Magnetic Bead-Coupled Proteins and Nucleic Acids
Creative BioMart provides expert Magnetic Bead Coupling Services for proteins, nucleic acids, peptides, and other biomolecules. Utilizing highly efficient bioconjugation techniques, we enable the covalent attachment of biomolecules to superparamagnetic beads, achieving coupling efficiencies of over 85%. Our platform supports a wide range of applications—from immunoprecipitation and protein purification to aptamer screening and immunodiagnostics—through customizable protocols and robust QC data. Whether you need streptavidin-biotin systems, enzyme coupling, or nucleic acid immobilization, our magnetic bead solutions offer speed, specificity, and scalability.
Background: The Power of Magnetic Bead Bioconjugation in Biomolecular Research
Bioconjugation, the process of covalently linking two biomolecules, is a cornerstone in modern life science research and diagnostics. Common biochemical coupling strategies include amine coupling (via lysine residues), sulfhydryl coupling (via cysteine), and photo-induced radical reactions, producing stable and functional bioconjugates for downstream use.
In recent years, the use of superparamagnetic beads—fine-particle microspheres that aggregate under magnetic fields and redisperse when removed—has revolutionized the separation and purification landscape. Their versatility makes them especially valuable for targeted biomolecular capture, diagnostics, and high-throughput screening.
At Creative BioMart, one of our most in-demand services is coupling magnetic beads to proteins and nucleic acids, creating powerful tools for tasks such as:
- Antibody and aptamer screening
- Nucleic acid purification and probe detection
- Target protein pull-down assays
- Enzyme immobilization
- Immunoprecipitation and immunodiagnostics
We specialize in both standard and novel biomolecule-bead conjugations—including biotin-streptavidin interactions , protein-protein coupling , and oligonucleotide labeling —to help our clients advance their research faster and more effectively.
What We Offer: Custom Magnetic Bead-Coupled Proteins and Nucleic Acids Services
Service Workflow
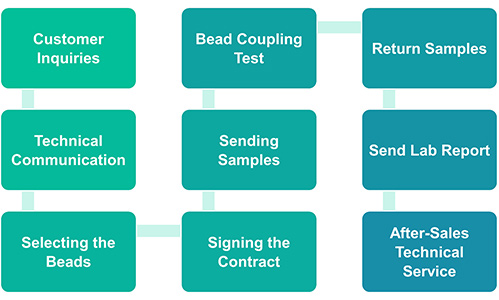
Service Details
|
Item |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Bead Selection & Preparation |
Choose from our diverse in-house magnetic bead library (e.g., streptavidin, carboxyl, epoxy-modified). |
|
Conjugation Chemistry Execution |
Apply optimized coupling protocols (e.g., EDC/NHS for carboxyl groups, maleimide-thiol coupling, click chemistry). |
|
Post-Coupling Purification |
Remove unbound biomolecules and buffer-exchange for storage compatibility. |
|
Quality Control |
Provide detailed QC including coupling efficiency (>85%), SDS-PAGE, UV/Vis analysis, and functional activity tests. |
Service Offerings
We offer magnetic bead conjugation for the following biomolecules:
-
Proteins & Antibodies
For pull-down assays , immunoprecipitation , or diagnostic platforms
-
Peptides
Including antigen-presenting constructs and bioactive fragments
-
DNA/RNA/Oligonucleotides
For hybridization assays, aptamer screening, and molecular probe development
-
Enzymes
For catalysis-based assays and immobilization systems
-
Biotinylated Molecules
Coupled to streptavidin or neutravidin-coated beads for high-specificity capture
Why Choose Us for Magnetic Bead-Coupling Solutions
- High Coupling Efficiency : Achieve >85% biomolecule binding, reducing waste of expensive reagents like antibodies and enzymes.
- Diverse Bead Library : Access a wide selection of magnetic beads tailored to your molecular targets and assay needs.
- Preserved Activity : Site-specific coupling ensures optimal orientation and retains biomolecule functionality for reliable downstream performance.
- Custom Protocols & Full QC Data : Receive full transparency with detailed SOPs and validation reports.
- Comprehensive Biomolecule Coverage : From proteins and nucleic acids to uncommon targets like synthetic polymers and oligosaccharides.
- Rapid Turnaround & Scalable Process : Speed up your R&D with flexible batch sizes and fast processing timelines.
