KRT17
-
Official Full Name
Keratin 17 -
Overview
This gene encodes the type I intermediate filament chain keratin 17, expressed in nail bed, hair follicle, sebaceous glands, and other epidermal appendages. Mutations in this gene lead to Jackson-Lawler type pachyonychiacongenita and steatocystoma multiplex. -
Synonyms
PC;K17;PC2;PCHC1;KRT17;keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17;39.1;CK-17;keratin-17;cytokeratin-17;OTTHUMP00000164770
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Bovine
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- S
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- GST
Background
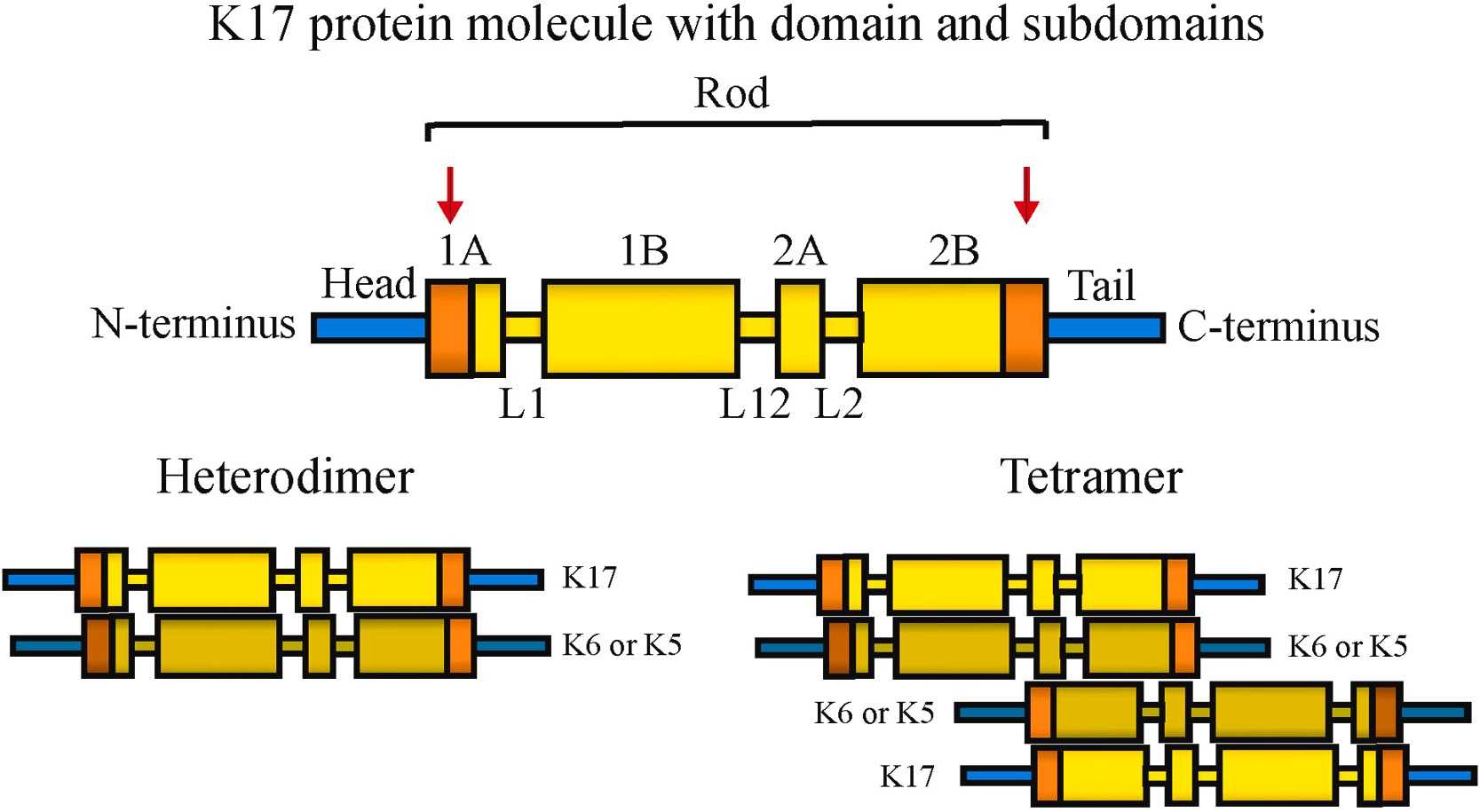
Fig1. Schematic depiction of the protein structure of K17 (Yiting Lin, 2022)
What is KRT17 Protein?
KRT17 gene (keratin 17) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. KRT17 protein is a type I intermediate filament protein, which is mainly expressed in skin attachments such as nail bed, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, etc. It plays a key role in maintaining the shape and orientation of skin and hair, and is essential for the proper growth of hair follicles, especially for maintaining the anagen state. KRT17 is also involved in tissue repair and may act as a marker for complex epithelial basal cell differentiation, indicating a certain type of epithelial "stem cell." In addition, KRT17 may contribute to the development of basal cell skin tumors by promoting a Th1/ Th17-dominated immune environment. The KRT17 protein is consisted of 432 amino acids and KRT17 molecular weight is approximately 48.1 kDa.
