Cd209a
-
Official Full Name
CD209a antigen -
Overview
Pathogen-recognition receptor expressed on the surface of immature dendritic cells (DCs) and involved in initiation of primary immune response. Thought to mediate the endocytosis of pathogens which are subsequently degraded in lysosomal compartments. The receptor returns to the cell membrane surface and the pathogen-derived antigens are presented to resting T-cells via MHC class II proteins to initiate the adaptive immune response. Probably recognizes in a calcium-dependent manner high mannose N-linked oligosaccharides in a variety of pathogen antigens, including HIV-1 gp120, HIV-2 gp120, SIV gp120, ebolavirus glycoproteins, cytomegalovirus gB, HCV E2, dengue virus gE, Leishmania pifanoi LPG, Lewis-x antigen in Helicobacter pylori LPS, mannose in Klebsiella pneumonae LPS, di-mannose and tri-mannose in Mycobacterium tuberculosis ManLAM and Lewis-x antigen in Schistosoma mansoni SEA.<br/>On DCs it is a high affinity receptor for ICAM2 and ICAM3 by binding to mannose-like carbohydrates. May act as a DC rolling receptor that mediates transendothelial migration of DC presursors from blood to tissues by binding endothelial ICAM2. Seems to regulate DC-induced T-cell proliferation by binding to ICAM3 on T-cells in the immunological synapse formed between DC and T-cells. -
Synonyms
CD209A;CD209a antigen;CIRE;CD209;CDSIGN;Dcsign;SIGNR5;DC-SIGN;SIGN-R1;DC-SIGN1;CD209 antigen-like protein A;dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD209A-3052M |
Active Recombinant Mouse Cd209a protein, HA-tagged
|
Mammalian Cells | Mouse | HA | Val73-Lys238 |
|
| Cd209a-7174M | Recombinant Mouse Cd209a protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&T7 | Phe115~Lys238 |
|
| Cd209a-166M | Recombinant Mouse Cd209a Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| Cd209a-166M-B | Recombinant Mouse Cd209a Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is CD209A protein?
CD209A gene (CD209a antigen) is a protein coding gene which is considered to be a homologue of the human DC-SIGN (hDC-SIGN). CD209a, also known as SIGNR5, is a protein found in mice, and CD209a is similar to hDC-SIGN in expression pattern and genomic localization in mice, so it is used as a model to study the function of hDC-SIGN. The expression of CD209a in the body is concentrated on myeloid cells in the skin and spleen, where the pathogen is most likely to be encountered. The CD209A protein is consisted of 238 amino acids and CD209A molecular weight is approximately 27.1 kDa.
What is the function of CD209A protein?
CD209A, also known as DC-SIGN, is a C-type lectin receptor expressed on dendritic cells and certain macrophages. It is mainly involved in the recognition of pathogens, and promotes the phagocytosis and processing of pathogens through its carbohydrate recognition domain binding to the sugar chains on the surface of pathogens. In addition, CD209A plays a key role in antigen presentation, mediating the endoannexation of antigens through MHC Class II molecules to present antigens to T cells and activate adaptive immune responses. CD209A is also involved in intercellular adhesion, contributing to the interaction between immune cells. In terms of immune regulation, CD209A affects the balance of inflammatory response and immune tolerance. In vaccine development, strategies targeting CD209A can effectively activate adaptive immune responses and induce specific T cell and antibody responses.
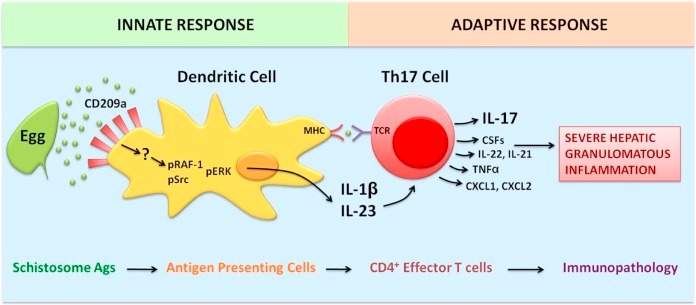
Fig1. CD209a-dependent induction of pathogenic Th17 cell response. (Holly E Ponichtera, 2015)
CD209A related signaling pathway
The CD209A protein, also known as DC-SIGN, participates in a signaling pathway primarily through its function as a C-type lectin receptor. It recognizes and binds to sugar chains on the surface of a variety of pathogens, activating downstream signaling pathways. In mice, CD209A is especially expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages, and by binding to pathogens, it can promote phagocytosis and processing of pathogens, while activating related signaling pathways, such as MAPK signaling pathway, and thereby inducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-23. These cytokines are essential for initiating and regulating the immune response. In addition, CD209A was able to quickly reappear on the cell surface after mediating endocytosis of the antigen, suggesting that it also plays an important role in antigen presentation. In immune cells such as dendritic cells, the expression of CD209A is critical for the pathogen-induced production of IL-1β and IL-23 and the subsequent differentiation of Th17 cells.
