Protein Binding Site Mapping
Precise localization of protein binding sites is essential for understanding biological mechanisms, guiding the development of therapeutic candidates, and optimizing drug design strategies. Creative BioMart provides a comprehensive Protein Binding Site Mapping Service that enables researchers to identify protein–ligand and protein–protein interaction sites with high accuracy. Leveraging advanced analytical platforms, customizable structural libraries, and deep expertise in protein engineering, our service supports projects of varying complexity—from early discovery through lead optimization. Whether mapping high-affinity interactions or subtle conformational epitopes, we offer fast, robust, and reliable solutions tailored to your target class and research needs.
Why Protein Binding Site Mapping Matters
The identification of interaction sites on a protein surface—whether for ligand binding, protein–protein recognition, or allosteric modulation—serves as a foundation for modern drug discovery and mechanistic biology. Proteins often participate in intricate molecular networks, and determining the precise residue-level details of their interactions is essential for understanding biological function, validating therapeutic targets, and designing molecules with improved potency and selectivity.
In early-stage drug discovery , researchers frequently encounter a significant challenge: the binding sites involved in molecular recognition are not yet known. This uncertainty can slow the search for active compounds, hinder structural biology efforts, and complicate the prioritization of druggable sites. Binding site mapping therefore becomes an essential investigative tool for identifying both orthosteric and allosteric regulatory sites.
As a research-focused biotechnology company, Creative BioMart has developed innovative methodologies to address these complexities. With extensive experience in the expression and purification, and characterization of native and recombinant proteins, we have expanded our capabilities to include advanced protein binding site mapping. Our featured platform enables researchers to investigate interactions involving ion channels, GPCRs, transporters, immuno-oncology targets, viral envelope proteins, and many other biologically and therapeutically relevant protein classes.
Our platform integrates sophisticated binding assays, customizable protein fragment libraries, and structural mimicry technologies—enabling high-resolution interpretation of binding events and confident assignment of interaction surfaces. These capabilities are particularly valuable for projects involving dynamic interfaces, transient interactions, or difficult-to-express protein regions. Ultimately, our goal is to provide researchers with actionable insights that guide drug design, validate hypotheses, and accelerate the selection and optimization of therapeutic leads.
Protein Binding Site Mapping: What We Offer
Creative BioMart provides a flexible and comprehensive Protein Binding Site Mapping Service that supports a wide range of research objectives. Our offerings include:
-
Residue-Level Binding Site Localization
We identify binding interfaces between proteins, peptides, ligands, or structural fragments with high precision. These studies help reveal the exact amino acids or motifs involved in molecular recognition.
-
Domain and Epitope Mapping
Our mapping strategies determine which domain, loop, tail, or region of a protein mediates the interaction, enabling clearer interpretation of structure–function relationships.
-
Comparative Interaction Profiling
We evaluate differences in binding between wild-type vs. mutant proteins; isoforms or splice variants; and full-length proteins vs. fragments or peptides. This helps clarify the biological consequences of sequence variation or structural changes.
-
Allosteric Site Identification
Our platform supports the detection of remote, regulatory interaction sites that influence protein activity—an essential component of modern drug discovery.
-
Customizable Structural Libraries
We design and generate libraries of protein fragments, structural mimics, peptides, post-translational modification mimics, or non-canonical residue-incorporated variants to probe complex interfaces thoroughly.
-
Quantitative Binding Characterization
In addition to identifying interaction sites, we measure the strength of molecular interactions, offering deeper insights into the stability and relevance of protein complexes.
With our dedicated team, optimized protocols, and high-throughput instrumentation, Creative BioMart provides accurate, reproducible, and publication-ready data.
Service Workflow
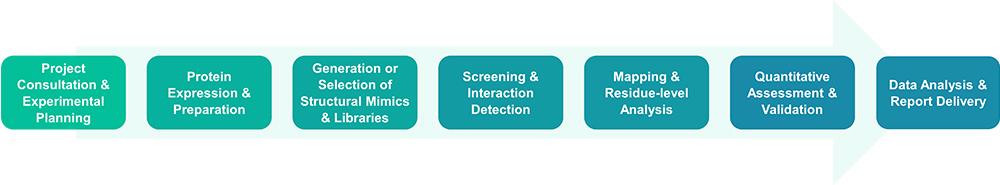
Service Features
-
Target Protein Types
We support binding site mapping for a diverse range of biomolecules, including:
- Wild-type proteins
- Mutant proteins
- Full-length proteins, truncated constructs, or discrete fragments
- Peptides or peptide-mimetic structures
- Cytoplasmic, extracellular, or membrane proteins
- Flexible loops, terminal tails, and dynamic regions
-
Interaction Types Investigated
- Protein–protein interactions (PPIs)
- Protein–peptide interactions
- Protein–ligand binding
- Allosteric modulation
- Isoform-specific interactions
- Mutational effects on binding
-
Methodological Capabilities
Creative BioMart’s platform includes multiple complementary technologies, allowing us to:
- Test low- and high-affinity interactions
- Perform rapid, robust interaction screens
- Incorporate PTM mimics or non-canonical amino acids
- Profile complex or transient interactions
- Include both positive and negative controls for reliability
-
Customized Project Designs
Recognizing the diversity of protein architectures and interaction modes, we provide flexible project designs that accommodate unique research requirements. Whether your study requires rapid preliminary mapping or an extensive residue-by-residue interrogation, our team adapts all experimental parameters accordingly.