What is the Function of KRT17 Protein?
KRT17 is involved in determining the shape and orientation of hair and is necessary for the normal growth of hair follicles, especially for maintaining the anagen state. In terms of immune response, KRT17 may contribute to the development of basal cell skin tumors by promoting a Th1/ Th17-dominated immune environment. KRT17 also plays a role in the nucleus, influencing nuclear morphology and chromatin organization, thereby affecting gene expression, cell proliferation, and RNA processing. In addition, it is also related to the occurrence and development of tumors, and affects the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells by regulating related signaling pathways.
KRT17 Related Signaling Pathway
In laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), KRT17 accelerates cell proliferation and invasion potential by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. KRT17 is also involved in regulating the Wnt/ beta-catenin signaling pathway, which plays a key role in the development and progression of multiple cancers, including squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. In pancreatic cancer, KRT17 acts through the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway, regulating cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. In gastric cancer, the interaction between CircKRT17 and miR-485-5p may affect the occurrence and development of gastric cancer through the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway.
KRT17 Related Diseases
The KRT17 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, particularly those associated with skin and hair, such as Jackson-Lawler type pachyonychia and multiple lipomas, which are often caused by mutations in the KRT17 gene. In addition, abnormal expression of KRT17 is also associated with the development of a variety of cancers, including laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, lung cancer, etc. It promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells by affecting AKT/mTOR, Wnt/β-Catenin and other signaling pathways, thus playing a role in tumor progression. Therefore, abnormal regulation of KRT17 may be closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of tumors, making it a potential target for cancer therapy.
Bioapplications of KRT17
The abnormal expression of KRT17 protein is closely related to the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases, especially skin-related diseases and cancers, so its relevant off-the-shelf applications are mainly concentrated in the field of medical research and clinical diagnosis. In medical research, KRT17 serves as a biomarker that can be used to study the mechanisms of cell proliferation, differentiation and tumor development. In clinical diagnosis, the detection of KRT17 is helpful for early diagnosis, prognosis assessment and treatment response monitoring of certain types of cancer. In addition, targeted therapeutic strategies for KRT17, such as modulating its expression through small molecule drugs or RNA interference techniques, are being explored in cancer therapy research with a view to developing new therapies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Liqiong Wu, 2023
This study investigated the role of KRT17 in TNBC-Dox resistance. Immuno-histochemical staining, qPCR, western blotting (WB), and immunofluorescence were used to detect the expression of KRT17 in TNBC-Dox-resistant patients and in TNBC-Dox-resistant MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231. The results showed that KRT17 was highly expressed in the TNBC-Dox-resistant cells. KRT17 regulated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The inhibitory effect of KRT17 knockdown on the proliferation and migration of TNBC-Dox-resistant cells was reversed by an activator of the Wnt signaling pathway.
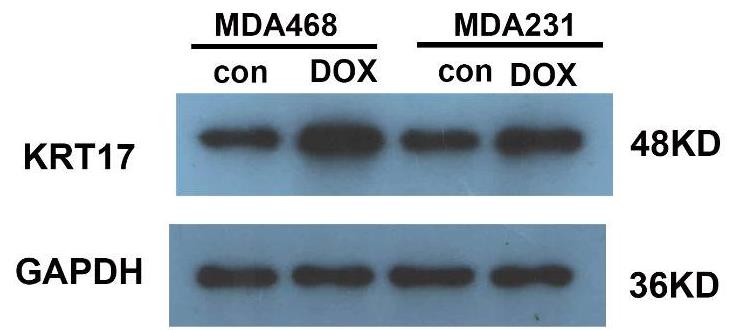
Fig1. KRT17 protein level detected by WB.
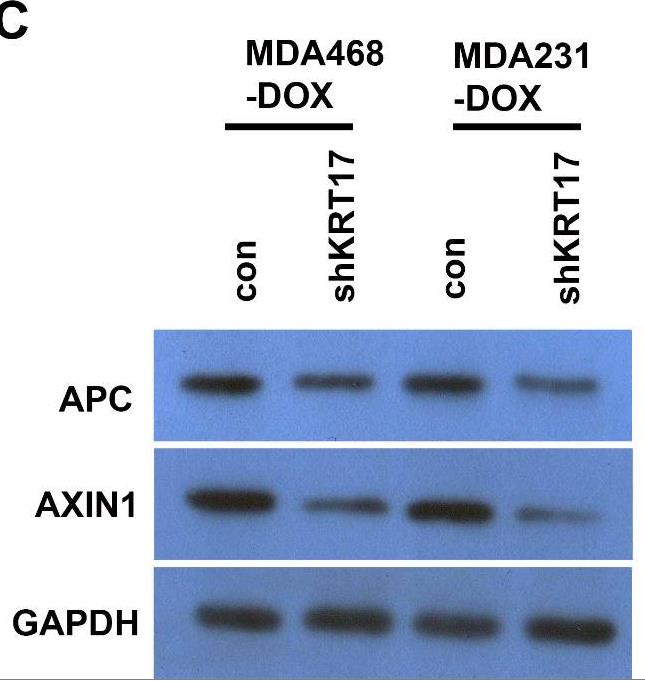
Fig2. The effect of KRT17 on the expression of APC and AXIN protein was detected by WB.
