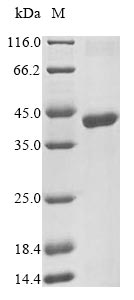
IVD of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1)
HSV-1 is a common viral infection that causes mucosal lesions such as cold sores in humans. Infection usually occurs in infancy, and the virus can remain dormant for years, sometimes even reactivating repeatedly, causing recurrent disease. In addition, HSV-1 is a neuroinvasive pathogen that usually leads to excessive accumulation of Aβ42 in the neurons of infected individuals, increased intracellular Tau protein levels, and rare encephalitis. After invading the host's peripheral nervous system, the virus may increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in older adults.
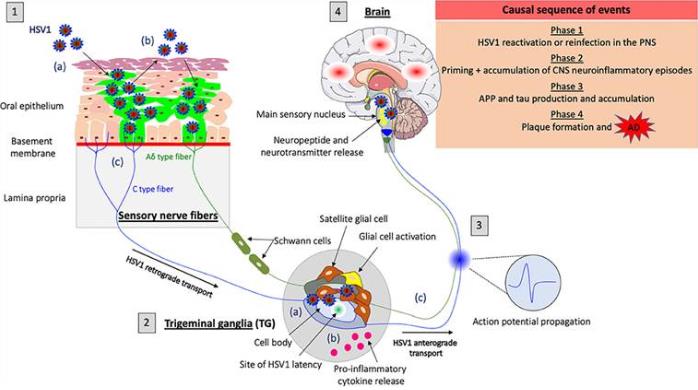 Figure 1. Model of HSV1-induced neuroinflammation in the PNS as a trigger for Alzheimer's disease (AD). (Laval K, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Model of HSV1-induced neuroinflammation in the PNS as a trigger for Alzheimer's disease (AD). (Laval K, et al., 2021)Main Methods of IVD for Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
- Utilize PCR technology for HSV-1 genetic testing. It is highly sensitive and can produce detection reports within a few hours.
- Serological testing. It mainly detects specific immunoblotting of glycoprotein G antibodies and uses Western blot to detect antibodies to various HSV-1 proteins.
- Perform in vitro cell culture. Sampling the lesion or collecting body fluid specimens such as cerebrospinal fluid to inoculate cells and culture and isolate the virus to make a diagnosis.
- Cellular immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques are used to detect herpes simplex virus antigen proteins, or in situ hybridization technology is used to detect its genetic components to further classify HSV-1.
Creative BioMart can provide high-quality recombinant HSV-1 antigens used for IVD, including ELISA, lateral flow assays, western blots, and other immunoassays.
Highlights of Our Products
- Completed biological functions and efficient activity.
- High sensitivity, high specificity, and high purity.
- A wide range of immune tests are available, such as ELISA, lateral flow, WB, and others.
- Easy to store and transport, conducive to large-scale production and use of vaccines.
- Outstanding success rate and fast development speed.
Our Outstanding Advantages
- With a professional R&D team and advanced laboratory facilities, we can conduct a variety of production research and development.
- Strict quality control can ensure product stability and reliability.
- A complete IVD protein platform can provide customized services to meet different scientific research needs.
- High-quality service, high-level experiments, and reliable analysis.
- IVD proteins can be used to test for a variety of diseases and conditions, making them valuable tools for diagnosing and monitoring health.
Other Applications of HSV-1 Proteins
1. Vaccine Development:
Subunit Vaccines: HSV-1 glycoproteins such as gD (glycoprotein D) are being studied as components of subunit vaccines. These proteins can elicit an immune response without the dangers associated with live or attenuated viruses.
2. Gene Therapy:
Vectors: HSV-1 is engineered as a vector for gene therapy due to its ability to infect a wide range of cell types and its large genome, which can accommodate substantial foreign genetic material. This vector system utilizes non-pathogenic forms of the virus where essential proteins play a role in the viral life cycle.
3. Oncolytic Viral Therapy:
Cancer Treatment: Modified HSV-1 viruses (oncolytic HSV) preferentially infect and kill cancer cells. Proteins like ICP34.5 are manipulated to improve tumor selectivity and immune response stimulation. An example is Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC), an FDA-approved oncolytic agent for melanoma.
4. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies:
Model Systems: HSV-1 proteins such as ICP0 and ICP27 are used to study protein-protein interactions, providing insights into viral replication and host-virus interactions. This information can be useful in therapeutics and antiviral drug design.
5. Immunological Studies:
Immune Response Profiling: HSV-1 proteins help in understanding the immune response mechanisms, particularly T-cell and B-cell epitopes. This knowledge is crucial for designing immune-based therapies and vaccines.
