Detergent Micelle Platform
The Detergent Micelle Platform at Creative BioMart provides an advanced and reliable approach for the extraction, solubilization, and purification of integral membrane proteins. By leveraging carefully selected detergents to mimic the natural lipid bilayer environment, our platform preserves protein structure, stability, and activity. Suitable for bacterial, yeast, insect, mammalian, and cell-free expression systems, the Detergent Micelle Platform enables efficient recovery of highly pure, homogeneous, and functional membrane proteins for structural and biochemical studies.
Background: How Detergent Micelles Facilitate Expression and Purification
Integral membrane proteins are embedded in lipid bilayers through hydrophobic interactions between lipid tails and the proteins’ hydrophobic domains. These proteins are insoluble in aqueous environments, often forming aggregates when isolated. To overcome this, detergent micelle technology is employed. Detergents form micellar structures that encapsulate the hydrophobic regions of membrane proteins, effectively simulating their natural lipid surroundings. This enables solubilization of otherwise insoluble proteins while maintaining their correct folding and biological function.
At Creative BioMart, we have developed a specialized Detergent Micelle Platform designed to address the challenges of membrane protein extraction and purification. Our experts tailor the detergent selection and experimental conditions to meet the unique requirements of each protein target, ensuring optimal solubilization efficiency and functional integrity.
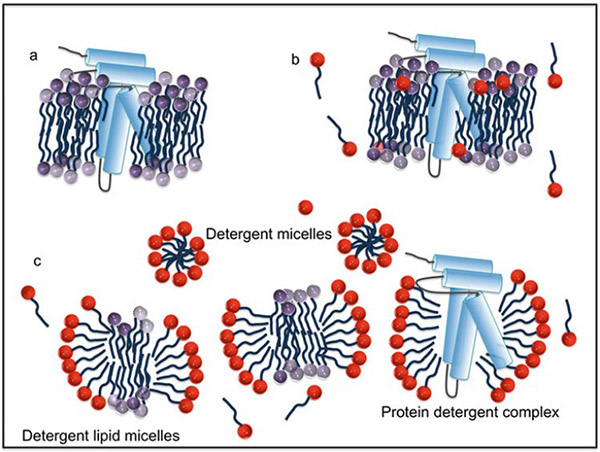
Figure 1. Representation of membrane protein solubilization. (a) Membrane protein embedded in the lipid bilayer. (b) Insertion of detergent monomers disrupting the lipid bilayer. (c) Solubilization of the lipid bilayer and extraction of membrane protein. (Anandan and Vrielink, 2016)
What Our Detergent Micelle Membrane Protein Expression Platform Deliver
Creative BioMart provides comprehensive membrane protein extraction and purification services using our Detergent Micelle Platform, including:
- Custom detergent screening to identify optimal solubilization agents and combinations.
- Membrane protein extraction from various expression systems (bacterial, yeast, insect, mammalian, and cell-free).
- Optimized purification workflows using ion exchange, affinity, and gel filtration chromatography.
- High-resolution separation for enhanced purity and homogeneity.
- Additive optimization to improve protein stability and prevent aggregation.
- Quality control and validation using gel-based or gel-free high-throughput analytical techniques.
Service Workflow

Choose “Right” Detergent for Your Protein
Creative BioMart’s random mutagenesis platform provides precise control and flexibility for designing high-quality mutant libraries tailored to specific research goals.
|
Detergent Type |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Nonionic Detergents |
Mild; maintain protein activity; minimize denaturation |
May yield lower solubilization efficiency |
|
Ionic Detergents (cationic/anionic) |
Highly effective at solubilization |
May cause denaturation; can interfere with ion exchange |
|
Amphoteric Ionic Detergents |
Combine benefits of ionic and nonionic types |
Greater potential for denaturation than nonionic detergents |
Service Features
- Expression Systems Supported: E. coli, yeast, insect cells, mammalian cells, and cell-free systems
- Purification Methods: Ion exchange, affinity, and size exclusion chromatography
- Applications: Structural biology; functional reconstitution; drug screening; biophysical characterization
Our Advantagess
- Comprehensive Expertise: Deep understanding of detergent chemistry and membrane protein biophysics.
- Tailored Optimization: Custom detergent screening, additive testing, and condition refinement for each target.
- Multi-System Compatibility: Support for a wide range of expression hosts from bacterial to mammalian systems.
- High Purity and Stability: Proven workflows yield homogeneous, functional proteins suitable for structural or biochemical analysis.
- Advanced Analytical Support: High-throughput QC ensures accuracy, reproducibility, and batch consistency.
- Reliable Partnership: Experienced scientists, responsive communication, and cost-effective solutions trusted by leading research groups.
