What is TRIM21 Protein
The TRIM21 protein (Tripartite Motif Containing 21), also known as Ro52, is part of the TRIM family of proteins. These proteins are recognized for their triple motif structure consisting of a RING finger domain, one or two B-box domains, and a coiled-coil domain. An essential member of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), the TRIM21 protein has been studied extensively for its scientific relevance, disease correlation, and potential applications in biomedicine.
The TRIM21 protein was discovered during the mid-1980s by researchers who were investigating autoimmune diseases, particularly Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). They noticed that certain patients had autoantibodies against a 52-kDa protein, later identified as TRIM21.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure
The human gene that encodes the TRIM21 protein is located on locus 11p15.5. It contains 7 exons and spans more than 14 kilobases. The TRIM21 protein itself boasts a characteristic structure of three motifs: a RING domain at the N-terminal, B-box domains in the middle, and a coiled-coil domain alongside a PRY/SPRY domain at the C-terminal.
TRIM21 Function
TRIM21 exhibits several important functions. It plays a crucial role in immune regulation due to its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that helps regulate innate immune signaling. It can also capture invading viruses in the cytoplasm by binding to the Fc region of antibodies. After capturing the virus, TRIM21 uses its ligase activity to mediate the ubiquitination and degradation of the invading pathogen. In addition to its immune functions, it is involved in apoptosis and cell cycle regulation.
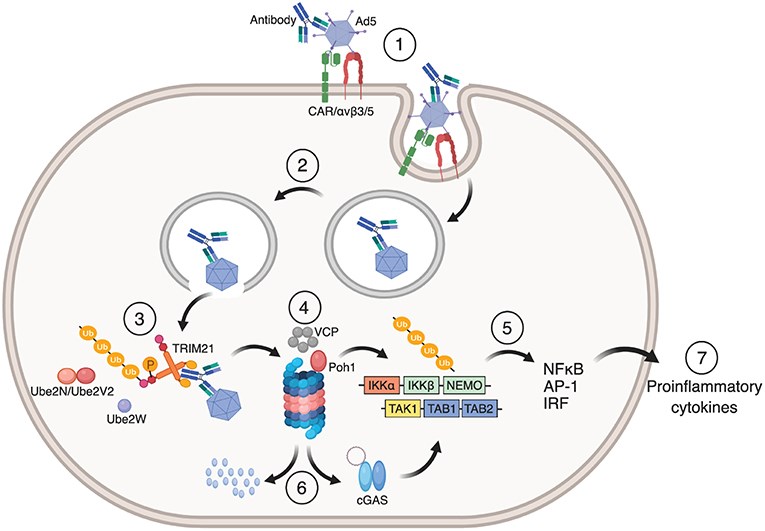
Fig1. Mechanism of TRIM21 mediated anti-viral function (Foss, S., et al. 2019)
TRIM21-related Signal Pathway
TRIM21 has been implicated in several signaling pathways, wherein it modulates protein stability and transcriptional activity. The most prominent include interferon (IFN) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. By acting as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, TRIM21 can modulate the turnover of several substrates involved in these pathways, influencing inflammatory and immune responses.
TRIM21-Related Diseases
Mutations or aberrant expressions of TRIM21 have been linked to numerous diseases, particularly autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. For example, elevated levels of TRIM21 antibodies are present in patients with Sjögren's syndrome, SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, and myositis. Additionally, polymorphisms in the TRIM21 gene have been associated with increased susceptibility to these diseases. Recent studies also suggest a potential role for TRIM21 in cancer, neurological disorders, and viral infections.
TRIM21 Protein's Applications in Biomedicine
The immunological and biological significance of TRIM21 has paved the way for its applications in biomedicine. Its ability to recognize, bind to, and degrade antibody-coated viruses suggest its potential as an antiviral therapy. It might also be manipulated to modulate immune responses, potentially treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Moreover, targeting TRIM21 could prevent or reduce the aggressive growth of certain types of cancer.
In conclusion, the TRIM21 protein plays a vital role in the immune response regulation, viral infections, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Its links to various diseases make it a promising target for therapeutic interventions. Continuous research and clinical trials are required to fully understand the potential of TRIM21 protein and its mechanistic pathways. The more we learn about this protein, the closer we become to breakthroughs in disease treatment and prevention.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIM21-5540H | Recombinant Human TRIM21 protein, His-tagged | Human | Yeast | His |
| TRIM21-0259H | Recombinant Human TRIM21 Protein, Tag Free | Human | Confidential | Tag Free |
| TRIM21-3037H | Recombinant Human TRIM21 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| TRIM21-537HF | Recombinant Full Length Human TRIM21 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| Trim21-6646M | Recombinant Mouse Trim21 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| Trim21-4539M | Recombinant Mouse Trim21 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| TRIM21-4768R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque TRIM21 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rhesus Macaque | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Foss, S., Bottermann, M., Jonsson, A., Sandlie, I., James, L. C., & Andersen, J. T. (2019). TRIM21—From Intracellular Immunity to Therapy. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 474156. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02049