Case Studies: Magnetic Bead-Coupled Biomolecule Applications in Real Projects
* NOTE: We prioritize confidentiality to safeguard our clients’ technology and intellectual property. As an alternative, we present selected published research articles as representative case studies. For details on the assay services and products used in these studies, please refer to the relevant sections of the cited literature.
Case 1: Affinity molecular assay for detecting Candida albicans
Shen et al. , 2024. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-53693-5
A magnetic bead-based molecular diagnostic method was developed to rapidly detect invasive fungal infections (IFIs), which are life-threatening for immunocompromised individuals. The approach combines affinity magnetic separation (AMS), silicon hydroxyl magnetic bead DNA extraction, and one-pot detection, achieving detection of C. albicans at just 30 CFU/mL within 2.5 hours—100× more sensitive than microscopy. For efficient fungal enrichment, various chitin-binding proteins (CBPs) were conjugated to carboxyl magnetic beads, with PfCBP-A showing optimal performance. The conjugation efficiency was validated via BCA assay and particle sizing. This cost-effective, highly specific platform offers rapid fungal diagnostics, especially for resource-limited clinical settings.
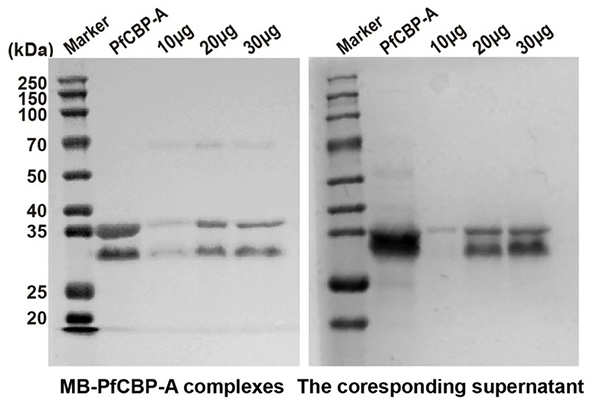
Figure 1. Detection of the protein required for saturation of 1 mg magnetic beads. Pre-conjugated protein PfCBP-A, MB-PfCBP-A complex and corresponding supernatant were assessed by 12.5% SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. (Shen et al ., 2024)
Case 2: Decoding AtGRP7 mRNA-protein interactions in Arabidopsis
Reichel et al ., 2024. doi:10.1186/s12870-024-05249-4
Magnetic bead-coupled nucleic acid technology enables high-specificity isolation of RNA-protein complexes, advancing our understanding of RNA regulation. In this study, RNA Interactome Capture (RIC) was used in Arabidopsis thaliana to identify proteins interacting with the AtGRP7 mRNA. UV crosslinking stabilized RNA-protein interactions, and bead-coupled antisense oligonucleotides, including enhanced LNA/DNA hybrids, were used to pull down the target RNA. A two-round capture strategy further improved yield. Mass spectrometry revealed 356 enriched RNA-binding proteins, including ALBA family members, with functional validation. This method demonstrates how magnetic bead-coupled oligonucleotides can precisely isolate specific mRNA-protein complexes, offering insights into RNA biology and expression regulation.
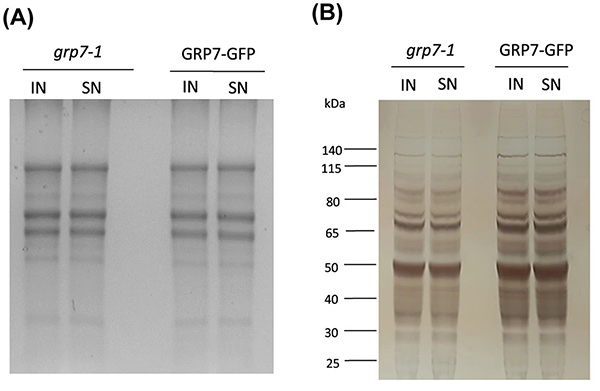
Figure 2. Mass spectrometry of proteins bound to AtGRP7 RNA after tandem capture. (A) RNA gel of lysate and post-hybridization supernatant from AtGRP7 -GFP and control plants. (B) Silver-stained protein gel of the same samples with molecular weight markers indicated. (Reichel et al ., 2024)
What Our Clients Say About Our Bead-Coupled Protein & Nucleic Acid Services
"We needed a reliable method for RNA-protein interaction studies, and Creative BioMart's magnetic bead-coupling service exceeded expectations. Their team coupled our custom antisense oligos to magnetic beads with over 90% efficiency, enabling successful pull-downs of low-abundance Arabidopsis transcripts."