Representative Case Studies
Case 1: Modular detergents tailor the purification and structural analysis of membrane proteins
Urner et al., 2020. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-14424-8
The detergent micelle platform using oligoglycerol detergents (OGDs) represents a major advance in membrane protein expression and purification. Traditional detergents like DDM are effective but lack flexibility for optimizing individual protein systems. OGDs, by contrast, feature a modular architecture that allows fine-tuning of solubilization and stabilization properties, enabling high-yield purification while preserving native lipid–protein interactions. Using bacterial membrane proteins such as AqpZ, AmtB, and MATE, as well as functional GPCRs, researchers demonstrated efficient extraction from E. coli membranes and purification via IMAC. The OGD platform thus provides a versatile, customizable approach for structural biology and lipid–protein interaction studies.
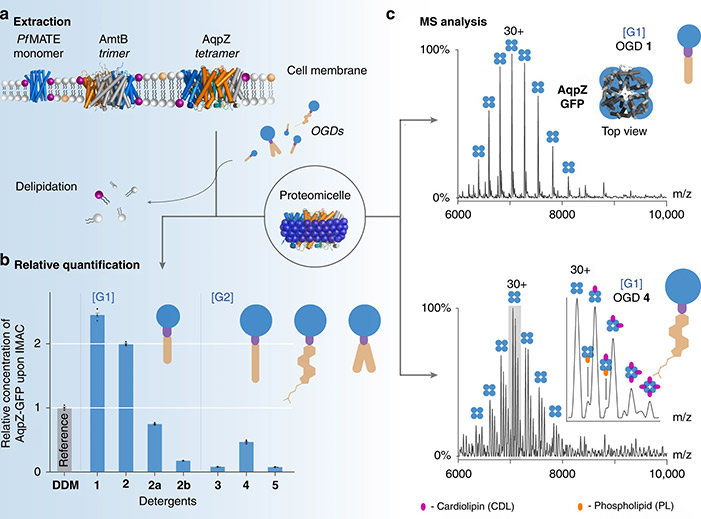
Figure 2. OGDs tailor the purification and native MS analysis of membrane proteins. (a) Three membrane proteins were extracted using OGDs 1–5. (b) [G1] OGDs yielded higher protein recovery, with the regioisomer mixture 2 (=2a + 2b) outperforming individual forms. (c) Mass spectra of AqpZ-GFP show no lipid complexes with [G1] OGDs, while [G2] OGDs (mixture 4) preserved native lipid–protein interactions under similar MS conditions. (Urner et al., 2020)
Case 2: Expression and purification of human BSEP and MDR3 in Pichia pastoris
Matar-Merheb et al., 2011. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018036
The human liver ABC transporters BSEP (ABCB11) and MDR3 (ABCB4) are essential for bile formation, translocating bile salts and phosphatidylcholine across hepatocyte membranes. Using Pichia pastoris as a heterologous expression system, both proteins and their GFP-fusion forms were successfully localized to the plasma membrane and purified—yielding approximately 1 mg of BSEP and 6 mg of MDR3 per 100 g wet cell mass. Screening over 100 detergents identified zwitterionic, lipid-like agents such as Fos-cholines and Cyclofos as optimal for solubilization. Purified proteins retained ATP-binding and substrate-dependent ATPase activity, establishing a foundation for detailed biochemical and functional studies.
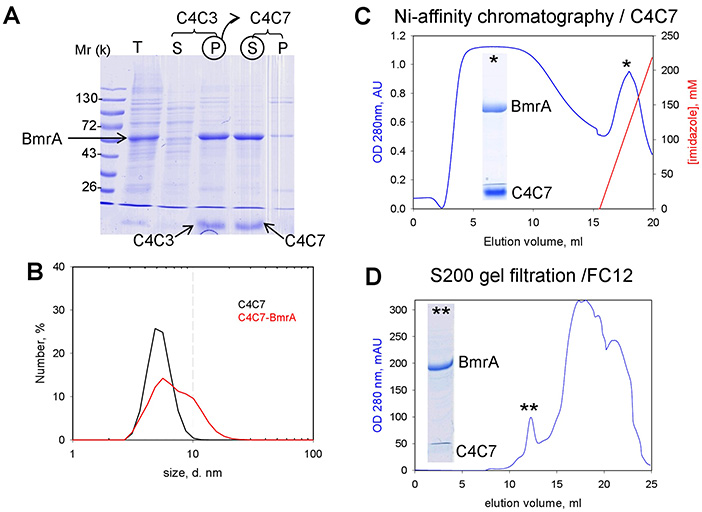
Figure 3. BmrA purification with C4Cn and detergent exchange. (A) SDS-PAGE of the sequential extraction of BmrA. the membrane fraction (lane T) was incubated with C4C3 and then centrifuged to give the supernatant S and the pellet P. The latter, enriched in BmrA, was suspended in the presence of C4C7 and then centrifuged to give the corresponding supernatant S and pellet P. Arrows indicate the position of BmrA, C4C3 and C4C7. The C4C7 supernatant was then subjected to DLS (B), Ni-affinity chromatography (C) and gel filtration carried out with FC12 (D) from which respective pools indicated by stars were loaded onto SDS-PAGE. (Matar-Merheb et al., 2011)
What Our Clients Say About Our Detergent Micelle Platform
“We collaborated with Creative BioMart to purify a challenging GPCR expressed in HEK293 cells for ligand-binding and crystallography studies. Their Detergent Micelle Platform enabled efficient solubilization with minimal loss of activity. The team screened multiple detergent combinations and identified a nonionic–amphoteric mix that maintained receptor stability for over three weeks. Their detailed analytical report and proactive communication made the process seamless from start to finish.”
