What is PGLYRP1 Protein
PGLYRP1, also known as peptidoglycan recognition protein 1, is a protein molecule encoded by the PGLYRP1 gene in humans. Peptidoglycan is a unique structural component predominantly found in bacterial cell walls. PGLYRP1 is part of a family of four human peptidoglycans recognition proteins (PGLYRPs) that function in innate immunity, which is the body's first line of defense against infection. These proteins, discovered in mammalian species, recognize peptidoglycan, an essential component of bacterial cell walls, thereby modulating immune responses in flies and mammals.
Function of PGLYRP1 Protein
PGLYRP1 is primarily synthesized in the liver and secreted into the bloodstream. Its key function is to identify peptidoglycan molecules present in bacterial cell walls and initiates an immune response. This recognition process helps the immune system to detect infections by bacteria and respond appropriately.
Distinct from other PGLYRPs, PGLYRP1 lacks bactericidal activity, but it plays a crucial role in the regulation of immune responses. By binding to peptidoglycans without degrading them, PGLYRP1 starts a series of chain reactions that leads to the production of proinflammatory cytokines, key players in the immune response.
PGLYRP1 Protein-Related Signal Pathway
When PGLYRP1 recognizes peptidoglycan, it triggers a signal pathway to activate immune cells. However, the exact mechanism of how PGLYRP1 stimulates certain immune responses is yet to be fully understood. Recent research points out that PGLYRP1 can activate the NOD-like receptor (NLRP3) inflammasome pathway, a key component in the innate immune system responsible for the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This pathway's activation leads to a response to pathogenic microbes and cellular damages, highlighting PGLYRP1's role in immune regulation.
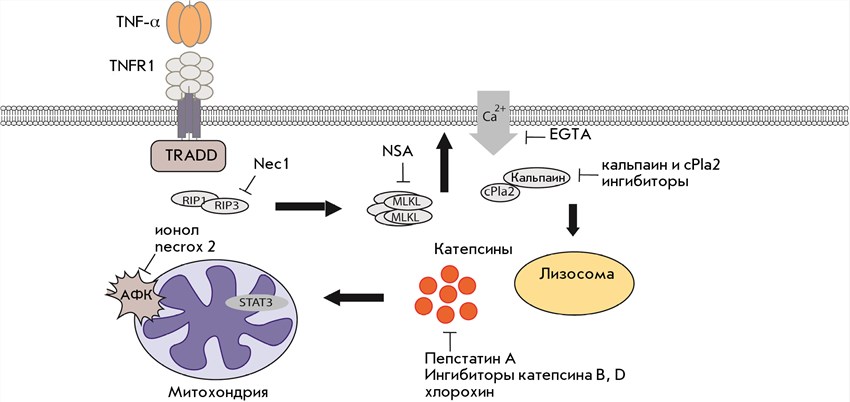
(Yashin D.V. et al. 2021)
PGLYRP1 Protein-Related Diseases
PGLYRP1 gene polymorphisms have been linked to susceptibility to several diseases. A study associated PGLYRP1 genetic variants with increased risk for Aspergillus-induced allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) in individuals with cystic fibrosis. The protein's role in immune regulation has also sparked interest in studying its potential implications in other diseases, especially autoimmune conditions.
Moreover, researchers have detected increased PGLYRP1 levels in patients with sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by the body's response to an infection. PGLYRP1 is now considered a credible biomarker for diagnosing severe infections, offering an insight into the critical role it plays in the immune response to pathogenic invasions.
Applications in Biomedical Fields
Due to its integral role in the immune response, PGLYRP1 has significant potential for diverse applications in the biomedical field. As it acts as a crucial mediator linking innate and adaptive immunity, understanding its function can offer novel therapeutic strategies for treating various infectious and inflammatory diseases.
One potential application of studying PGLYRP1 is in immunotherapy. Developing techniques to modulate the activity of this protein could provide a unique approach to treat diseases related to immune dysfunction. In particular, adjusting the PGLYRP1 pathway could contribute to managing sepsis, which currently lacks specific targeted therapies.
In conclusion, the PGLYRP1 protein is an essential part of the immune system machinery, recognizing peptidoglycan on bacterial cell walls, and initiating immune responses. Despite the complex nature of its interactions with other components of the immune system, the implications and potential roles that this protein could have in preventing and managing diseases are undeniable. Continued research into PGLYRP1 protein is vital to unlock its potential in diagnostics, therapy, and medical science as a whole.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGLYRP1-1667H | Recombinant Human PGLYRP1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PGLYRP1-1312H | Recombinant Human PGLYRP1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| PGLYRP1-1661H | Recombinant Human PGLYRP1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Pglyrp1-571M | Recombinant Mouse Pglyrp1, His tagged | Mouse | Human Cell | His |
| PGLYRP1-4068R | Recombinant Rat PGLYRP1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| PGLYRP1-787C | Recombinant Cynomolgus PGLYRP1 Protein, His-tagged | Cynomolgus | HEK293 | His |
Reference
- Yashin D.V., Saschenko L.P., Georgiev G.P. Mechanisms of Action of the PGLYRP1/Tag7 Protein in Innate and Acquired Immunity // Acta Naturae. - 2021. - Vol. 13. - N. 1. - P. 91-101. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11102

