What is OTX2 Protein
The OTX2 protein, also known as Orthodenticle homeobox 2, was discovered as an essential protein responsible for the early development of organisms, especially in the brain and sensory organs. First identified in the Drosophila melanogaster or fruit fly in genetic studies aimed at understanding development of the head, OTX2 was later found to have close counterparts in vertebrates including humans.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure of OTX2
The gene for OTX2 protein is located on the human chromosome 14, precisely at 14q22-q23. The protein consists of 297 amino acids and displays a molecular mass of approximately 33 kDa. The protein structure possesses a conserved 60-amino acid region known as the homeodomain, which allows it to bind to specific DNA sequences and thereby regulate the transcription of target genes.
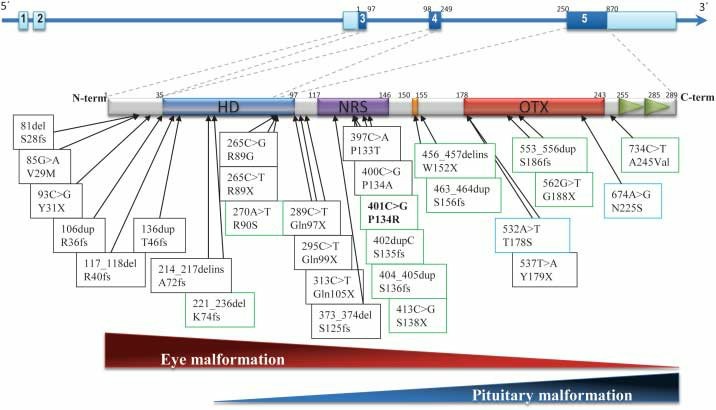
Fig1. OTX2 structure and mutation mapping (Gorbenko del Blanco, et al. 2012)
Function of OTX2 Protein
The primary function of OTX2 protein lies in embryonic development. It plays a crucial role in the development of the head and brain, particularly the forebrain and midbrain, along with roles in sensory organ development including eyes and ears. In addition, OTX2 protein regulates the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep patterns, by activating the transcription of genes necessary for melatonin synthesis.
OTX2 Protein Related Signal Pathway
OTX2 protein has been observed in the Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) signaling pathway, which plays a key role in cell proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation. OTX2 exerts its regulatory influence by controlling the expression of FGF8, a critical growth factor in the mid-hindbrain region during developmental stages.
OTX2 Protein Related Diseases
Several diseases and health conditions have been associated with alterations in the OTX2 gene that ultimately affects the OTX2 protein. Mutations in this gene are linked to severe eye malformations including anophthalmia and microphthalmia, which are characterized by the absence or small size of one or both eyes, respectively. In addition, these mutations may lead to brain-related abnormalities such as intellectual disability and seizures.
OTX2 also holds significance in oncology, with heightened expression associated with several cancers, including medulloblastomas, retinoblastomas, and small-cell lung carcinomas.
OTX2 Protein's Applications in Biomedical Sciences
Given the integral role of OTX2 in normal developmental processes, its potential for therapeutic applications has garnered interest across biomedical sciences. By understanding its functions and the mechanisms behind these processes, researchers could develop ways to exploit OTX2 protein in treating various diseases related to developmental defects.
Moreover, its significant role in several cancers has made it a promising potential target for novel therapeutic strategies. By inhibiting OTX2 protein activity, researchers hope to halt cancer cell proliferation and induce tumor regression.
Overall, the OTX2 protein carries substantial importance in understanding embryological development, studying disease progression, and creating new therapeutic strategies. However, like many genetic discoveries, our understanding of this protein and its complex roles within different biological systems remains a work in progress. It is through continued research that future breakthroughs will undoubtedly unfold, opening doors to novel treatment possibilities.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTX2-193H | Recombinant Human OTX2 protein, T7/His-tagged | Human | E.coli | T7/His |
| OTX2-390H | Recombinant Human OTX2 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| OTX2-3310H | Recombinant Human OTX2 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| Otx2-3311M | Recombinant Mouse Otx2 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Gorbenko del Blanco, Darya & Romero, Christopher & Diaczok, Daniel & De Graaff, Laura & Radovick, Sally & Hokken-Koelega, Anita. (2012). A novel OTX2 mutation in a patient with combined pituitary hormone deficiency, pituitary malformation, and an underdeveloped left optic nerve. European journal of endocrinology / European Federation of Endocrine Societies. 167. 441-52. 10.1530/EJE-12-0333.

