What is CDH17 Protein
CDH17, also known as Cadherin-17, is a vital protein that plays a crucial role in various biological processes. Its official full name, Cadherin-17, reflects its membership in the cadherin family of proteins. Synonyms for CDH17 include LI-cadherin, liver-intestine cadherin, and HPT-1. This cell adhesion molecule is integral to cell-cell interactions, influencing tissue development and maintenance.
Belonging to the cadherin superfamily, CDH17 shares structural characteristics with other members. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein with extracellular domains responsible for cell adhesion. Recent research advances have shed light on the intricate details of CDH17's structure and classification within the cadherin family, providing a deeper understanding of its functional significance.
CDH17 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of CDH17 are diverse and impactful. Primarily expressed in the liver and intestine, CDH17 contributes significantly to the maintenance of tissue integrity and architecture. It facilitates cell adhesion, ensuring the structural integrity of organs and tissues. At the molecular level, CDH17 engages in homophilic binding, meaning it interacts with other CDH17 molecules on neighboring cells, forming a robust cellular network.
Beyond its structural role, CDH17 is implicated in signaling pathways that regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Its involvement in Wnt signaling pathways highlights its influence on critical cellular processes, making it a key player in the intricate dance of molecular events governing cell behavior.
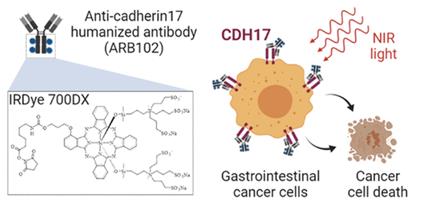
Figure 1. CDH17 targeted near-infrared photoimmunotherapy for treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. (Lum Y L, et al., 2020)
CDH17 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways associated with CDH17 provide valuable insights into its regulatory mechanisms. One notable pathway is the Wnt signaling pathway, where CDH17 acts as a mediator. Wnt signaling plays a pivotal role in embryonic development and tissue homeostasis, and CDH17's involvement underscores its significance in these fundamental processes.
CDH17's interaction with Wnt signaling cascades influences cell fate determination, cell migration, and tissue regeneration. The intricate interplay between CDH17 and Wnt signaling highlights the complexity of cellular regulation and underscores the potential therapeutic implications of targeting these pathways in disease states.
CDH17 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of CDH17 has been associated with various diseases, making it a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target. Studies have linked abnormal CDH17 expression to certain cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal cancer. The overexpression of CDH17 in these malignancies suggests its potential as a diagnostic biomarker for early detection.
Understanding the role of CDH17 in disease pathogenesis opens avenues for targeted therapies. Researchers are exploring ways to modulate CDH17 expression or activity to intervene in cancer progression. This targeted approach holds promise for developing more effective and less invasive treatments for CDH17-associated diseases.
CDH17's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of CDH17 make it a valuable asset in various biomedical applications. In diagnostics development, the detection of CDH17 expression levels can serve as a diagnostic tool for certain cancers. Utilizing CDH17 as a biomarker enables early detection and personalized treatment strategies, improving patient outcomes.
In vaccine development, CDH17's role in cell adhesion and its association with diseases make it an interesting candidate for targeted immunotherapies. Exploring the potential of CDH17-based vaccines may pave the way for innovative approaches in preventing or treating diseases associated with CDH17 dysregulation.
Therapeutically, CDH17 modulation presents a promising avenue for drug development. Targeting CDH17 in cancer therapy, for instance, may disrupt the adhesive properties of cancer cells and impede their ability to proliferate and metastasize. These targeted approaches aim to enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects on healthy tissues.
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDH17-2094H | Recombinant Human CDH17 protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| CDH17-29102TH | Recombinant Human CDH17 | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
| CDH17-0978H | Recombinant Human CDH17 Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CDH17-3898H | Recombinant Human CDH17 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CDH17-2639H | Active Recombinant Human CDH17 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CDH17-2043H | Recombinant Human CDH17 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CDH17-3042H | Active Recombinant Human CDH17 protein, mFc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | mFc |
| CDH17-0807H | Recombinant Human CDH17 Protein (Arg89-Ala406), His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CDH17-3043H | Active Recombinant Human CDH17 protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His-Avi |
| CDH17-0975H | Recombinant Human CDH17 Protein (Arg89-Ala406), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
Reference
- Lum Y L, et al. Cadherin-17 targeted near-infrared photoimmunotherapy for treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. Molecular Pharmaceutics. 2020, 17(10): 3941-3951.

