Fabp4
-
Official Full Name
fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte -
Overview
FABP4 encodes the fatty acid binding protein found in adipocytes. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. It is thought that FABPs roles include fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
FABP4;fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte;aP2;ALBP;AFABP;A-FABP;HEL-S-104;fatty acid-binding protein, adipocyte;fatty acid-binding protein 4;adipocyte lipid-binding protein;epididymis secretory protein Li 104;adipocyte-type fatty acid-binding protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Pig
- Rat
- Cattle
- Sheep
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- Baculovirus
- GST
- His
- Non
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
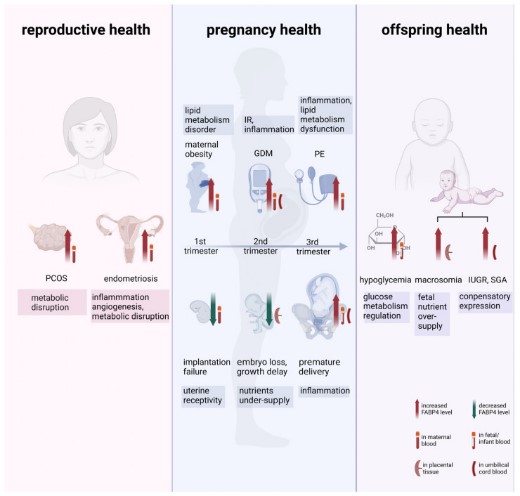
Fig1. The impact of altered FABP4 levels on female reproduction, pregnancy outcomes, and offspring health. Alternations in FABP4 levels are observed in various diseases.
What is FABP4 protein?
FABP4 (fatty acid binding protein 4) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8q21. FABP4 encodes the fatty acid binding protein found in adipocytes. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. It is thought that FABPs roles include fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. The FABP4 protein is consisted of 132 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 14.7 kDa.
What is the function of FABP4 protein?
FABP4 can bind and transport free fatty acids from the cell membrane to the cell, thereby affecting the formation and function of adipose tissue; FABP4 interacts with related enzymes such as fat synthetase and fatty acid oxidase to regulate the synthesis, decomposition and oxidative metabolism of fatty acids. FABP4 is involved in the insulin signal transduction pathway, which can regulate the effect of insulin and the sensitivity of cells to insulin, thus affecting the regulation of blood sugar. It also regulates the production and release of inflammatory factors.
FABP4 Related Signaling Pathway
FABP4 regulates fatty acid uptake, transport and metabolism, as well as biological processes such as inflammation and insulin resistance by participating in a variety of signaling pathways, such as PPARγ, JNK/IKK, AMPK, insulin and NF-κB. In the PPARγ pathway, FABP4 is a target gene for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ). By interacting with PPARγ, FABP4 can regulate the intake and storage of fatty acids, thereby affecting the formation and function of adipose tissue.
FABP4 Related Diseases
Abnormal FABP4 function has been linked to a variety of diseases, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, and tumors. The abnormal expression of FABP4 in tumor cells may be involved in the genesis and development of tumors by regulating the production and release of cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Bioapplications of FABP4
The biological process of FABP4 involves many aspects such as lipid metabolism, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc. There are a lot of mechanism studies and therapeutic strategies development about FABP4 in current scientific research. FABP4 levels are associated with disease development and prognosis in some diseases and can also be used as a biomarker for diagnosis, prognostic assessment and disease surveillance.
Case Study
Case study 1: Jiasi Chen, 2023
Ferroptosis, which is caused by an iron-dependent accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides, is a type of cell death linked to diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Previous research has shown that fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) is involved in the regulation of ferroptosis in diabetic retinopathy. The present study was constructed to explore the role of FABP4 in the regulation of ferroptosis in DKD. Firstly the expression of FABP4 and proteins related to ferroptosis in renal biopsies of patients with DKD were detected. Then, a FABP4 inhibitor and small interfering RNA were used to investigate the role of FABP4 in ferroptosis induced by high glucose in human renal proximal tubular epithelial (HG-HK2) cells.
