Mammalian Two-Hybrid System
The Mammalian Two-Hybrid (M2H) System is a powerful and convenient platform for analyzing protein–protein interactions directly within transfected mammalian cells. Creative BioMart’s Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assay employs a highly sensitive secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter system, allowing interaction measurements without the need for cell lysis or extensive sample handling. By performing the assay in a mammalian cellular environment, proteins are more likely to adopt their native conformations and undergo physiologically relevant post-translational modifications. This enables the identification, confirmation, and characterization of biologically meaningful interactions with greater accuracy than yeast-based platforms.
Introduction to Membrane-Based Yeast Two-Hybrid System
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) lie at the core of nearly every biological process, from receptor signaling and transcription regulation to metabolic control and immune responses. Tools that allow researchers to map these interactions in a reliable and biologically relevant manner are therefore essential for understanding molecular mechanisms and developing therapeutic strategies.
While classical yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) systems have long served as the cornerstone of PPI research, they exhibit intrinsic limitations. Proteins expressed in yeast may fail to fold correctly, may lack key mammalian-specific post-translational modifications, or may require cellular stimuli that yeast cannot provide. Many mammalian proteins—particularly signaling molecules, receptors, and regulatory factors—display interaction behaviors that depend strongly on the native cellular environment. Consequently, interactions detected in yeast may not always predict functional relationships in mammalian systems.
The Mammalian Two-Hybrid System was developed to overcome these drawbacks. By conducting PPI studies directly in mammalian cells, the system ensures that analyzed proteins experience appropriate folding pathways, encounter native chaperones, and undergo correct post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, or ubiquitination. These features dramatically increase the physiological relevance of interaction data.
Creative BioMart’s Mammalian Two-Hybrid platform further improves the workflow by utilizing a SEAP secreted reporter. Instead of harvesting and lysing cells, researchers simply collect culture medium to measure reporter activity. This design enhances assay convenience, reduces processing variability, and facilitates real-time or kinetic monitoring of protein interactions.
For researchers needing functional validation of yeast-based hits, detailed mapping of interaction domains, or mammalian-specific PPI investigation, our Mammalian Two-Hybrid System provides a reliable, sensitive, and biologically accurate solution.
What Our Mammalian Two-Hybrid System Deliver
Creative BioMart provides comprehensive Mammalian Two-Hybrid services tailored specifically to the needs of academic laboratories, biotechnology companies, and pharmaceutical research groups. Our service portfolio includes:
-
Customized Experimental Strategy Development
We work closely with clients to evaluate research objectives and design project-specific assay strategies. This includes selecting optimal vectors, choosing appropriate mammalian cell lines, and determining whether domain-truncation constructs or mutation studies are necessary.
-
Vector Construction and Cloning
Our team generates high-quality bait and prey constructs fused to activation and DNA-binding domains required for the Mammalian Two-Hybrid assay. All constructs are sequence-verified and optimized for robust expression.
-
Transfection and Reporter-Based Interaction Detection
Using optimized transfection procedures, we deliver precise, reproducible expression of fusion proteins. SEAP reporter detection in culture supernatants enables effective measurement of interaction strength without disturbing cells.
-
Quantitative and Qualitative Data Analysis
We provide detailed analytical reports including fold-activation values, assay normalization, signal-to-background ratios, and interpretive commentary based on biological knowledge of the proteins studied.
-
Optional Interaction Confirmation Services
For clients who require additional verification, we offer complementary assays such as co-immunoprecipitation, pull-down assays, and FRET/BRET-based interaction studies.
-
Flexible Project Scale Options
Whether your project involves a single pair of proteins, multiple domain variants, or larger interaction screens, we offer scalable workflow formats to meet your research needs and timelines.
Service Workflow

Assay Principle
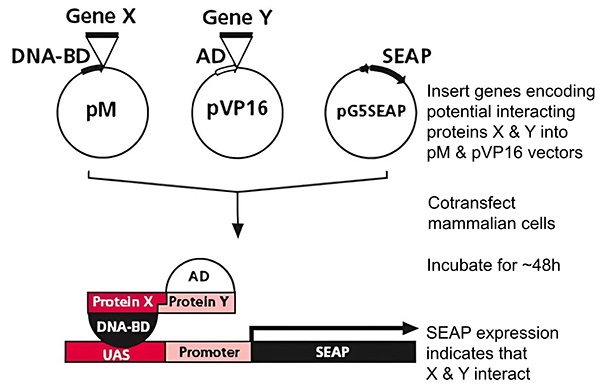
Figure 1. Conventional mammalian two-hybrid assay.