What Sets Us Apart
- Advanced Protein Interaction Technologies: We utilize leading binding site mapping platforms, enabling precise localization of interaction regions, even in challenging protein systems such as GPCRs or membrane-associated targets.
- Tailor-Made Structural Libraries: Our custom libraries incorporate structural fragments, modified peptides, and PTM-mimicking elements to interrogate binding interfaces with unmatched granularity.
- Expertise in Difficult Protein Classes: With deep experience in membrane proteins, ion channels, immuno-oncology targets, and viral proteins, we excel in projects requiring specialized knowledge and optimized workflows.
- Quantitative, High-Confidence Interpretation: All results include strength-of-binding assessments and detailed mapping that supports decision-making in drug discovery and target validation.
- Flexible, Efficient Project Execution: From initial design through final deliverables, our workflows are optimized for speed while maintaining scientific rigor and reproducibility.
- Comprehensive Reporting and Follow-Up Support: Every project includes a detailed scientific report, complete data interpretation, and expert consultation to guide subsequent experimental or computational studies.
Protein Binding Site Mapping: Case Studies
Case 1: An NMR based binding site mapping program for fast chemical exchange protein-ligand systems
Krishnamoorthy et al., 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008943
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, particularly N Heteronuclear Single Quantum Correlation (HSQC), provides atomic-resolution insights into protein–ligand interactions. To improve binding site identification in fast chemical exchange systems, an automated program, Auto-FACE, was developed. By analyzing HSQC spectra from proteins titrated with ligands, Auto-FACE calculates chemical shift perturbation rates, binding constants, and perturbation magnitudes to distinguish binding site residues from non-binding residues. Using the BH3I-1 ligand as a model, primary and secondary binding sites were accurately mapped, and site-specific affinities quantified. This approach offers precise, high-throughput mapping of interaction sites and mechanistic insights beyond conventional NMR analysis.
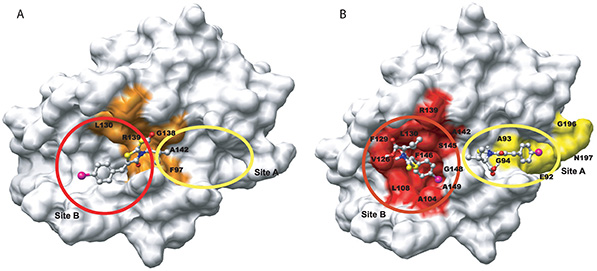
Figure 1. Comparison of the previous and current docked models of BH3I-1 on to hBclxL. (A) and (B) compares the published and current docked models of BH3I-1 on hBclxL, respectively. (Krishnamoorthy et al., 2010)
Case 2: Comparative study of allosteric GPCR binding sites and their ligand ability potential
Peter et al., 2024. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00819
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) present diverse allosteric binding sites, yet few drugs exploit them due to limited structural understanding. This study introduces a systematic GPCR-specific annotation scheme to classify binding sites by receptor class, transmembrane contacts, and membrane sublocation. Applied to 107 structures, 24 unique allosteric sites were analyzed using BioGPS, SiteMap, and FTMap, with BioGPS identifying 22 sites most accurately. Extrahelical sites were challenging, showing shallow pockets and ligand-induced shaping effects. The study highlights ligand–receptor similarity for assessing ligand ability and provides a standardized framework for mapping GPCR allosteric sites, aiding drug discovery targeting these non-canonical pockets.
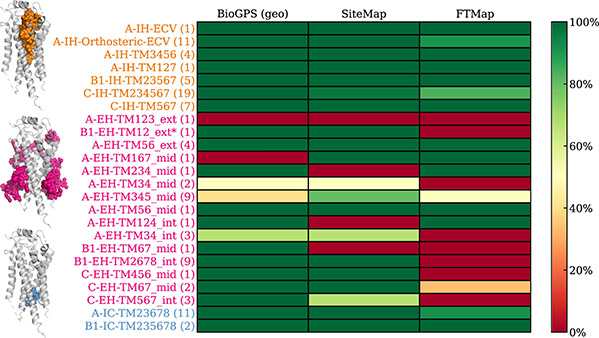
Figure 2. Allosteric binding site detection by BioGPS, SiteMap, and FTMap. The site detection is considered successful if the bound ligand is partially covered by the predicted pocket. The binding sites are sorted vertically by their location within the receptor: intrahelical (IH), extrahelical (EH), and intracellular (IC) binding sites are highlighted in orange, pink, and blue, respectively. (Peter et al., 2024)
Protein Binding Site Mapping: Customer Feedback
“We engaged Creative BioMart to map the binding interface between a therapeutic monoclonal antibody and its GPCR target. Their team designed a fragment library covering extracellular loops and performed systematic interaction analysis. The results pinpointed the exact epitope and identified a potential allosteric site, which allowed us to refine our antibody design and improve specificity. The high-resolution data and detailed report were instrumental in advancing our candidate into preclinical studies.”
