What is PARP1 Protein
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) stands at the forefront of cellular biology, wielding its influence over critical processes that safeguard genomic integrity.
What is PARP1 Protein?
PARP1, a nuclear enzyme discovered in the early 1960s, is a linchpin in the cellular machinery, intricately linked with DNA repair, replication, and transcription processes. Located within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, PARP1's significance lies in its ability to detect and initiate the repair of DNA damage, a perpetual threat from endogenous and exogenous factors.
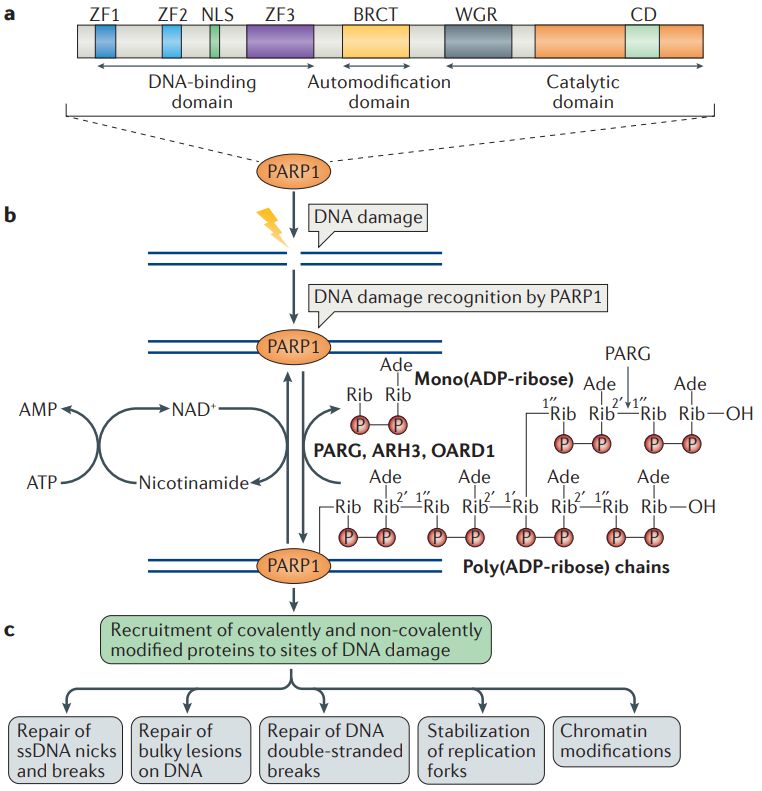
Figure 1. The biochemical functions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 in DNA damage repair. (Ray Chaudhuri, A., et al. 2017)
The Function of PARP1 Protein
At its core, PARP1 is the guardian of genomic stability. When DNA strands fracture, PARP1 swiftly responds by catalyzing the addition of poly(ADP-ribose) chains to target proteins, creating a molecular scaffold for the recruitment of repair proteins. This orchestrated repair process ensures the maintenance of genomic integrity.
Beyond its role in DNA repair, PARP1 regulates chromatin structure and gene expression. Its interaction with histones and chromatin-associated proteins modulates DNA accessibility, showcasing its influence on gene regulation and cellular responses to various stimuli.
PARP1-Related Diseases
While PARP1 is critical for maintaining genomic stability, dysregulation of its functions has been implicated in various diseases. One of the most studied aspects is its involvement in cancer. PARP1 inhibitors have gained attention as potential therapeutic agents, particularly in the treatment of certain types of breast and ovarian cancers. By inhibiting PARP1, these drugs compromise the ability of cancer cells to repair DNA damage, leading to cell death.
Additionally, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's have been associated with PARP1 dysfunction. The enzyme's overactivation in response to oxidative stress can lead to excessive poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation, contributing to neuronal cell death. Understanding the intricate balance of PARP1 activity in the context of neurodegenerative diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases, also exhibit dysregulated PARP1 activity. The enzyme's involvement in the modulation of inflammation suggests its potential as a therapeutic target for mitigating inflammatory responses in these conditions.
PARP1 Related Signaling Pathways
PARP1 orchestrates its functions through intricate signal pathways, most notably the DNA damage response (DDR). In the face of DNA damage, PARP1 activation initiates a cascade of events, recruiting repair proteins and maintaining genomic stability. This pathway is pivotal in preventing the accumulation of mutations that could lead to cancer.
PARP1's influence extends beyond DNA repair, intertwining with cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. Inhibition of PARP1 can lead to persistent DNA damage, activating programmed cell death pathways—an insight with implications for cancer therapy.
The enzyme's modulation of inflammation-related pathways, including NF-κB, underscores its impact on broader cellular processes beyond DNA repair.
Applications of PARP1 in Biomedical Research
The multifunctionality of PARP1 positions it as a focal point in biomedical research, with promising applications across diverse domains.
- Cancer Therapy
PARP inhibitors emerge as trailblazers in cancer treatment. Exploiting synthetic lethality, these inhibitors target cancer cells with defective DNA repair mechanisms, offering a paradigm shift in the treatment of breast and ovarian cancers, particularly those associated with BRCA mutations.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases
The intricate link between PARP1 dysfunction, oxidative stress, and neurodegenerative diseases places PARP1 as a potential therapeutic target. Modulating its activity may hold the key to mitigating neuronal cell death in conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Inflammation and Autoimmune Disorders
PARP1's role in inflammation opens avenues for therapeutic interventions in inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Inhibiting PARP1 stands as a potential strategy to modulate excessive inflammatory responses, offering novel approaches to managing diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cardiovascular Diseases
Exploration of PARP1's involvement in cellular processes, including inflammation and oxidative stress, positions it as a potential player in cardiovascular diseases. Research delves into the impact of PARP1 inhibition in conditions such as ischemia-reperfusion injury and atherosclerosis.
- Aging and Longevity
The connection between DNA damage, cellular senescence, and aging prompts investigation into PARP1's role in the aging process. Modulating PARP1 activity emerges as a potential avenue to unravel mechanisms influencing longevity.
As our understanding of PARP1 deepens, so does the potential for therapeutic interventions across a spectrum of diseases, ranging from cancer to neurodegenerative disorders. The ongoing research into PARP1-related signal pathways and the expanding applications of PARP inhibitors underscore the significance of this protein in shaping the future of biomedical research and clinical medicine.
Recommended Products for PARP1 Protein
Reference
- Ray Chaudhuri, A., Nussenzweig, A. The multifaceted roles of PARP1 in DNA repair and chromatin remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017, 18: 610–621.