The Mammalian Two-Hybrid System is an adaptation of the classical two-hybrid concept but optimized for mammalian cell environments. In this system:
- One protein (bait) is fused to a DNA-binding domain.
- The interacting partner (prey) is fused to a transcription activation domain.
If the bait and prey interact, the fused domains come together to form a functional transcriptional activator, driving expression of the SEAP reporter gene. Because SEAP is secreted into the culture medium, interaction strength is measured without disrupting the cells.
Major Features
- Fast and convenient PPI analysis with minimal sample handling
- SEAP secreted reporter, eliminating tedious lysis procedures
- High biological relevance, as mammalian proteins fold correctly and undergo appropriate post-translational modification
- Suitable for mapping interacting domains, mutation studies, and confirmation of yeast two-hybrid hits
Applications
- Confirm suspected protein-protein interactions identified by other platforms
- Investigate signaling pathways in mammalian systems
- Map functional domains responsible for protein binding
- Study interactions requiring mammalian-specific modifications
- Explore effects of disease-related mutations on protein binding
- Validate targets for therapeutic development
Advantages Over Yeast Two-Hybrid
- Mammalian cell lines support native protein folding
- Proper post-translational modifications increase accuracy
- Interactions requiring external stimuli (e.g., hormones, growth factors) can be studied
- Suitable for proteins toxic or misfolded in yeast
What Sets Us Apart
- Expertise in Mammalian Interaction Systems: Our team has extensive experience developing, optimizing, and applying Mammalian Two-Hybrid assays across diverse protein classes and signaling pathways.
- Biologically Relevant Assay Environment: By conducting interaction studies in mammalian cells, we ensure that protein behavior reflects physiological conditions, increasing confidence in functional conclusions.
- Convenient SEAP Reporter Workflow: Our SEAP-based detection platform eliminates cell lysis—reducing hands-on time, improving reproducibility, and enabling kinetic or time-course measurements.
- Comprehensive and Customizable Solutions: We tailor experimental designs, vector selection, and cell line strategies to meet unique project requirements, including domain-mapping and variant analysis.
- Reliable Data and Expert Interpretation: Clients receive detailed, thoroughly analyzed results, including comparable activity metrics and clear biological interpretation from our scientific staff.
- Flexible Scale and Fast Turnaround: Whether you require a small-scale validation assay or a more complex multi-construct study, our workflows are optimized for efficiency and timely delivery.
Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assay: Case Studies
Case 1: Mammalian two-hybrid system for virus–host interaction mapping
Corneillie et al., 2023. doi:10.3390/v15122412
To better understand hepatitis E virus (HEV) biology, researchers applied two high-throughput mammalian two-hybrid platforms—MAPPIT and KISS—to identify host proteins interacting with viral factors. The screens uncovered 37 ORF2-, 187 ORF3-, and 91 ORF4-associated host proteins, many linked to pathways exploited by other viruses. Two ORF3 interactors, SHARPIN and RNF5, were further validated due to their roles in the RLR-MAVS and interferon signaling pathways. Gene knockout studies showed altered IFN responses and changes in HEV infection efficiency, confirming their functional relevance. This work demonstrates the value of mammalian two-hybrid systems for dissecting virus–host interaction networks.