CD209A related diseases
CD209A is a C-type lectin receptor expressed on dendritic cells and certain macrophages, which plays a key role in the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases. It is involved in the recognition and presentation of a variety of pathogens, including HIV, Ebola virus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Candida albicans, schistosoma and Helicobacter pylori, helping to activate the host immune response. Furthermore, CD209A expression in schistosomiasis is associated with a Th17 cell response, which may lead to severe immunopathological changes. In a sepsis model, CD209A improved survival in mice by activating macrophages. CD209A may also be associated with tumor development and prognosis and may serve as a potential target for immunotherapy. It also plays a role in the regulation of autoimmune diseases and immune tolerance. Overall, CD209A plays a multifaceted role in infectious diseases, immune-mediated pathological processes, and possibly tumor immunotherapy.
Bioapplications of CD209A
In the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases, CD209A has potential application value in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases due to its ability to recognize multiple pathogens. In addition, CD209A is also a key target in vaccine development, and by coupling antigens to CD209A, it can effectively deliver antigens to dendritic cells, thereby activating adaptive immune responses and enhancing vaccine effectiveness. In terms of disease diagnosis, the expression level of CD209A may serve as a biomarker in some diseases, such as colon cancer, and contribute to the early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of the disease. In terms of immune regulation, CD209A plays a role in regulating the immune response and may affect the balance of inflammatory response and immune tolerance. In addition, CD209A also plays a role in the study of immune escape mechanism, for example, in immune checkpoint therapy, CD209A may be involved in regulating the sialylation modification of antibodies and affecting the function of antibodies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Weiwei Chen, 2019
The study investigated the role of DC-SIGN in intestinal cells during sepsis. Male C57BL/6 mice were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture, and the human intestinal cell line FHs74Int was stimulated with LPS to induce sepsis. DC-SIGN expression was suppressed with siRNA, and its expression, along with ERK1/2 and NF-κB/p65 phosphorylation, was analyzed. The study found that DC-SIGN upregulation in response to sepsis could be mitigated by siRNA, leading to reduced inflammatory cytokines, decreased organ damage, and improved survival rates in mice, and reduced cytokine release in intestinal cells.
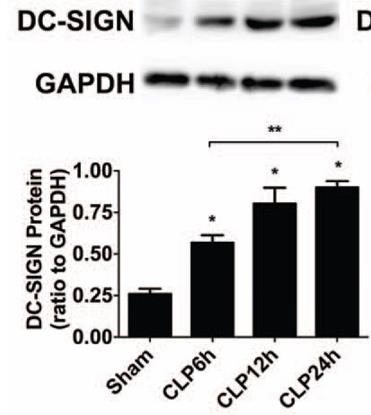
Fig1. CLP stimulation induced the upregulation of DC-SIGN in IECs in vitro.
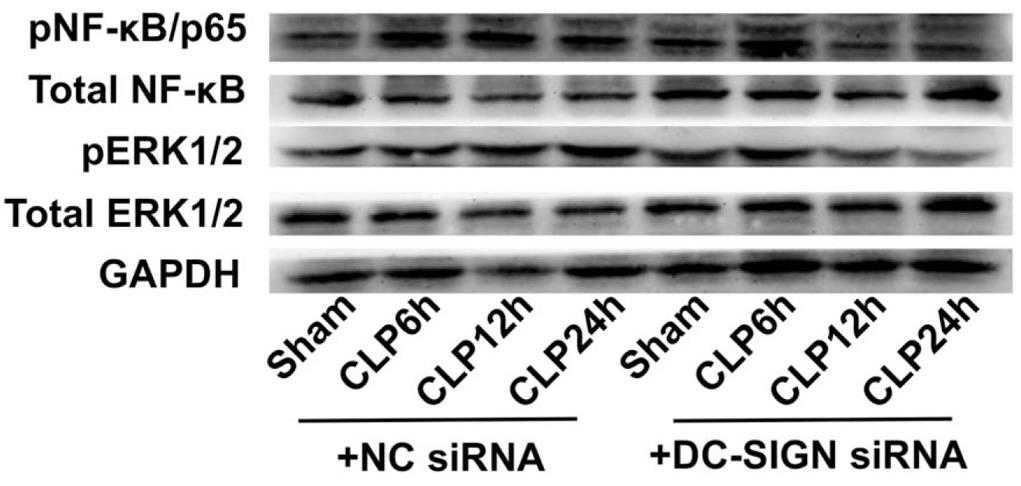
Fig2. Inhibition of DC-SIGN blocked ERK1/2-NF-κB signaling activation.
