What is DUSP4 Protein
DUSP4, or Dual Specificity Phosphatase 4, also known by the official full name of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase MKP-2 and aliases such as MAP Kinase Phosphatase 2 (MKP-2), stands at the crossroads of cellular signaling pathways, orchestrating a delicate balance crucial for cellular homeostasis. It belongs to the dual-specificity phosphatase (DUSP) family, a group of proteins renowned for their ability to dephosphorylate both tyrosine and serine/threonine residues in their target proteins.
DUSP4 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, DUSP4 boasts a conserved catalytic domain characterized by the presence of a CX5R motif crucial for its phosphatase activity. Recent research advances have shed light on its intricate structure, unveiling how post-translational modifications and conformational changes influence its catalytic efficiency.
DUSP4 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of DUSP4 are multifaceted, emphasizing its pivotal role in modulating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascades. Acting as a molecular switch, DUSP4 delicately fine-tunes cellular responses by dephosphorylating MAPKs, including ERK, JNK, and p38. This regulatory dance ensures proper control of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
Molecularly, DUSP4 achieves this by dephosphorylating specific threonine and tyrosine residues on MAPKs, leading to the attenuation of downstream signaling. This exquisite control mechanism is imperative for preventing aberrant activation of MAPK pathways, which can contribute to various pathological conditions.
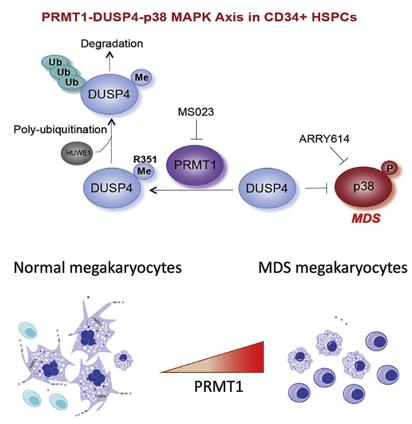
Figure 1. PRMT1-DUSP4-p38 MAPK Axis in CD34+ HSPCs. (Su H, et al., 2021)
DUSP4 Related Signaling Pathway
DUSP4 intricately interweaves with MAPK signaling pathways, serving as a critical checkpoint in cellular responses. Its dynamic interaction with ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPKs dictates the outcome of various biological processes.
In cancer, for instance, reduced DUSP4 levels unleash the unbridled activation of ERK, fostering uncontrolled cell growth and survival. Conversely, in inflammatory conditions, the downregulation of DUSP4 contributes to sustained JNK and p38 activation, fueling the inflammatory response. Deciphering the nuances of DUSP4's involvement in these pathways is paramount for designing targeted therapeutic strategies.
DUSP4 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of DUSP4 has been implicated in several diseases, underscoring its significance as a potential therapeutic target. In cancer, reduced DUSP4 expression has been associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Furthermore, DUSP4's involvement in inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, highlights its broader impact on human health.
Understanding the molecular underpinnings of DUSP4-related diseases provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring the delicate balance of MAPK signaling.
DUSP4's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique attributes of DUSP4 position it as a promising player in biomedical applications. Diagnostic development stands to benefit from the identification of DUSP4 as a potential biomarker for diseases where its dysregulation plays a pivotal role. Monitoring DUSP4 levels could offer insights into disease progression and treatment response.
In vaccine development, harnessing DUSP4's ability to modulate immune responses opens new avenues. Fine-tuning its expression might enhance vaccine efficacy, offering improved protection against infectious agents.
Therapeutically, strategies aimed at restoring or augmenting DUSP4 levels hold promise for diseases characterized by aberrant MAPK signaling. Small molecule modulators targeting DUSP4 could emerge as precision tools to restore cellular balance, offering a more nuanced approach to disease management.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUSP4-2645H | Recombinant Human DUSP4 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| DUSP4-2919H | Recombinant Human DUSP4 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| DUSP4-106H | Active Recombinant Human DUSP4 Protein, His-tagged | Human | Insects cell | His |
| DUSP4-105H | Recombinant Human DUSP4 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| DUSP4-4890M | Recombinant Mouse DUSP4 Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Dusp4-2690M | Recombinant Mouse Dusp4 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| DUSP4-2572M | Recombinant Mouse DUSP4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| DUSP4-1976R | Recombinant Rat DUSP4 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| DUSP4-1635R | Recombinant Rat DUSP4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| DUSP4-11388Z | Recombinant Zebrafish DUSP4 | Zebrafish | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Su H, et al. Methylation of dual-specificity phosphatase 4 controls cell differentiation. Cell Reports. 2021, 36(4).