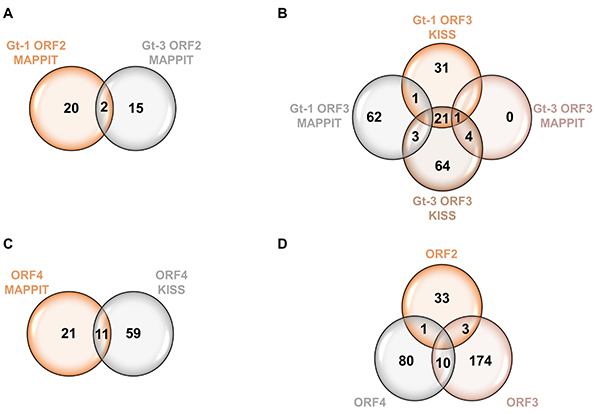
Figure 2. Venn diagrams depicting HEV ORF interactors identified by MAPPIT and KISS analyses. (A) Interactors of the ORF2 protein identified by MAPPIT analyses. (B) Interactors of the ORF3 protein identified by both MAPPIT and KISS analyses. (C) Interactors of ORF4 protein identified by both MAPPIT and KISS analyses. (D) Venn diagram shows distinct and overlapping interacting proteins of all HEV proteins analyzed. (Corneillie et al., 2023)
Case 2: Mammalian two-hybrid system for CFTR interaction mapping
Lim et al., 2022. doi:10.15252/msb.202110629
To advance therapeutic strategies for Cystic Fibrosis (CF), researchers applied a high-throughput Mammalian Membrane Two-Hybrid System (MaMTH-HTS) to map interaction networks of wild-type and F508del-mutant CFTR. This approach enabled systematic identification of proteins influencing CFTR folding, stability, and function. Follow-up validation across multiple CF disease models highlighted several candidate modulators, including Fibrinogen-Like 2 (FGL2). In patient-derived intestinal organoids, FGL2 significantly affected CFTR functional expression, suggesting its potential as a novel therapeutic target. This study demonstrates the power of MaMTH-HTS in uncovering actionable CFTR interactors for personalized CF treatment development.
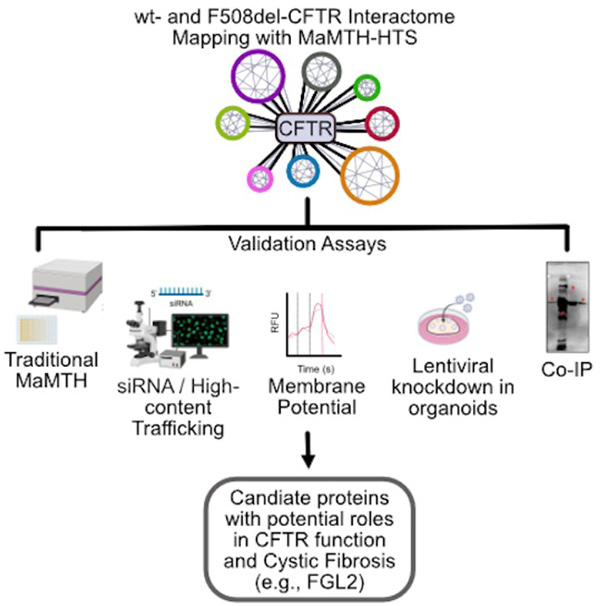
Figure 3. A new MaMTH‐HTS platform is used with a Human ORFeome library to map the protein‐protein interactions of full‐length wildtype and F508del CFTR. Functional validations in multiple disease models uncovered proteins with potential roles in CFTR function and cystic fibrosis. (Lim et al., 2022)
Mammalian Two-Hybrid System: Customer Feedback
“We relied on Creative BioMart’s Mammalian Two-Hybrid System to confirm several interaction candidates emerging from our phospho-proteomics screen. Their team cloned all bait and prey constructs, optimized the transfections, and delivered clear SEAP-based interaction data that aligned remarkably well with our downstream co-IP assays. Their ability to troubleshoot difficult phosphorylation-dependent interactions saved us months of effort.”
— R&D Director, Cellular Signaling Division | Global Pharmaceutical Company
“Our group needed to dissect the interaction domains of a transcription factor implicated in autoimmune disorders. Creative BioMart generated a full panel of truncation mutants and mapped binding regions using their M2H platform with exceptional precision. The domain map they produced directly supported our mechanistic study and strengthened our recent publication. Their scientific insight was invaluable.”
— Principal Investigator | Academic Medical Research Institute
“We approached Creative BioMart to validate interactions involving GPCR cytoplasmic tails—targets notoriously difficult to work with in yeast. Their mammalian system delivered robust, reproducible results, and the SEAP secreted reporter made screening incredibly efficient. The dataset helped us prioritize two GPCR complexes for our small-molecule screening program.”
