What is NT5E Protein
The NT5E protein, also known as CD73, is a protein that is encoded by the NT5E gene in humans.
The NT5E protein remains under intense scientific scrutiny since its discovery. It is encoded by the NT5E gene located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 6 at position 14.2, specifically from base pair 76,445,959 to base pair 76,528,360. The NT5E gene gives the cellular instructions necessary to produce the NT5E protein.
The protein structure of NT5E is complex, composed of several key features that allow it to carry out its functions effectively. It consists of both extracellular and intracellular components, highlighting a transmembrane protein. The extracellular portion is the functionally critical component, as it facilitates phosphohydrolytic cleavage. This portion contains two similar tandem repeats of around 150 amino acids, each binding one calcium ion.
Functions of the NT5E Protein
The NT5E protein functions primarily as an enzyme, playing a critical role in purine metabolism by catalyzing the conversion of extracellular nucleoside monophosphates to nucleosides - a type of molecule that plays a significant role in various biological processes. It acts primarily on adenosine monophosphate (AMP), converting it into adenosine, an anti-inflammatory molecule that suppresses the immune response.
It's also involved in cellular proliferation, adhesion, and migration, playing a role in angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels). In certain tissues, this protein behaves as a bifunctional enzyme, exhibiting both 5'-nucleotidase activity and protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.
NT5E Protein Related Signal Pathway
The main signaling pathway related to NT5E revolves around adenosine production and its subsequent impact on cellular processes. Adenosine, produced by the activity of NT5E, binds with adenosine receptors (ARs) present on the cell surface. This produces several effects depending on which subtype of AR is activated.
For example, interaction with the A1 AR can inhibit adenylyl cyclase and decrease the cellular cAMP level, leading to decreased protein kinase A (PKA) activity. This can influence various cellular functions including heart rate, sleep-wake cycles, and neuronal excitability. On the other hand, binding with the A2B AR can increase intracellular calcium levels, triggering intracellular pathways that promote tissue repair and immunosuppression.
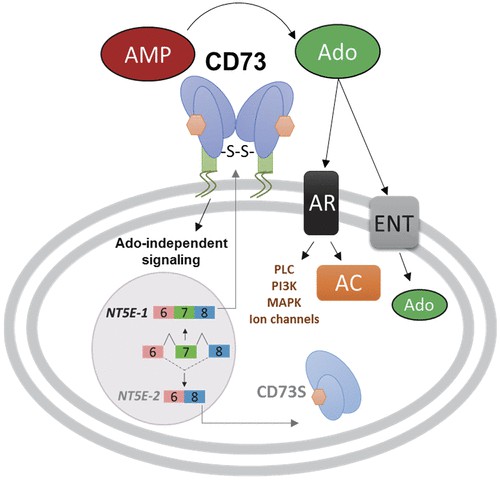
Fig1. NT5E signaling (Minor, M., et al. 2019)
NT5E Related Diseases
Interestingly, NT5E protein's function and signaling pathways make it implicated in various pathological conditions. Higher levels of NT5E expression have been associated with several types of cancer, primarily due to the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of adenosine that it enables. These include but are not limited to, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer.
Furthermore, the aberrant function of NT5E has been linked with a rare condition called arterial calcification due to deficiency of CD73 (ACDC). This condition is characterized by severe calcification of arteries, particularly those in the lower limbs, and the joints of the hands and feet.
NT5E Protein's Applications in Biomedical
Given its unique functionality and disease linkage, NT5E serves pivotal in multiple biomedical applications. It is a potential diagnostic biomarker, particularly for cancer, wherein overexpression may suggest disease presence. More promisingly, NT5E emerged as an attractive target for cancer treatment. Several therapeutic strategies revolve around inhibiting NT5E to reduce extracellular adenosine levels, thereby fighting the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
The NT5E protein is a fascinating entity with diverse implications in biological processes and disease pathogeneses. With its diverse roles and potential applications in biomedical fields, NT5E will continue to be a subject of immense scientific interest, promising promising advancements in our understanding and treatment of various diseases.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT5E-580H | Active Recombinant Human NT5E, Fc-tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| NT5E-3859H | Recombinant Human NT5E, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| NT5E-1302H | Recombinant Human NT5E Protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| NT5E-2681H | Active Recombinant Human NT5E protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| Nt5e-2302M | Recombinant Mouse Nt5e, His tagged | Mouse | Human Cell | His |
| Nt5e-34R | Recombinant Rat Nt5e, His tagged | Rat | Human Cell | Fc |
| NT5E-6719C | Recombinant Cattle NT5E protein, His & T7-tagged | Cattle | E.coli | His/T7 |
Reference
- Minor, M., Alcedo, K. P., Battaglia, R. A., & Snider, N. T. (2019). Cell type- and tissue-specific functions of ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73). American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. https://doi.org/C-00285-2019