— Director of Biologics R&D | Global Pharmaceutical Company
“Our project required differentiation between wild-type and mutant forms of a kinase involved in tumor signaling. Creative BioMart mapped the interaction domains responsible for protein–protein recognition and revealed a subtle conformational change caused by the mutation. This information guided our medicinal chemistry team in designing selective inhibitors and accelerated our lead prioritization process.”
— Senior Scientist, Protein Sciences | Mid-Size Biotechnology Firm
“We sought to identify the minimal binding region on a viral envelope protein critical for host receptor interaction. Creative BioMart generated a series of overlapping peptide and protein fragment libraries and performed quantitative interaction assays. They successfully mapped the key residues involved and validated their functional relevance. The detailed analysis greatly informed our vaccine design strategy and streamlined subsequent antibody screening efforts.”
— Principal Investigator | Academic Research Institute
“Our team needed to identify the exact residues of a cytoplasmic target protein that engage with our candidate peptide inhibitor. Creative BioMart used custom structural mimics and PTM-incorporated variants to map the interaction with high precision. The results allowed us to optimize peptide affinity, improve stability, and reduce off-target effects. Their comprehensive report and expert recommendations were invaluable for our lead optimization campaign.”
— Head of Molecular Design | Biotechnology Startup
Protein Binding Site Mapping Service: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: What types of proteins can you map binding sites for?
A: Our service supports a wide variety of proteins, including full-length, truncated, or mutant constructs, cytoplasmic, extracellular, or membrane proteins, and flexible regions such as loops or tails. We can also work with peptides, fragments, or post-translationally modified mimics to probe complex or transient interactions. -
Q: Can you map both protein–protein and protein–ligand interactions?
A: Yes. We are equipped to map interaction sites for protein–protein complexes, protein–peptide interactions, and protein–small molecule or ligand binding. Our platform allows high-resolution detection of both orthosteric and allosteric binding sites. -
Q: How precise is the binding site mapping?
A: Our platform is designed to provide residue-level insights whenever possible. By using structural fragment libraries, PTM mimics, and systematic mutational approaches, we can identify exact domains, loops, or critical residues involved in binding with high confidence. -
Q: Can you compare interactions between wild-type and mutant proteins or isoforms?
A: Absolutely. Our service can directly assess how sequence variations, mutations, or isoform differences affect binding interfaces. This is especially useful for drug design, functional studies, and understanding disease-related mutations. -
Q: How do you handle low-affinity or transient interactions?
A: Our customized library design, sensitive detection methods, and high-throughput assays allow us to reliably map low-affinity or transient interactions that might be missed by conventional approaches. -
Q: Are positive and negative controls included in the study?
A: Yes. Every project includes well-designed positive and negative controls to validate binding events, ensure assay specificity, and provide confidence in the mapping results. -
Q: Can your approach be customized for complex or unique projects?
A: Yes. We offer fully flexible project designs to accommodate challenging targets, multi-domain proteins, or unconventional constructs. This includes designing structural mimics, incorporating non-canonical residues, and adjusting assay conditions to suit your research needs. -
Q: What kind of data and deliverables will I receive?
A: Clients receive a comprehensive report detailing mapped binding sites, interacting domains, quantitative interaction strength, experimental design, control validation, and expert interpretation. Our reports are suitable for guiding drug development, structural studies, or publication. -
Q: How can protein binding site mapping accelerate my drug discovery project?
A: Mapping interaction sites provides critical insights for rational drug design, lead optimization, and identification of allosteric sites. By revealing the residues and domains involved in binding, our service enables more precise targeting, minimizes off-target effects, and supports efficient therapeutic candidate development.
Other Resources
Related Services
- Protein Interaction Service
- Drug Discovery Screening
- Protein Expression and Purification Services
- Protein Characterization
- Protein Microarray Service
Related Products
References:
- Krishnamoorthy J, Yu VCK, Mok YK. Auto-face: an NMR based binding site mapping program for fast chemical exchange protein-ligand systems. Van Veen HW, ed. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(2):e8943. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008943
- Peter S, Siragusa L, Thomas M, et al. Comparative study of allosteric GPCR binding sites and their ligandability potential. J Chem Inf Model. 2024;64(21):8176-8192. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00819
- Wakefield AE, Kozakov D, Vajda S. Mapping the binding sites of challenging drug targets. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 2022;75:102396. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102396
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

