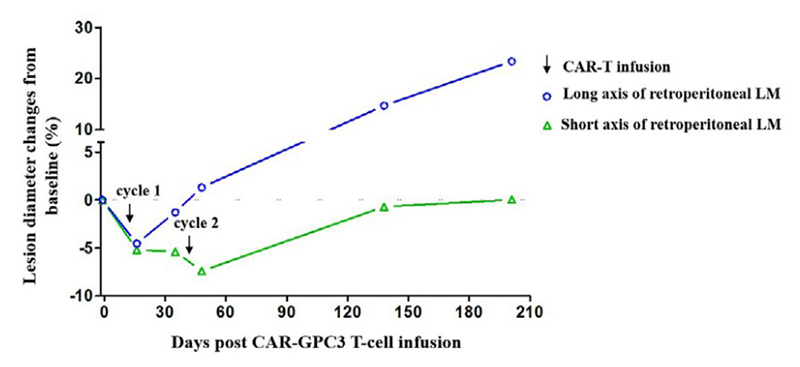
(Yaoping Shi, 2023)
Fig4. Dynamic changes in the retroperitoneal lymphatic metastasis after
CAR-GPC3 T-cell infusions.
Advantages
- Wide range of products: We offer up to 200 different label proteins such as fluorescent
labeling and biotinylation.
- Customized services: Since each patient's cancer is unique and different research needs are
unique, we are able to customize CAR-T-related proteins for each project.
- Strict quality control: The whole process of the production line has a high standard of
production delivery supervision standards to ensure high quality products.
- Ongoing support: In addition to providing products, we also provide ongoing technical support
and services to ensure your satisfaction.
FAQ
-
Q: What fluorescent-labeled proteins can you provide?
A: We mainly provide common CAR-T-associated protein labeling with R-PE or APC for the
labeling of proteins inside and outside cells.
-
Q: What is the difference between R-PE or APC markings?
A: The excitation wavelength of R-PE is usually 561nm, and the fluorescence color is red. The
excitation wavelength of APC is 488nm, and the fluorescence color is between orange and red.
References
- Amatya C.; et al. Optimization of anti-CD19 CAR T cell production for treatment of patients with
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024;32(1):101212.
- Albinger N.; et al. Primary CD33-targeting CAR-NK cells for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood Cancer J. 2022;12(4):61.











