What is ATPIF1 Protein
The ATPIF1 protein, officially known as ATPase Inhibitory Factor 1, is a crucial player in cellular energy regulation. Also referred to as IF1 (Inhibitory Factor 1 of ATP synthase), this protein belongs to the Mitochondrial ATPase Inhibitor (MAI) family. Its synonyms include IF1, HIRIP5, and ATPIF1. Understanding the structural characteristics of ATPIF1 is pivotal in deciphering its function. Classified as a member of the α-helical protein family, ATPIF1 interacts intricately with the mitochondrial ATP synthase complex, modulating its activity.
ATPIF1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The primary biological function of ATPIF1 revolves around its role as an inhibitor of the mitochondrial ATP synthase enzyme complex. ATP synthase is responsible for generating ATP, the cell's energy currency, through oxidative phosphorylation. ATPIF1, by binding to ATP synthase, acts as a potent regulator, preventing the unnecessary consumption of cellular energy.
Molecular mechanisms underlying ATPIF1's function are intricately tied to its binding to the catalytic F1 domain of ATP synthase. This interaction inhibits ATP hydrolysis, strategically conserving cellular energy during conditions such as ischemia or hypoxia. Recent research advances in structural biology and molecular dynamics simulations have shed light on the nuances of ATPIF1 binding, providing a deeper understanding of its regulatory role in cellular energetics.
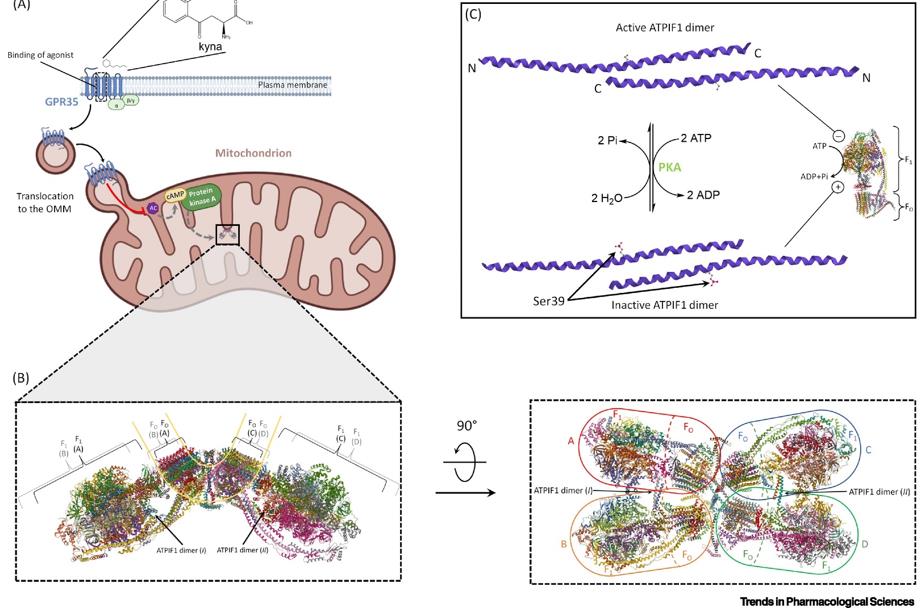
Figure 1. Anti-ischemic ATPIF1-ATP synthase interaction. (Nesci S, 2022)
ATPIF1 Related Signaling Pathway
The ATPIF1-related signal pathway intricately connects with cellular signaling cascades governing energy metabolism. During conditions of cellular stress or oxygen deprivation, ATPIF1 expression is upregulated, initiating a cascade of events that culminate in the inhibition of ATP synthase. This adaptive response helps cells conserve energy and survive adverse conditions. Elucidating the signaling pathways modulating ATPIF1 expression and activity is crucial for comprehending its broader physiological implications.
ATPIF1 Related Diseases
Dysregulation of ATPIF1 has been implicated in various pathological conditions, underscoring its significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis. In instances where ATP synthase activity is dysregulated, such as in certain cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic diseases, ATPIF1 may contribute to disease progression. Targeting the ATPIF1 pathway could hold therapeutic potential in mitigating these diseases, making it a promising avenue for future research.
ATPIF1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of ATPIF1 make it an attractive target for biomedical applications. Researchers are exploring its potential in diagnostics, vaccine development, and therapeutics.
- Diagnostics Development: ATPIF1's involvement in various diseases opens avenues for diagnostic advancements. Detection of aberrant ATPIF1 levels or mutations could serve as biomarkers for specific diseases, facilitating early diagnosis and targeted treatment.
- Vaccine Development: Understanding ATPIF1's role in diseases allows researchers to design vaccines that target this protein or the pathways it regulates. Such vaccines could offer innovative approaches to disease prevention and treatment.
- Therapeutics: Targeting ATPIF1 in therapeutic interventions holds promise in diseases where energy dysregulation is a key factor. Developing pharmaceuticals that modulate ATPIF1 activity could provide novel strategies for treating conditions like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic diseases.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATPIF1-10061H | Recombinant Human ATPIF1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| ATPIF1-1025H | Recombinant Human ATPIF1 protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| ATPIF1-276H | Recombinant Human ATPIF1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| ATPIF1-1508HF | Recombinant Full Length Human ATPIF1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| ATPIF1-2185M | Recombinant Mouse ATPIF1 Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| ATPIF1-894M | Recombinant Mouse ATPIF1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Atpif1-677M | Recombinant Mouse Atpif1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | MYC/DDK |
| ATPIF1-2180M | Recombinant Mouse ATPIF1 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| ATPIF1-898R | Recombinant Rat ATPIF1 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Atpif1-3764R | Recombinant Rat Atpif1, GST-tagged | Rat | E.Coli or Yeast | GST |
Reference
- Nesci S. GPR35, ally of the anti-ischemic ATPIF1-ATP synthase interaction. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 2022.

