What is THRA Protein
What is THRA Protein?
The THRA protein, or Thyroid Hormone Receptor Alpha, a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, governs the cellular response to thyroid hormones. Structurally, THRA comprises distinct domains - an N-terminal A/B domain, a DNA-binding domain (DBD), a hinge region, and a ligand-binding domain (LBD) at the C-terminus. The A/B domain facilitates interaction with co-regulators, the DBD recognizes thyroid hormone response elements (TREs), and the LBD accommodates thyroid hormone binding, enabling transcriptional regulation.
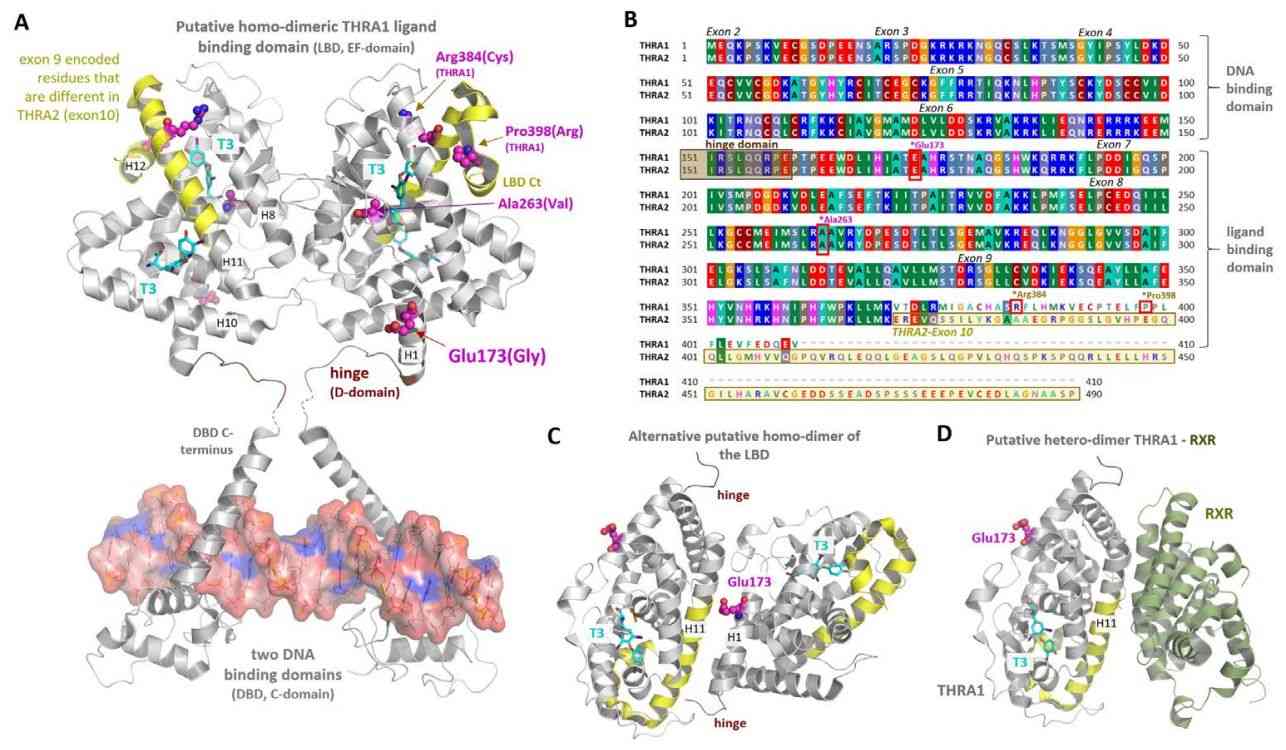
Figure 1. Structural implications for THRA position Glu173. (Paisdzior, S., et al. 2021)
The Function of THRA Protein
As a transcription factor, THRA plays a central role in mediating the effects of thyroid hormones on gene expression. Upon binding to triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), THRA undergoes conformational changes, modulating the transcription of target genes. This regulatory cascade influences vital physiological processes, including metabolism, growth, and development.
THRA-Related Diseases
Dysregulation or mutations in the THRA gene give rise to resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH), a rare genetic disorder. This condition manifests with symptoms such as goiter, cognitive impairment, and disrupted metabolic function. Mutations affecting hormone binding or co-regulator interactions in THRA contribute to the pathogenesis of RTH, highlighting the critical role of THRA in maintaining thyroid hormone homeostasis.
THRA Related Signaling Pathways
The THRA signaling pathway is a complex cascade triggered by the synthesis and release of thyroid hormones. Circulating T3 binds to THRA in target cells, initiating conformational changes that enable interaction with co-regulators. Binding to specific DNA sequences (TREs) results in the modulation of gene expression, regulating cellular functions. The intricacies of this pathway provide a framework for understanding and potentially manipulating thyroid hormone signaling for therapeutic purposes.
Applications of THRA in Biomedical Research
- Cancer Research
THRA's involvement in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis positions it as a potential player in cancer. Aberrant THRA expression is observed in certain cancers, suggesting its role in tumorigenesis. Investigating THRA in cancer research may unveil novel therapeutic targets for cancer treatment.
- Metabolic Disorders
Given THRA's role in metabolic regulation, research explores its potential in addressing disorders like obesity and diabetes. Understanding how THRA influences metabolic pathways could lead to the development of drugs targeting THRA to modulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis.
- Neurological Disorders
The influence of THRA on brain development and function makes it a potential target in neurological disorders. Ongoing research seeks to elucidate THRA's role in neurodevelopmental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, providing avenues for therapeutic interventions.
- Drug Development
The ligand-binding domain of THRA offers a target for drug development. Small molecules modulating THRA activity could be developed as therapeutics for conditions involving dysregulated thyroid hormone signaling. Tailoring drugs to enhance or inhibit THRA's transcriptional activity presents a promising avenue for precision medicine.
The THRA protein, with its intricate structure and multifaceted functions, serves as a linchpin in thyroid hormone signaling. The ongoing scientific exploration of THRA opens new frontiers for understanding cellular processes and holds promise for advancing biomedical research and improving human health.
Recommended Products for THRA Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THRA-1199H | Human | Active Recombinant Human THRA, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| THRA-1198H | Human | Active Recombinant Human THRA, His-tagged | Sf9 Insect Cell | His |
| THRA-31521TH | Human | Recombinant Human THRA | E.coli | N/A |
| THRA-595H | Human | Recombinant Human THRA Protein, DDK-tagged | Sf9 Insect Cell | DDK |
| THRA-1945H | Human | Recombinant Human THRA Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| THRA-3578H | Human | Recombinant Human THRA protein, His-B2M-tagged | E.coli | His-B2M |
| THRA-16756M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse THRA Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Thra-6419M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Thra Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| THRA-5715R | Rat | Recombinant Rat THRA Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| THRA-6865C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken THRA | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Paisdzior, S., et al. A New Mechanism in THRA Resistance: The First Disease-Associated Variant Leading to an Increased Inhibitory Function of THRA2. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22(10): 5338.