— Head of Discovery Biology | Mid-Sized Biotech Company
“Our oncology team needed to evaluate how several patient-derived mutations affected the interaction between a tumor suppressor and its regulatory partner. Creative BioMart’s Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assay provided clean quantitative data showing exactly which variants disrupted binding. Their report included thoughtful interpretation and suggestions for follow-up validation, which accelerated our biomarker development pipeline.”
— Senior Scientist, Cancer Research Unit | Precision Medicine Startup
Mammalian Two-Hybrid System Service: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: Why should I choose a Mammalian Two-Hybrid System over a yeast two-hybrid assay?
A: The Mammalian Two-Hybrid System offers far more biologically relevant results for mammalian proteins. Many proteins—especially signaling molecules, transcription factors, receptors, and enzymes—require mammalian-specific folding pathways, chaperones, or post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation or glycosylation). These modifications are often absent in yeast, leading to false negatives or misleading interactions. By working directly in mammalian cells, our M2H platform provides interaction data that better reflect physiological conditions. -
Q: What makes Creative BioMart’s M2H service more convenient than other platforms?
A: Our system uses a SEAP secreted reporter, which means interaction strength is measured directly from the culture medium. Unlike other reporter systems, there is no need for cell lysis, eliminating multiple processing steps, reducing variability, and allowing time-course or kinetic measurements. This dramatically simplifies the workflow while improving data consistency. -
Q: Can the Mammalian Two-Hybrid System detect weak or transient interactions?
A: Yes. The increased biological relevance of mammalian cells allows proteins to interact under natural conditions, including the presence of essential cofactors and modifications. This environment makes it possible to detect interactions that may not form—or may be unstable—in yeast, making our system particularly valuable for signaling proteins and regulatory complexes. -
Q: What types of projects is the M2H system best suited for?
A: Our Mammalian Two-Hybrid platform is ideal for:- Confirming Y2H screening hits in a mammalian environment
- Mapping interacting domains using truncation or mutagenesis strategies
- Studying interactions dependent on post-translational modifications
- Evaluating disease-associated mutations that affect binding
- Validating complex interactions for drug discovery and target characterization
-
Q: How do you ensure construct quality and reliable expression?
A: All bait and prey constructs are sequence-verified and optimized for expression in mammalian cells. We also provide expert guidance on domain selection, localization signals, and potential modification sites to ensure proper folding and functionality. Our optimized transfection workflow further guarantees reproducible protein expression across experiments. -
Q: Can you help if my proteins previously failed in yeast systems?
A: Absolutely. Many clients come to us specifically because their proteins misfold, mislocalize, or remain inactive in yeast. Our mammalian system is designed to overcome these issues. By replicating the natural cellular environment, we can often rescue interactions that are otherwise undetectable in yeast-based assays. -
Q: Do you offer additional validation methods if needed?
A: Yes. For projects requiring deeper confirmation, we offer complementary assays such as co-immunoprecipitation, pull-down assays, and fluorescence-based interaction assays (e.g., FRET/BRET). These optional add-ons help strengthen your conclusions and support publication or regulatory submissions. -
Q: Is the service scalable for larger screening projects?
A: Yes. Whether you need to evaluate a single protein pair, test multiple domain variants, or analyze dozens of mutants, our workflow supports both small-scale and mid-throughput studies. We tailor the project scope based on your timelines and research objectives.
Other Resources
Related Services
- Protein Interaction Service
- Membrane-Based Yeast Two-Hybrid System
- Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Service
- Pull-Down Assays
- Phage Display Platform
- Protein Phosphorylation Site Identification and Mapping Service
- Protein Glycosylation Labeling Service
- Protein Acetylation Assay
- Protein Ubiquitination Service
References:
- Corneillie L, Lemmens I, Weening K, et al. Virus–host protein interaction network of the hepatitis E virus ORF2-4 by mammalian two-hybrid assays. Viruses. 2023;15(12):2412. doi:10.3390/v15122412
- Lim SH, Snider J, Birimberg‐Schwartz L, et al. CFTR interactome mapping using the mammalian membrane two ‐hybrid high‐throughput screening system. Molecular Systems Biology. 2022;18(2):e10629. doi:10.15252/msb.202110629
- Patrício D, Fardilha M. The mammalian two-hybrid system as a powerful tool for high-throughput drug screening. Drug Discovery Today. 2020;25(4):764-771. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2020.01.022
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