6. Diagnostic Tools:
Antigen Production: HSV-1 proteins can be used as antigens in serological assays to detect HSV-1 infections in patients.
7. Neurobiology Research:
Neuronal Studies: HSV-1 has a natural tropism for neurons. Proteins and modified viral particles are used to deliver genes or track neuronal processes, aiding in neurobiological research and neurodegenerative disease studies.
8. Antiviral Testing:
Drug Screening: The HSV-1 proteins are targets for antiviral drugs. Testing their function and interaction with potential antiviral compounds facilitates drug discovery and development.
9. Structural Biology:
Protein Structure Analysis: The study of HSV-1 protein structures informs the understanding of viral biology and can assist in the development of structural-based drug design.
10. Molecular Biology Tools:
Promoter Regions: HSV-1 promoters (e.g., from genes like IE-175) are strong and widely used in expression vectors for driving high levels of gene expression in research and biotechnology applications.
Case Study
Case 1: Ahmad I, Wilson DW. HSV-1 Cytoplasmic Envelopment and Egress. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 19;21(17):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175969. PMID: 32825127; PMCID: PMC7503644.
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a structurally complex enveloped dsDNA virus that has evolved to replicate in human neurons and epithelia. Viral gene expression, DNA replication, capsid assembly, and genome packaging take place in the infected cell nucleus, which mature nucleocapsids exit by envelopment at the inner nuclear membrane then de-envelopment into the cytoplasm. Once in the cytoplasm, capsids travel along microtubules to reach, dock, and envelope at cytoplasmic organelles.
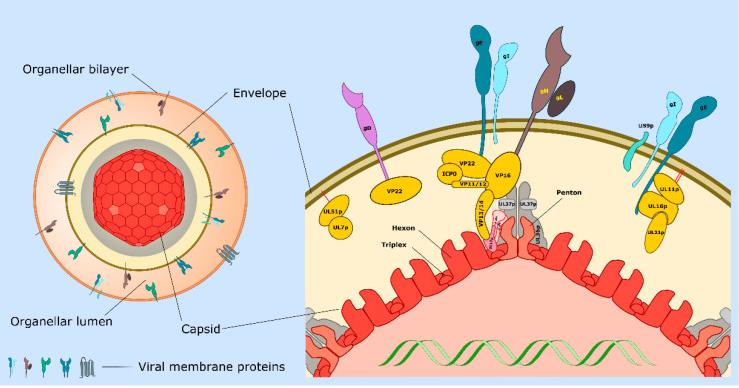 Fig2. Structure of the cytoplasmic herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) particle during egress. Left: The organelle-associated enveloped virion (OEV). The icosahedral capsid (with red hexons and pale red pentons) is bound to inner tegument proteins including UL36p and UL37p (gray layer), which provide the foundation for attachment of outer tegument (yellow). Tegument connects the capsid to the surrounding envelope (dark brown line) containing numerous single and multiple membrane-spanning envelope proteins. The mature virion resides within the lumen (orange) of the organelle utilized for envelopment. Prior to capsid envelopment the lipid bilayer of the bounding organelle must contain all of the membrane proteins that become incorporated into the mature envelope. This figure assumes that these envelope proteins persist in the bounding membrane of the OEV, though in most cases this is unknown. Right: Expanded view of a region of the capsid shell (red), inner- (gray), and outer- (yellow) tegument proteins and the envelope (dark brown bilayer). VP5 hexons and pentons are colored as in left-hand particle, and hexons, pentons, and triplexes are indicated. At the penton vertices each copy of VP5 is connected to a UL36p dimer and to adjacent triplexes via a UL17p/(UL25p)2 complex (for clarity the figure shows only two copies of VP5 at the vertex, and one copy of UL17p/(UL25p)2). Envelope proteins gD, gE/gI, gH/gL, and US9p (Table 1) are shown imbedded in the envelope bilayer such that their cytoplasmic tails project inward to connect with tegument proteins. Red lines indicate lipid anchors stabilizing the interaction of UL11p and UL51p with the envelope. Some proteins (for example gE and VP22) participate in multiple interactions within the tegument. These are drawn as separate complexes for clarity, but we do not mean to imply that these associations are necessarily exclusive of one another.
