What is RIPK3 Protein
The Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase 3 (RIPK3) protein is a key player in cellular response mechanisms, particularly those governing cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis and necroptosis. Necroptosis is a form of programmed cell death that is elicited by certain pathological conditions, and the role of RIPK3 in these processes has prompted significant interest in its potential as a therapeutic target.
The RIPK3 gene was first cloned and sequenced in 1999, the discovery of which was published by Meylan et al. in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. It was initially identified due to its interaction with RIPK1, another protein implicated in the regulation of apoptosis and necroptosis. The RIPK3 gene resides on the 14th chromosome (14q11.2) in humans and encodes a protein of 518 amino acids.
The protein structure of RIPK3 comprises an amino-terminal kinase domain followed by a helical intermediate domain and a carboxyl-terminal domain containing a receptor-interacting protein homotypic interaction motif. This unique configuration allows RIPK3 to interact with several other kinases and modulate various cellular processes.
Function of RIPK3 protein
Functionally, the RIPK3 protein acts as a key signaling molecule in controlling the process of necroptosis, a programmed cell death different from apoptosis where the cell undergoes swelling and rupturing, thus alerting the immune system. This role of RIPK3 is largely facilitated by its interaction with RIPK1; together, they form a necrosome that activates the mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), another crucial player in the necroptosis pathway.
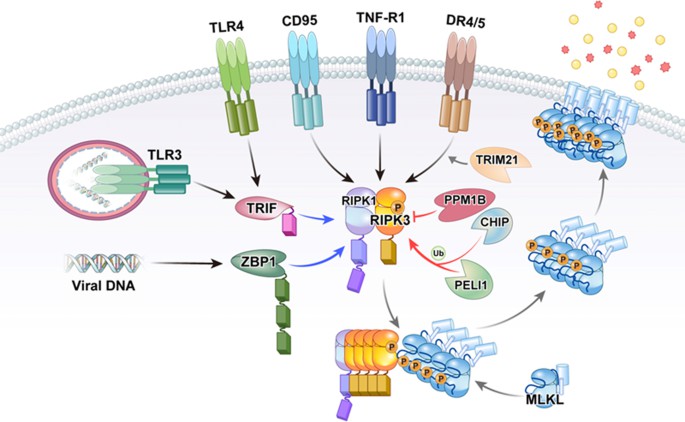
Fig1. Activation of RIPK3 by multiple stimuli. (Morgan, M. J., & Kim, Y. 2022)
Aside from its role in necroptosis, recent studies have also highlighted the involvement of the RIPK3 in inflammation and immune responses. RIPK3 can initiate the production of inflammatory cytokines, thus acting as a key player in both innate and adaptive immunity.
RIPK3 protein related diseases
Aberrant signaling involving RIPK3 has been implicated in several pathological conditions. These include various forms of cancer, where either upregulation or downregulation of RIPK3 can contribute to tumour progression. For instance, RIPK3 has been found to be deleted or silenced in several types of human cancers. On the other hand, RIPK3 upregulation can lead to excessive necroptosis and inflammatory responses, contributing to tissue damage in diseases such as ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, and sepsis.
Furthermore, recent research has highlighted a connection between dysregulation of RIPK3 and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. Abnormal RIPK3 expression can lead to neuronal loss through necroptosis, thus forming the basis of neuronal damage in such conditions.
RIPK3 protein's applications in biomedical
Given its wide-ranging role in disease pathways, RIPK3 has emerged as a significant focus in biomedicine. Therapeutic interventions targeting RIPK3 signaling could potentially offer new avenues for the treatment of various conditions, especially those marked by chronic inflammation or uncontrolled cell death. For instance, the development of small molecule inhibitors of RIPK3 is being actively investigated for their potential utility in cancer and inflammatory diseases.
Moreover, RIPK3 expression can serve as an important biomarker for several types of cancers, aiding in their diagnosis and potentially prognostication. Its involvement in necroptosis also makes it a useful tool in the study of this less understood form of cell death to potentially uncover new therapeutic opportunities in necroptosis-related pathological conditions.
In conclusion, RIPK3 is a multifunctional protein with significant implications in human health and disease. Further understanding of its roles and signals, particularly in relation to necroptosis, inflammation, and immunity, will be instrumental in developing novel therapeutic strategies for a wide range of medical conditions.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIPK3-2313H | Recombinant Human RIPK3, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| RIPK3-2348H | Recombinant Human RIPK3 protein, His&Myc-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His&Myc |
| RIPK3-4978H | Recombinant Human RIPK3 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| RIPK3-1756H | Recombinant Human RIPK3 Protein (1-518 aa), His-tagged | Human | Yeast | His |
| Ripk3-1262M | Recombinant Mouse Ripk3 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| Ripk3-2349R | Recombinant Rat Ripk3 protein, His&Myc-tagged | Rat | Insect Cell | His&Myc |
| RIPK3-4712R | Recombinant Rat RIPK3 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Morgan, M. J., & Kim, Y. (2022). Roles of RIPK3 in necroptosis, cell signaling, and disease. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 54(10), 1695-1704. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-022-00868-z