In kidney biopsies of DKD patients, the expression of FABP4 was elevated, In HG-HK2 cells, the induction of ferroptosis was accompanied by an increase in FABP4. Inhibition of FABP4 in HG-HK2 cells changed the redox state, sup-pressing the production of reactive oxygen species, ferrous iron (Fe2+), and malondialdehyde, increasing superoxide dismutase, and reversing ferroptosis-associated mitochondrial damage.
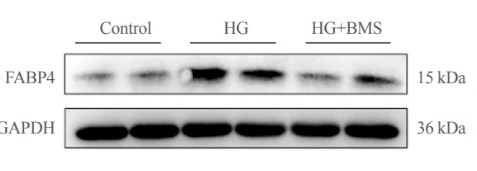
Fig1. Expression of FABP4 in the three groups indicated.
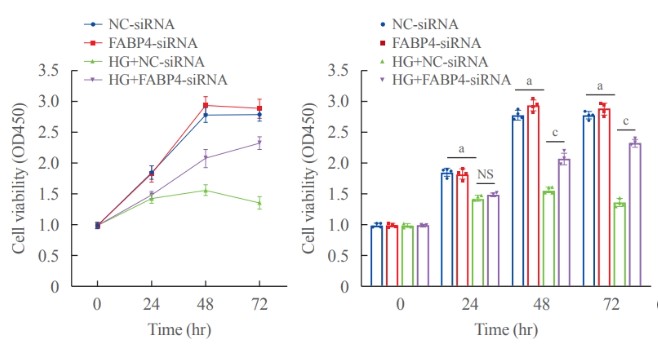
Case study 2: Emmanuelle Berger, 2023
Adipose tissue expandability depends on adipocyte size and number. In mature adipocytes, lipid accumulation as triglycerides into droplets is imbalanced by lipid uptake and lipolysis. The present study aims to decipher the mechanisms involved in fat mass regulation by fatty acid/FAT-CD36 signalling.
Human adipose stem cells, 3T3-L1, and its 3T3-MBX subclone cell lines were used in 2D cell cultures or co-cultures to monitor in real-time experiments proliferation, differentiation, lipolysis, and/or lipid uptake and activation of FAT/CD36 signalling pathways regulated by oleic acid, during adipogenesis and/or regulation of adipocyte size. Both FABP4 uptake and its induction by fatty acid-mediated FAT/CD36-PPARG gene transcription induce accumulation of intracellular FABP4, which in turn reduces FAT/CD36, and consequently exerts a negative feedback loop on FAT/CD36 signalling in both adipocytes and their progenitors.
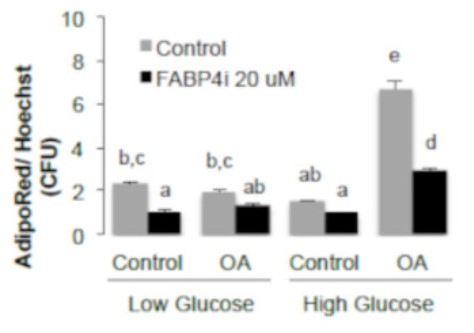
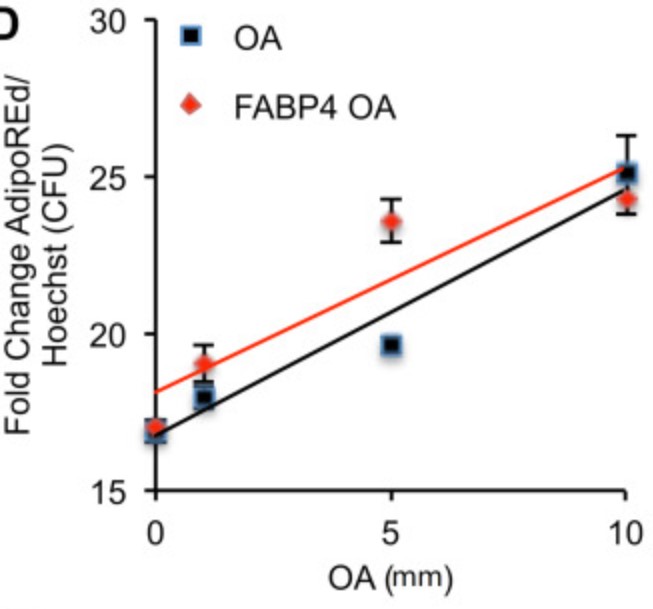
Fig3. 3T3-MBX adipocytes treated during 24 h in low glucose (LG, 1 g/L), high glucose (HG, 4.5 g/L) with or without OA (10 μM) and or inhibitor of FABP4 (FABP4i 20 μM) then analyzed by image quantification of Adipored and Hoechst (n = 8 biological replicates).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FABP4-440H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FABP4-2561H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