— Principal Investigator | Academic Research Institute
"Creative BioMart helped us couple magnetic beads with fungal cell wall-binding proteins for our Candida detection assay. Their high-efficiency coupling and comprehensive QC data made it easy to integrate the reagents into our workflow. We were able to detect C. albicans down to 30 CFU/mL—game-changing sensitivity!"
— R&D Director | Biotech Startup Focused on Diagnostics
"We commissioned magnetic bead-coupled antibodies for high-throughput immune screening, and Creative BioMart delivered with precision and speed. Their streptavidin-biotin system maintained binding integrity across batches, helping us screen hundreds of targets with confidence. Truly scalable and reproducible."
— Senior Scientist | Pharmaceutical Company (Immuno-Oncology)
"For our viral RNA interactome project, we required bead-coupled oligo(dT) probes compatible with UV-crosslinking protocols. Creative BioMart not only provided high-quality LNA/DNA bead conjugates, but also supported our optimization process. Their support enabled successful RIC-MS profiling in just weeks."
— Group Leader | Government Research Lab (Virology Division)
FAQs About Magnetic Bead-Coupled Protein and Nucleic Acid Services
-
Q: What types of biomolecules can be coupled to magnetic beads in your service?
A: We offer magnetic bead conjugation for a wide range of biomolecules, including proteins (e.g., antibodies, enzymes, peptides), nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, oligos), and even more specialized targets such as biotinylated probes, carbohydrates, and synthetic polymers. If your target isn't listed—just ask! Custom coupling is our specialty. -
Q: What’s the typical coupling efficiency, and why does it matter?
A: Our proprietary protocols consistently achieve >85% coupling efficiency, minimizing waste of costly reagents like antibodies and peptides. High coupling efficiency also translates into stronger binding capacity, better assay sensitivity, and lower background in applications like pull-down assays, immunoprecipitation, or diagnostic tests. -
Q: Can you customize bead types or surface chemistries for specific applications?
A: Yes! We maintain a diverse inventory of magnetic beads (carboxyl, streptavidin, amine, epoxy, etc.) and will match the bead chemistry to your biomolecule and intended use. Whether you need high-capacity beads for purification or gentle-release beads for reversible binding—we’ve got you covered. -
Q: Do you provide quality control and validation data with each project?
A: Absolutely. Every coupling project includes QC data such as BCA protein quantification, particle size analysis, and binding activity confirmation (e.g., via ELISA or pull-down test). You'll receive a detailed report with each batch to ensure reproducibility and performance. -
Q: What are the typical turnaround times for a custom magnetic bead conjugation project?
A: Standard projects are typically completed within 3–6 weeks, depending on molecule complexity and scale. We also offer expedited services for urgent timelines—just let us know your needs upfront. -
Q: What are common downstream applications for your magnetic bead-coupled products?
A: Our customers use bead-coupled biomolecules for applications like:- RNA and protein interactome mapping (e.g., RIC, CLIP, pull-down)
- High-throughput antibody and aptamer screening
- Fungal and bacterial pathogen detection
- Targeted protein purification
- Cell sorting and biomarker capture
If you’re unsure how to integrate our service into your workflow, our technical team is happy to advise.
Resources
Related Services
- Protein Bioconjugation Services
- Quality Control
- Enzyme Immobilization
- Pull-Down Assays
- High-Throughput Screening
- Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Service
- Protein Expression and Purification Services
Related Products
References:
- Reichel M, Schmidt O, Rettel M, et al . Revealing the Arabidopsis AtGRP7 mRNA binding proteome by specific enhanced RNA interactome capture. BMC Plant Biol . 2024;24(1):552. doi:10.1186/s12870-024-05249-4
- Shen S, Wang W, Ma Y, et al . Affinity molecular assay for detecting Candida albicans using chitin affinity and RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a. Nat Commun . 2024;15(1):9304. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-53693-5
- Weng Y, Song C, Chiang CW, Lei A. Single electron transfer-based peptide/protein bioconjugations driven by biocompatible energy input. Commun Chem . 2020;3(1):171. doi:10.1038/s42004-020-00413-x
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