— Senior Scientist, Structural Biology | Global Pharmaceutical Company
“Our project focused on an ion channel expressed in insect cells that was notoriously unstable during purification. Creative BioMart’s Detergent Micelle Platform delivered excellent results—over 30 mg/L of homogeneous protein that retained full electrophysiological activity after purification. Their scientists quickly optimized the detergent type and extraction temperature, which saved us considerable development time. The quality of the purified material exceeded our internal performance benchmarks.”
— Director of Biophysics | Mid-size Biotech Company
“We approached Creative BioMart to isolate a membrane transporter for drug screening and structural analysis. Our previous attempts using harsh ionic detergents led to aggregation and inactivity. Their experts implemented a tailored detergent screening workflow, identifying a mild nonionic detergent that preserved protein function. The purified transporter was highly stable and suitable for cryo-EM. Their technical insight and responsiveness were top-notch throughout the collaboration.”
— Principal Investigator | Academic Research Institute
“For our large-scale production of a bacterial efflux pump complex, Creative BioMart’s Detergent Micelle Platform proved indispensable. They optimized detergent extraction conditions and developed a scalable purification protocol that preserved native oligomeric states. We obtained gram-level yields of active protein suitable for formulation studies. Their systematic approach and deep understanding of membrane protein chemistry made them an invaluable extension of our team.”
— Director of Process Development | Global Pharmaceutical Company
FAQs About Detergent Micelle Platform
-
Q: What is the Detergent Micelle Platform?
A: The Detergent Micelle Platform is our specialized system for solubilizing and purifying integral membrane proteins using optimized detergent micelles. These detergents mimic the lipid bilayer environment, allowing proteins to remain stable and functional outside of cell membranes. -
Q: Why are detergents important in membrane protein purification?
A: Membrane proteins are naturally insoluble in water. Detergents form micelles that encapsulate hydrophobic regions, preventing aggregation and enabling purification while maintaining native-like structure and activity. -
Q: What types of detergents do you use?
A: We work with nonionic, ionic, and amphoteric detergents, selecting or combining them based on your target protein’s properties. Each detergent type has specific benefits and limitations, and our scientists optimize the choice for maximum solubilization and stability. -
Q: Which expression systems are compatible with this platform?
A: The Detergent Micelle Platform supports bacterial, yeast, insect, mammalian, and cell-free systems, allowing flexible adaptation to your expression strategy and experimental goals. -
Q: How do you ensure the protein remains functional after solubilization?
A: We carefully control detergent type, concentration, extraction time, and temperature. Functional validation through ligand-binding or activity assays confirms the protein’s integrity after purification. -
Q: What is the typical project timeline?
A: Most projects—from detergent screening to purified, validated protein—are completed within 6–10 weeks, depending on target complexity and downstream requirements. -
Q: Can you screen multiple detergents in parallel?
A: Yes. We routinely perform parallel detergent screening to identify the most effective solubilization conditions. This approach speeds up optimization and increases the likelihood of obtaining active, monodisperse protein. -
Q: What quality control methods do you use?
A: We apply gel-based and gel-free high-throughput analysis to assess purity, homogeneity, and stability. All QC data are included in the final project report for full transparency. -
Q: Is the process scalable for larger quantities?
A: Absolutely. The platform is designed for scalable purification, from small research batches to larger preclinical production runs, without compromising protein quality or consistency.
Other Resources
Related Services
References:
- Anandan A, Vrielink A. Detergents in membrane protein purification and crystallisation. In: Moraes I, ed. The Next Generation in Membrane Protein Structure Determination. Vol 922. Springer International Publishing; 2016:13-28. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-35072-1_2
- Matar-Merheb R, Rhimi M, Leydier A, et al. Structuring detergents for extracting and stabilizing functional membrane proteins. Hoheisel J, ed. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(3):e18036. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018036
- Urner LH, Liko I, Yen HY, et al. Modular detergents tailor the purification and structural analysis of membrane proteins including G-protein coupled receptors. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):564. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-14424-8
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

