What is DLL4 Protein
DLL4, or Delta-like ligand 4, is a crucial protein that plays a pivotal role in various cellular processes. Officially known as Delta-like 4 or Drosophila Delta homolog 4, DLL4 is also recognized by synonyms such as Delta4 and Dll4. This protein belongs to the Delta/Serrate/LAG-2 (DSL) family, a group of ligands that are essential components of Notch signaling pathways. Notably, DLL4 has garnered significant attention in recent research, revealing its intricate involvement in cellular functions and signaling cascades.
DLL4 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
DLL4, like other members of the DSL family, possesses a conserved Delta/Serrate/LAG-2 (DSL) domain that is crucial for its interaction with Notch receptors. The DSL domain is characterized by specific amino acid sequences that enable DLL4 to bind to Notch receptors, initiating a cascade of events that regulate cellular processes. Structurally, DLL4 is a transmembrane protein, with its extracellular domain facilitating interactions with neighboring cells, and its intracellular domain influencing downstream signaling.
Recent Research Advances about DLL4 Protein
Recent research has shed light on DLL4's significance in developmental processes and disease progression. Studies have identified DLL4 as a key player in angiogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation. This protein is particularly crucial in the formation of new blood vessels, a process essential for embryonic development and tissue regeneration. Additionally, DLL4 has been implicated in various pathological conditions, making it a potential target for therapeutic interventions.
DLL4 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
DLL4's biological functions are diverse and far-reaching. Primarily, DLL4 is recognized for its role in the Notch signaling pathway, a highly conserved pathway crucial for cell communication and fate determination. As a ligand, DLL4 binds to Notch receptors on neighboring cells, initiating a series of events that regulate cellular differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis.
In angiogenesis, DLL4 assumes a central role in orchestrating the formation of new blood vessels. Its interaction with Notch receptors on endothelial cells influences tip cell selection, vessel branching, and overall vascular network patterning. This intricate regulation ensures the proper development and maintenance of the vascular system.
The molecular mechanisms underlying DLL4's functions involve complex interactions within the Notch signaling pathway. Upon DLL4 binding to Notch receptors, a series of proteolytic cleavages occur, releasing the Notch intracellular domain (NICD). NICD translocates to the nucleus, where it forms a transcriptional complex with other proteins, ultimately regulating the expression of target genes. This cascade of events dictates cellular responses, influencing various aspects of development and homeostasis.
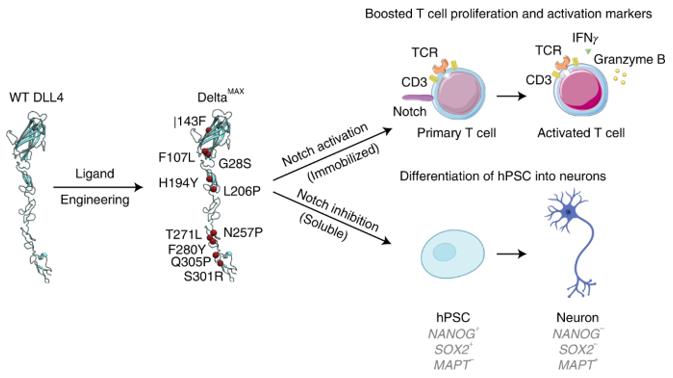
Figure 1. Affinity-matured DLL4 ligands as Notch signaling modulators. (Gonzalez-Perez D, et al., 2023)
DLL4 Related Signaling Pathway
DLL4's role extends beyond the Notch signaling pathway, as emerging research identifies cross-talk with other cellular pathways. Crosstalk between DLL4 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathways, for example, further modulates angiogenesis. This intricate interplay highlights the interconnected nature of cellular signaling and provides avenues for exploring targeted therapeutic interventions.
DLL4 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of DLL4 has been implicated in several diseases, highlighting its significance in maintaining physiological balance. Aberrant DLL4 signaling is associated with cancer progression, particularly in tumors where angiogenesis is a crucial component. The overexpression of DLL4 in certain cancers contributes to increased angiogenesis, fostering tumor growth and metastasis. Understanding and targeting DLL4 signaling pathways hold promise for developing novel therapies to curb angiogenesis-dependent diseases.
DLL4's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of DLL4 make it a promising candidate for various biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, DLL4 can serve as a biomarker for diseases with dysregulated angiogenesis, aiding in early detection and monitoring of disease progression. Furthermore, DLL4's involvement in the immune response has spurred interest in its potential applications in vaccine development, harnessing its properties to enhance immune system activation.
In therapeutics, targeting DLL4 has shown promise in anti-angiogenic therapies for cancer treatment. Inhibiting DLL4 signaling can impede angiogenesis in tumors, hindering their growth and metastasis. This opens up avenues for developing targeted therapies that selectively disrupt pathological angiogenesis while preserving normal vascular function.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLL4-2235H | Active Recombinant Human DLL4 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| DLL4-2687H | Recombinant Human DLL4 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| DLL4-26674TH | Recombinant Human DLL4 | Human | N/A | |
| DLL4-934H | Recombinant Human Delta-like 4 (Drosophila) | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| DLL4-686H | Active Recombinant Human DLL4 protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| DLL4-26672TH | Recombinant Human DLL4, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| DLL4-2147H | Recombinant Human DLL4 Protein (Leu16-Ala539), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| DLL4-201H | Recombinant Human DLL4 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| DLL4-1349H | Recombinant Human DLL4 Protein, His&GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His&GST |
| Dll4-2288M | Active Recombinant Mouse Dll4 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His |
Reference
- Gonzalez-Perez D, et al. Affinity-matured DLL4 ligands as broad-spectrum modulators of Notch signaling. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(1): 9-17.