Case Study 2: Sjoerd T T Schetters, 2018
Studying the role of human DC-SIGN in vaccines is challenging due to the presence of eight similar molecules in mice. This research focused on CD209a/SIGNR5, considered the mouse DC-SIGN equivalent, to examine its ability to stimulate adaptive immunity. It is expressed in cultured dendritic cells and macrophages and rapidly recycles after internalizing antigens. Using an OVA-coupled antibody, researchers triggered immune responses in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, which were enhanced by a TLR4 ligand. In healthy conditions, mDC-SIGN is mainly found in skin and spleen myeloid cells. Subcutaneous injections showed specific targeting to skin DCs. Vaccination with the antibody induced a strong antibody and T cell response. The study concludes that mDC-SIGN is similar to hDC-SIGN and is a useful target for in vivo immune function research.
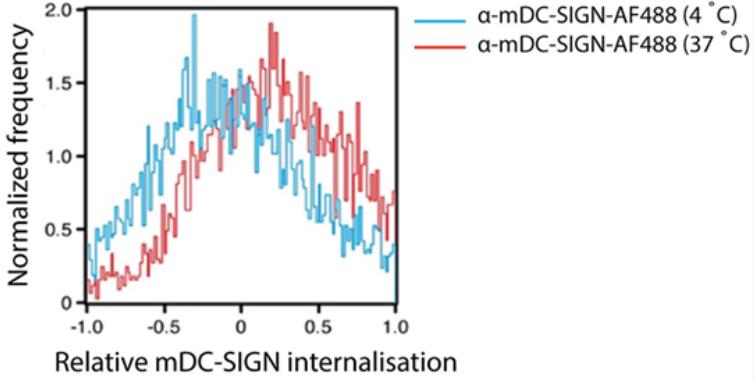
Fig3. Upon binding, mDC-SIGN is quickly internalized at 37°C for 1 h.
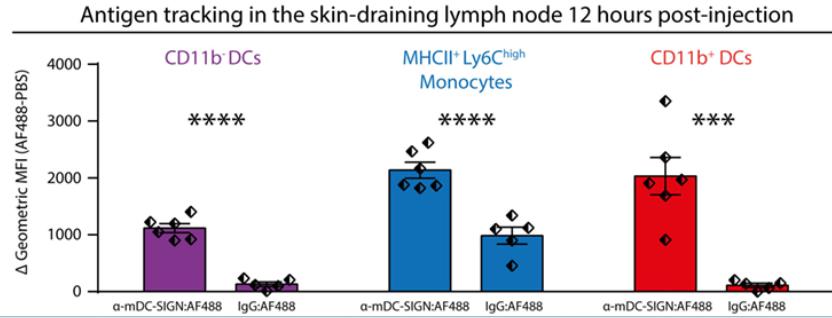
Fig4. Anti-mDC-SIGN-AF488 antibody-labeled APCs can be found in the skin-draining lymph node (LN) 12 h after injection.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cd209a-7174M)
Involved Pathway
Cd209a involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Cd209a participated on our site, such as Phagosome,Tuberculosis,Measles, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Cd209a were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Measles | TRAF6,PIK3R3,IFNA13,IL2RA,RAB9A,IFNGR2,TNFRSF10C,MYD88,CD209C,CD46 |
| Tuberculosis | CALM1,HLA-DRA,CAP18,ARHGEF12,MYD88,MAPK9,LBP,CAMK2D,MRC2,LAMP2 |
| Phagosome | ITGAV,ITGB5,ATP6AP1,H2-AA,ATP6V1E1B,CALR3B,THBS2,C1R,TUBA1B,CORO1A |
Protein Function
Cd209a has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium-dependent protein binding,carbohydrate binding,carbohydrate derivative binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Cd209a itself. We selected most functions Cd209a had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Cd209a. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mannose binding | Acr,COLEC10,BSG,MAN2B1,MBL1,LMAN2L,CD209,CD209C,CLN5,DPM1 |
| carbohydrate binding | Fcer2a,LGALS2A,CLEC2B,KLRK1,MAN2A2,Siglec1,UAP1,SORD,MAN2B2,LGALSL |
| carbohydrate derivative binding | FCNA |
| virus receptor activity | ITGAV,SLC10A1,CD80,MRC1,CLDN1,SLC20A2,SELPLG,TNFRSF4,DPP4,XPR1 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | NRXN1,CHP,SYN1,FCN2,S100B,TNNI3,MBL2,VPS37B,ANXA1,SLC9A1 |
| metal ion binding | CNOT7,DDAH1,C6AST3,CACNA2D4,EGR4,CAR15,ATP8B3,ZFP346,TRMT1,MICALL2 |
Interacting Protein
Cd209a has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Cd209a here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Cd209a.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



