What is SYT3 Protein
SYT3 protein, formally known as Synaptotagmin-3, is a protein that exists in humans and is encoded by the SYT3 gene. The understanding of this protein has developed significantly since its discovery, unveiling the crucial roles it plays in various biological processes and the potential implications in disease pathogenesis and treatment.
The SYT3 gene, mapped on the chromosome 1q32 locus, encodes the SYT3 protein extensively expressed in the human brain. The protein comprises of multiple domains, including two calcium-binding regions, known as C2 domains, and a membrane-associating domain. These regions coordinate to facilitate the protein's functions.
The discovery of SYT3 protein stems from the study of synaptotagmins, a family of membrane-trafficking proteins critical for exocytosis, the process whereby cells transport molecules out of the cell. As part of this family, it was not until later that SYT3 protein was identified as an essential variant that plays specific roles that distinguish it from the rest of its family.
Function of SYT3 protein
The primary function of SYT3 protein lies in regulating the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane. It serves as a calcium sensor in the exocytosis of these vesicles, controlling their release into the synapse. This role is crucial for nervous system functioning, especially in the synaptic transmission of neuronal signals.
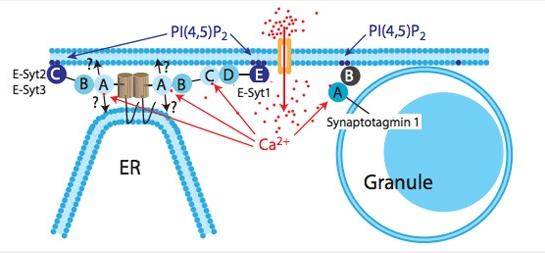
(Olof Idevall-Hagren et al. 2015)
SYT3 protein related signal pathway
Although primarily known for its function in neurotransmitter release, recent research suggests that SYT3 protein may be implicated in various signal pathways, thus contributing to multiple biological processes. One such pathway is the calcium-dependent vesicle trafficking process. In this pathway, SYT3 protein senses intracellular calcium signals and triggers vesicle membrane fusion, leading to the release of cargo molecules into the extracellular space.
Besides, recent studies hypothesize that SYT3 protein might play a role in the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway. TCR signaling is a vital process in the adaptive immune response, with SYT3 protein possibly helping to mediate vesicle trafficking and release in T cells, thus regulating immune cell activation.
SYT3 protein related diseases
Given SYT3 protein's essential roles in significant physiological processes, it is unsurprising that its dysfunction is associated with several human diseases. For instance, mutations in the SYT3 gene have been linked to some neurological disorders. Disruptions in the normal functioning of SYT3 protein can result in improper neurotransmitter release, which can throw off the delicate balance of neuronal activity, potentially leading to disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Furthermore, aberrant expression of SYT3 protein has been detected in cancers. High levels of SYT3 protein were found in samples of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, suggesting a possible relationship between SYT3 protein and tumor development. However, the exact role of SYT3 in tumorigenesis remains to be further explored in future research.
SYT3 protein's applications in biomedical
Biomedical research has found various applications for SYT3 protein due to its vital cellular functions. In neuroscience, the protein becomes a critical focus in the study of synaptic mechanisms and neurotransmission. Also, as an emerging biomarker in cancer, it may pave the way for diagnostic or therapeutic strategies in oncology. Moreover, since the functionality of SYT3 protein influences immune response, future studies on its involvement in immune regulation might provide insights into novel treatments for immunological diseases.
To conclude, the SYT3 protein, encoded by the SYT3 gene, plays several crucial roles in cellular physiology. Its involvement in different signal pathways makes it influential in various biological processes and disease development. Future research exploring the SYT3 protein promises to bring new insights into its functions and applications, potentially making significant contributions to biomedical sciences and therapeutics.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYT3-3084H | Recombinant Human SYT3, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| SYT3-2792H | Recombinant Human SYT3 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Syt3-6260M | Recombinant Mouse Syt3 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| RFL11037MF | Recombinant Full Length Mouse Synaptotagmin-3(Syt3) Protein, His-Tagged | Mouse | E.coli expression system | His |
| SYT3-5540R | Recombinant Rat SYT3 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Olof Idevall-Hagren, Alice Lü, Beichen Xie, Pietro De Camilli. Triggered Ca2+ influx is required for extended synaptotagmin 1-induced ER-plasma membrane tethering. The EMBO Journal (2015)34:2291-2305 https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201591565

