What is PINK1 Protein
PTEN-Induced Kinase 1, better known by its acronym PINK1, is a protein that plays a significant role within our bodies. This small, yet potent protein is coded by the PINK1 gene in humans and is primarily found in the mitochondria, an essential part of our cells.
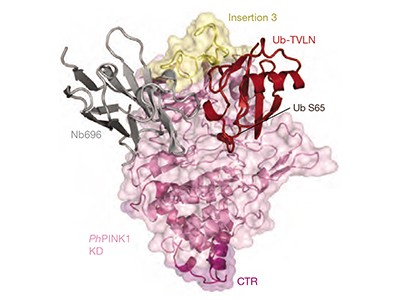
Fig1. Vivid views of the PINK1 protein (Daou, S. et al, 2017)
Function of PINK1 Protein
PINK1 protein has several vital functions within the body. Its primary role revolves around maintaining the health of mitochondria. These cellular entities are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell as they produce most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecular unit of currency of intracellular energy transfer. To ensure our cells have the necessary energy to perform their designated functions, the mitochondria must be in a state of good health.
When the mitochondria suffer damage, become stress-induced, or are dysfunctional, the PINK1 protein plays a key role in their repair process. Usually, this protein remains in the inner mitochondrial membrane. However, upon dysfunction of the mitochondria, PINK1 protein accumulates on the external membrane. By doing so, it acts as a flag, marking the defected mitochondria for destruction by the cell's waste management system, thereby ensuring cell homeostasis.
PINK1 Protein Related Signal Pathway
The signal pathway involving the PINK1 protein is called the PINK1-Parkin pathway. This pathway is intricately involved in the process of mitophagy, the selective degradation of mitochondria by autophagy. Instinctively, when the PINK1 protein senses a change or damage in the mitochondrial membrane potential, it stabilizes itself on the outer mitochondrial membrane and recruits another protein called Parkin from the cytosol.
Parkin is an E3 ubiquitin ligase, and together with the PINK1 protein, numerous Parkin molecules are activated, ubiquitin tags are added to targeted proteins residing on the mitochondria's outer membrane, triggering the process of autophagy. This results in the engulfment and eventual degradation of the damaged mitochondria – a critical process to prevent the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria that could harm the cell.
PINK1 Protein Related Diseases
One of the major diseases associated with the PINK1 protein is Parkinson's disease. Mutations in the PINK1 gene, that codes for PINK1 protein, have been evidenced as one of the leading causes of recessive familial Parkinson's disease. The absence or dysfunction of the PINK1 protein hinders the typical process of mitophagy, leading to the accumulation of damaged, dysfunctional mitochondria. Over time, this results in an increased level of oxidative stress, which could cause the death of dopamine-producing neurons - a significant characteristic of Parkinson's disease.
PINK1 Protein's Applications in Biomedical Research
Given its major role in mitochondrial health and the link to neurological diseases, the PINK1 protein is an influential subject of biomedical research. Therapies targeting the PINK1-Parkin pathway could provide promising approaches for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Drug screening platforms are being developed to identify potential compounds capable of modulating PINK1-Parkin mediated mitophagy, offering new avenues for therapeutic intervention. The use of genetically modified organisms to further understand the role and workings of the PINK1 protein is also a significant area of research, given the crucial role of this protein in cellular homeostasis.
In conclusion, the PINK1 protein and its function are of immense importance in the understanding of cellular processes, notably those of the mitochondria. While this protein is minute, its influence on the health of biologic cells is conclusive evidence of its potency. Ongoing research into manipulating this protein's function and understanding related diseases presents us with exciting prospects in respect of potential treatments and cures for some of today's most challenging neurodegenerative disorders.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PINK1-3194H | Recombinant Human PINK1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PINK1-357H | Recombinant Human PTEN Protein, His-tagged | Human | E. coli | His |
| PINK1-6749M | Recombinant Mouse PINK1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| PINK1-1917Z | Recombinant Zebrafish PINK1 | Zebrafish | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Daou, S., & Sicheri, F. (2017). Vivid views of the PINK1 protein. Nature, 552(7683), 38-39. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-017-07691-x

