What is TRXB Protein
TRXB, or Thioredoxin Reductase, is a vital protein playing a crucial role in cellular redox regulation. The official full name of this protein is Thioredoxin-disulfide Reductase, with common synonyms including TXNRD and TrxR. Belonging to the family of oxidoreductases, TRXB is a member of the pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family. Its structural characteristics involve a selenocysteine residue, which is essential for its enzymatic activity. Recent research has brought about significant advances in our understanding of TRXB, shedding light on its diverse functions and the intricacies of its classification within the oxidoreductase family.
TRXB Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of TRXB are multifaceted, showcasing its importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis. One of its primary roles is to catalyze the reduction of thioredoxin (Trx), a small redox-active protein, utilizing NADPH as an electron donor. This reduction is pivotal in preventing and repairing oxidative damage to cellular components. TRXB's molecular mechanisms involve the transfer of electrons through its selenocysteine residue, serving as a key player in redox signaling pathways.
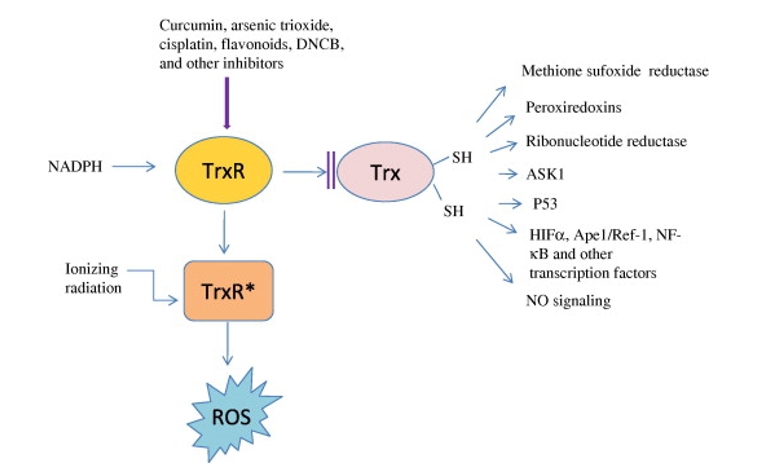
Figure 1. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. (Holmgren A, et al., 2010)
TRXB Related Signaling Pathway
The signal pathway associated with TRXB is intricate and interconnected with various cellular processes. TRXB is a crucial component in the thioredoxin system, which participates in redox signaling cascades. This pathway is involved in the regulation of transcription factors, such as NF-κB and p53, influencing cell survival, proliferation, and apoptosis. The modulation of these pathways by TRXB underscores its significance in maintaining cellular integrity and responding to environmental stresses.
TRXB Related Diseases
Dysregulation of TRXB has been implicated in various diseases, highlighting its significance in health and disease. Studies have linked abnormal TRXB activity to conditions such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. In cancer, for instance, altered TRXB expression has been observed in tumor cells, contributing to increased cell proliferation and resistance to oxidative stress. Understanding the role of TRXB in these diseases opens avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions.
TRXB's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of TRXB make it an attractive candidate for various biomedical applications. In diagnostics development, TRXB is utilized as a biomarker for oxidative stress-related diseases. Monitoring its activity provides insights into the redox status of cells, aiding in the early detection and diagnosis of conditions like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, TRXB has been explored in vaccine development, where its involvement in immune regulation offers potential for enhancing vaccine efficacy.
In therapeutics, targeting TRXB has emerged as a promising strategy for combating diseases characterized by oxidative stress. Small molecule inhibitors designed to modulate TRXB activity are under investigation as potential therapeutic agents. These inhibitors have shown promise in preclinical studies, demonstrating their ability to selectively target cancer cells and enhance the efficacy of conventional chemotherapy. The development of TRXB-targeted therapeutics represents a novel approach in the quest for more effective and selective treatment options.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRXB-2037B | Recombinant Bacillus subtilis TRXB protein, His-tagged | Bacillus subtilis | E. coli or Yeast | His |
| trxB-2366E | Recombinant E.coli Thioredoxin Reductase | E.coli | E.coli | N/A |
Reference
- Holmgren A, Lu J. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: current research with special reference to human disease. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2010, 396(1): 120-124.