Fabp4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Fabp4 participated on our site, such as PPAR signaling pathway,Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Fabp4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| PPAR signaling pathway | AQP7,ACSL4A,CYP4A12A,RXRGB,MMP1,RXRB,Scd1,ADIPOQ,ACSL5,PLIN1 |
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | PIK3CD,GNAI2,AKT1,PIK3CA,GNAI3,TSHB,INS2,PIK3R3,AQP7,INSR |
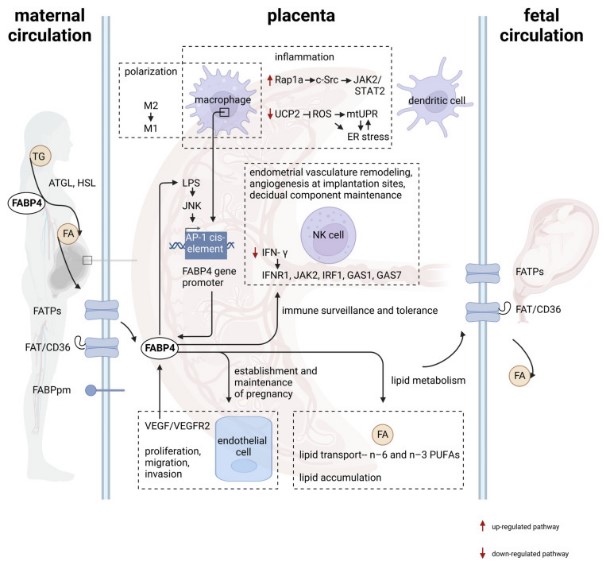
Fig1. The diverse role of FABP4 in pregnancy health by regulating immunological and metabolic hemostasis in the placenta. (Yue Shi, 2023)
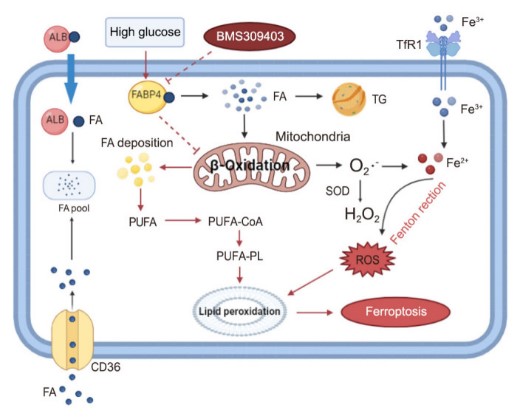
Fig2. Potential mechanism of fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) involvement in ferroptosis-mediated renal tubule injury induced by high glucose. (Jiasi Chen, 2023)
Protein Function
Fabp4 has several biochemical functions, for example, fatty acid binding,transporter activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Fabp4 itself. We selected most functions Fabp4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Fabp4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transporter activity | MUP17,TTPAL,CRABP2A,SLCO1A6,SLCO4C1,LBFABP,OSTA,AP1B1,HIATL1,SLC2A15A |
| fatty acid binding | GPR120,PMP2,FABP10A,Alb,HNF4A,FABP7A,CYP4A14,FABP1,APOC1,PTGDS |
Interacting Protein
Fabp4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Fabp4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Fabp4.
VIM;SNCG;OSTF1;EXT2;USP15;ZBED1;ZNF16;PRKCI;ACTB;CHD3;TFAP2C
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Girona, J; Rosales, R; et al. FABP4 Induces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Migration through a MAPK-Dependent Pathway. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).
- Bee, C; Abdiche, YN; et al. Determining the Binding Affinity of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies towards Their Native Unpurified Antigens in Human Serum. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).