Fig2. Structure of the cytoplasmic herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) particle during egress. Left: The organelle-associated enveloped virion (OEV). The icosahedral capsid (with red hexons and pale red pentons) is bound to inner tegument proteins including UL36p and UL37p (gray layer), which provide the foundation for attachment of outer tegument (yellow). Tegument connects the capsid to the surrounding envelope (dark brown line) containing numerous single and multiple membrane-spanning envelope proteins. The mature virion resides within the lumen (orange) of the organelle utilized for envelopment. Prior to capsid envelopment the lipid bilayer of the bounding organelle must contain all of the membrane proteins that become incorporated into the mature envelope. This figure assumes that these envelope proteins persist in the bounding membrane of the OEV, though in most cases this is unknown. Right: Expanded view of a region of the capsid shell (red), inner- (gray), and outer- (yellow) tegument proteins and the envelope (dark brown bilayer). VP5 hexons and pentons are colored as in left-hand particle, and hexons, pentons, and triplexes are indicated. At the penton vertices each copy of VP5 is connected to a UL36p dimer and to adjacent triplexes via a UL17p/(UL25p)2 complex (for clarity the figure shows only two copies of VP5 at the vertex, and one copy of UL17p/(UL25p)2). Envelope proteins gD, gE/gI, gH/gL, and US9p (Table 1) are shown imbedded in the envelope bilayer such that their cytoplasmic tails project inward to connect with tegument proteins. Red lines indicate lipid anchors stabilizing the interaction of UL11p and UL51p with the envelope. Some proteins (for example gE and VP22) participate in multiple interactions within the tegument. These are drawn as separate complexes for clarity, but we do not mean to imply that these associations are necessarily exclusive of one another.Case 2: Marcocci ME, Napoletani G, Protto V, Kolesova O, Piacentini R, Li Puma DD, Lomonte P, Grassi C, Palamara AT, De Chiara G. Herpes Simplex Virus-1 in the Brain: The Dark Side of a Sneaky Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2020 Oct;28(10):808-820. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 May 5. PMID: 32386801.
Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) establishes latency preferentially in sensory neurons of peripheral ganglia. A variety of stresses can induce recurrent reactivations of the virus, which spreads and then actively replicates to the site of primary infection (usually the lips or eyes). Viral particles produced following reactivation can also reach the brain, causing a rare but severe form of diffuse acute infection, namely herpes simplex encephalitis. In this review the authors discuss the different cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the acute and long-term damage caused by HSV-1 infection in the brain.
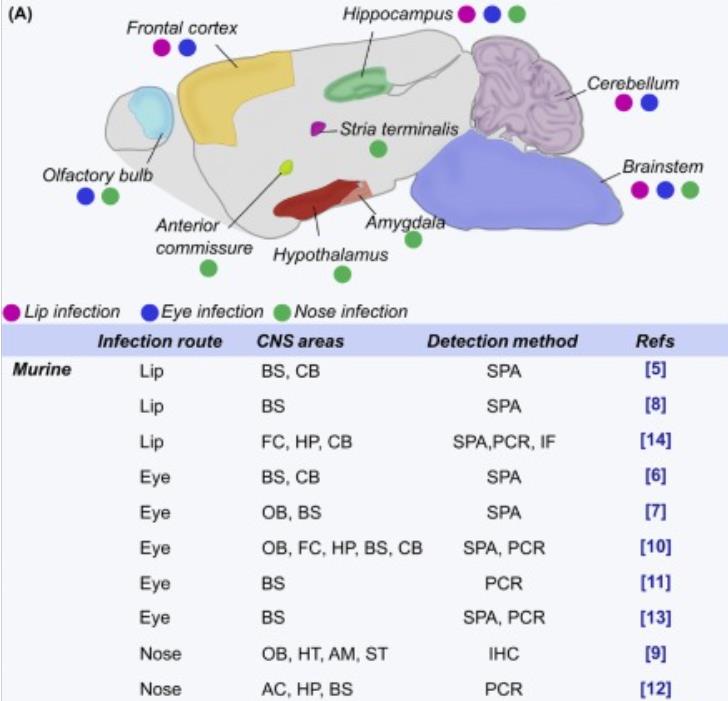 Figure 2Schematic Representation of Herpes Simplex Virus-1 (HSV-1) Detection in Human and Murine Brain Areas. Sagittal representation of murine brain showing the areas in which HSV-1 is detected after oral, nasal, or ocular inoculation (indicated with colored dots) in in vivo models; related studies, detection methods, and primary site of HSV-1 inoculation are listed below.
Figure 2Schematic Representation of Herpes Simplex Virus-1 (HSV-1) Detection in Human and Murine Brain Areas. Sagittal representation of murine brain showing the areas in which HSV-1 is detected after oral, nasal, or ocular inoculation (indicated with colored dots) in in vivo models; related studies, detection methods, and primary site of HSV-1 inoculation are listed below.In addition, Creative BioMart also offers a series of viral proteins and protein-related services to provide customers with high-quality, low-cost active recombinant proteins to meet different needs and assist in preclinical drug development.
Reference
- Laval K, Enquist L W. (2021). The potential role of herpes simplex virus type 1 and neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Frontiers in Neurology. 12: 658695.