What is RAB5A Protein?
Background and Discovery of RAB5A Protein
The RAB5A protein was first identified in a research study conducted by Stenmark and colleagues in 1995. This study discovered the existence of three related isoforms – RAB5A, RAB5B, and RAB5C – which show an overlapping expression pattern in endocytic organs such as the liver, pancreas, and kidney. It has since become an object of ongoing scientific interest due to its critical roles in cellular functions.
The gene encoding the RAB5A protein is located on the long arm of chromosome 3 at the locus of 3q21.3. The protein commonly measures 215 amino acids in length with a molecular weight of approximately 23.5 kDa. The protein comprises a GTPase domain responsible for binding guanosine triphosphate (GTP) or guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and a second region required for the functional interaction of activated Rab with its effector proteins.
What Is The Function of RAB5A Protein?
The function of the RAB5A protein is directly associated with the regulation of the endocytic pathway, controlling the early stages of endosome fusion and trafficking. Notably, it plays an essential role in the uptake of nutrients, downregulation of receptors and associated signaling cascades, and antigen presentation. RAB5A achieves these complex processes through a cycle of binding and hydrolyzing GTP, which enables it to shift between an inactive GDP-bound state and an active GTP-bound state. It is the active state that allows RAB5A to interact with a cohort of effector proteins to drive vesicle motility and tethering, eventually leading to membrane fusion.
RAB5A protein related signal pathway
The RAB5A protein also plays a significant role in several signaling pathways, including the autophagy pathway, the mTOR signaling pathway, and the endocytic pathway. RAB5A activation can lead to the recruitment of RICTOR, a key component of the mTORC2 complex, thus triggering the mTOR signaling pathway. Furthermore, the endocytic function of RAB5A is closely linked with the EGF receptor signaling pathway, which affects cell division and drives organ size and tissue homeostasis.
RAB5A protein related diseases
Studies have linked aberrations of the RAB5A protein to several human diseases, primarily those related to metabolic and neurodegenerative disorders. For instance, abnormal RAB5A activity contributes to the pathogenic process of Alzheimer's disease, possibly by impairing endosomal trafficking and increasing the production and accumulation of beta-amyloid peptide. Furthermore, altered expression levels of RAB5A have been observed in several types of cancer, implicating this protein in tumorigenesis. Additionally, RAB5A dysregulation has been suggested as a factor in the progression of diabetes and other metabolic diseases.
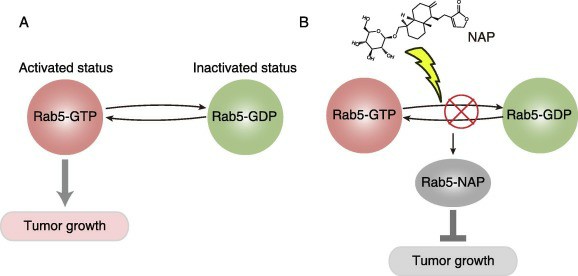
Fig1. A novel inhibitor of Rab5 to suppress cancer growth
RAB5A protein's applications in biomedical
Given the crucial roles of the RAB5A protein in many cellular functions, it has quite a number of applications in biomedicine. As its abnormal expression levels have been identified in several types of cancers and neurodegenerative disorders, research into the function and processes of this protein could inform the development of targeted therapeutics. In cancer, RAB5A might serve as a promising biomarker for the early detection of malignant tumors or as a target for personalized cancer treatment. Moreover, understanding the role of RAB5A in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease may lead to novel diagnoses and treatment methods for this devastating neurodegenerative disorder.
In conclusion, the RAB5A protein is a molecular switch that regulates various aspects of intracellular trafficking. While it performs a multitude of essential cellular functions, its dysregulation can result in a variety of pathological conditions, from metabolic disorders to cancer. Ongoing and future biomedical research spotlighting RAB5A will undoubtedly contribute not only to a deeper understanding of many cellular processes, but also to the development of innovative therapeutic strategies for a diverse range of diseases.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAB5A-374H | Recombinant Human RAB5A | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| RAB5A-30979TH | Recombinant Human RAB5A protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| RAB5A-2130H | Recombinant Human RAB5A, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| RAB5A-1838H | Recombinant Human RAB5A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| RAB5A-3403H | Recombinant Human RAB5A protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| RAB5A-13834M | Recombinant Mouse RAB5A Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| RAB5A-7360M | Recombinant Mouse RAB5A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Zhang, J., Sun, Y., Zhong, L., Yu, N., Ouyang, L., Fang, R., Wang, Y., & He, Q. (2019). Structure-based discovery of neoandrographolide as a novel inhibitor of Rab5 to suppress cancer growth. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 18, 3936-3946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.033