Case Study 2: Wenfeng Liang, 2023
Poor infiltration of T lymphocytes has been regarded as a crucial mechanism of tumor immune escape. Here, researchers demonstrate a protective role of KRT17 in colorectal cancer, where KRT17 reversed the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment by increasing T-lymphocyte infiltration. High-throughput RNA sequencing suggested that KRT17 was significantly upregulated in deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) tumors compared with proficient mismatch repair (pMMR) tumors. Krt17 overexpression decreased xenograft tumor growth in immune-competent mice. T-cell depletion in a murine model showed that the presence of T lymphocytes was necessary for Krt17-mediated disruption of tumorigenesis. Mass spectrometry and coimmunoprecipitation assays suggested KRT17 caused YTHDF2 degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. KRT17 synergized with anti-PD-1 for better tumor control in an immunotherapy-resistant murine model. In a cohort of patients with colorectal cancer receiving pembrolizumab, high KRT17 expression was found within the tumors of responders.
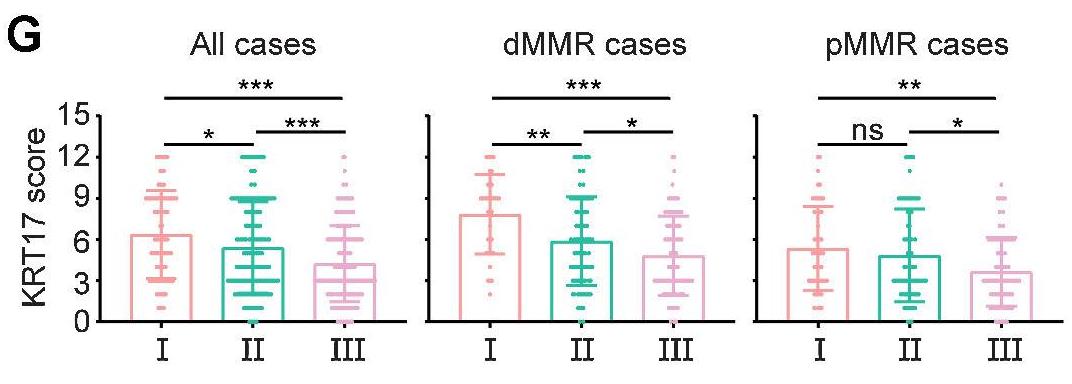
Fig3. Quantification of KRT17 expression by IHC score in all 446 human colorectal cancer samples.
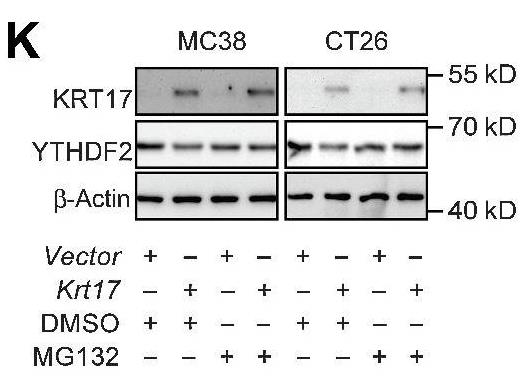
Fig4. Western blot analysis of KRT17 and YTHDF2 protein levels.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (KRT17-017H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (KRT17-4392H)
Involved Pathway
KRT17 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways KRT17 participated on our site, such as EGFR1 Signaling Pathway,Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with KRT17 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network | SMARCC2,POU2F1,SMARCA4,BGLAP,NR1I3,KRT5,EGR1,SMARCD1,KRT14,CSN2 |
| EGFR1 Signaling Pathway | KRT8,ZPR1,KRT7,DNM1,SPRY2,WNK1,APPL2,EEF1A1,AP2A1,RALBB |
Protein Function
KRT17 has several biochemical functions, for example, MHC class II protein binding,MHC class II receptor activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by KRT17 itself. We selected most functions KRT17 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with KRT17. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MHC class II receptor activity | HLA-DPA1,HLA-DOB,HLA-DOA,HLA-DRB3,HLA-DRB1,HLA-DRB4,HLA-DRA,HLA-DQB1,HLA-DQA1,HLA-DQB2 |
| structural constituent of cytoskeleton | BFSP1,ARPC4,TUBB2,MSN,TLN2A,KRT6B,TPM1,KRT2,TUBGCP2,ARPC1B |
| MHC class II protein binding | CD4,CD74B,LAG3,MARCH8,CD74,CD74A |
| protein binding | YIPF4,ZNF572,PARVB,MTAP1A,NRL,NKAP,RMND1,LPAR1,EMP1,SP4 |
Interacting Protein
KRT17 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with KRT17 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of KRT17.
CCDC85B;USP1;UCHL1;KDM1A;SNAPIN;KRT6A;APC;ZDHHC17;midostaurin;EGFR;CFTR;GRB2;YWHAZ;NETO2;GABARAPL1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



