What is EFNB2 Protein
The EFNB2 protein, officially named Ephrin-B2, is encoded by the EFNB2 gene. This gene is situated on human chromosome 13q33.3. Commonly referred to as Ephrin-B2, this protein is also known by synonyms such as LERK-5, EFL-5, Htk-L, and Elk-L5.
EFNB2 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Belonging to the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases, Ephrin-B2 plays a crucial role in mediating cell-cell communication. Structurally, this transmembrane protein comprises an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain harbors the Eph receptor-binding region, allowing interaction with Eph receptors on adjacent cells.
Ephrin-B2 is classified as a type I membrane protein, tethered to the cell membrane by a transmembrane region. Its classification within the Eph family positions it as a key participant in processes like axon guidance, cell migration, and tissue development.
Recent Research Advances about EFNB2 Protein
Recent research on EFNB2 has unveiled its involvement in angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation. Studies have demonstrated that Ephrin-B2, in collaboration with Eph receptors, regulates vascular development, influencing endothelial cell migration and vessel patterning. These findings open new avenues for understanding and potentially manipulating angiogenesis in various physiological and pathological contexts.
EFNB2 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of EFNB2 are diverse and pivotal. Primarily recognized for its role in axon guidance during neural development, Ephrin-B2 facilitates the precise wiring of the nervous system by mediating repulsive or attractive signals that guide axonal growth. Beyond the nervous system, this protein contributes to various developmental processes, including angiogenesis, tissue boundary formation, and skeletal development.
The molecular mechanisms underlying EFNB2's functions involve interactions with Eph receptors, triggering signaling cascades that modulate cellular responses. Ephrin-B2 can induce repulsion or attraction depending on the context, promoting cell migration, adhesion, and tissue morphogenesis. The intricate dance between Ephrin-B2 and Eph receptors regulates cellular behaviors crucial for the proper development and functioning of diverse tissues.
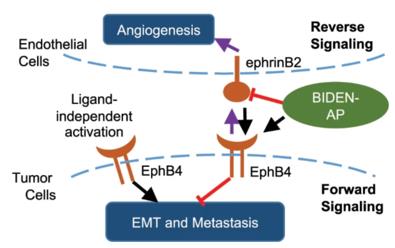
Figure 1. Proposed mechanism of action of BIDEN-AP. (Xiong C, et al., 2020)
EFNB2 Related Signaling Pathway
The signal pathway orchestrated by EFNB2 involves the activation of Eph receptors upon binding. This activation triggers intracellular signaling cascades, including phosphorylation events and changes in gene expression. In angiogenesis, for instance, EFNB2-mediated signaling influences endothelial cell behavior, impacting blood vessel formation and remodeling.
EFNB2 Related Diseases
While EFNB2's normal functions are essential for development, dysregulation or mutations in the EFNB2 gene can contribute to various diseases. Notably, aberrant Ephrin-B2 signaling has been implicated in cancer progression, where it can influence tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. Understanding these disease-associated mechanisms holds promise for developing targeted therapies to intervene in cancer progression.
EFNB2's Applications in Biomedicine
- Diagnostic Development
The unique expression patterns of EFNB2 in various tissues and its involvement in diseases make it a potential biomarker for diagnostic purposes. Detecting aberrant levels or localization of EFNB2 could aid in the early diagnosis and monitoring of diseases such as cancer, providing valuable information for treatment strategies.
- Vaccine Development
The involvement of EFNB2 in angiogenesis and tissue development positions it as a potential target for therapeutic interventions. Research into EFNB2-targeted vaccines may open avenues for designing vaccines that modulate angiogenesis in conditions like cancer, offering innovative approaches to disease treatment.
- Therapeutics
Exploring EFNB2 as a therapeutic target holds promise for developing novel drugs to intervene in diseases associated with its dysregulation. Targeted therapies that modulate Ephrin-B2 signaling could prove effective in controlling cancer progression, angiogenesis-related disorders, and other conditions where EFNB2 plays a central role.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EFNB2-2240H | Active Recombinant Human EFNB2, Fc-His tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| EFNB2-2032H | Active Recombinant Human EFNB2 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| EFNB2-480H | Recombinant Human EFNB2 | Human | Mammalian Cell | His |
| EFNB2-272H | Recombinant Human EFNB2, ENLYFQ tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| EFNB2-3104H | Recombinant Human EFNB2 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| EFNB2-3191H | Recombinant Human EFNB2, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| EFNB2-1134H | Recombinant Human EFNB2 protein, His & GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/GST |
| EFNB2-5264H | Recombinant Human Ephrin-B2, His-tagged | Human | HEK293E | His |
| EFNB2-6870H | Recombinant Human Ephrin-B2, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Efnb2-3315M | Active Recombinant Mouse Efnb2 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His |
Reference
- Xiong C, et al. Targeting forward and reverse EphB4/EFNB2 signaling by a peptide with dual functions. Scientific Reports. 2020, 10(1): 520.

