What is TUBA1A Protein
TUBA1A, an acronym for Tubulin Alpha 1A, belongs to the Tubulin family, which are globular proteins integral to the structure and function of microtubules. Microtubules are cytoskeletal components that are crucial for various fundamental cellular processes, including cell shape, division, and intracellular transport in organisms across the biological spectrum from yeast to humans.
Functions of the TUBA1A Protein
The primary function of the TUBA1A protein lies in its essential role in forming microtubules, one of the vital components of the cytoskeleton. In collaboration with Tubulin Beta (TUBB) protein, TUBA1A polymerizes into a heterodimer, functioning as the building block for microtubules construction. Microtubules are dynamic structures that interconvert between polymerized and depolymerized states, providing necessary machinery for cell division, intracellular transport, and maintaining cell shape and structure. In neurons, they are critical for axonal transport- transporting essential elements to and from the neuron's cell body and synapse.
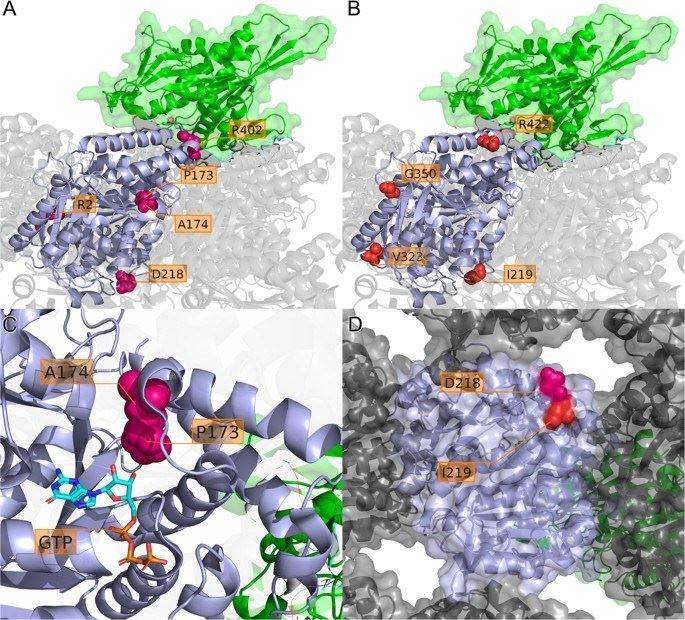
Fig1. Localization of missense variants in a TUBA1A protein model. (Schröter, J., et al. 2022)
TUBA1A Protein and Signaling Pathway
Intracellular events orchestrated by TUBA1A are part of cellular signaling pathways, ensuring smooth communication within and between cells. Stability and dynamics of microtubules are regulated by a number of pathways involving various enzymes and cellular components like Microtubule-Associated Proteins (MAPs), plus and minus end proteins, and Tubulin isoforms. Post-translational modifications of the TUBA1A protein, like detyrosination-tyrosination cycle, acetylation, and polyglutamylation, add unparalleled complexity to this regulation, influencing microtubule dynamics, stability and cellular functions.
TUBA1A Protein related Diseases
Alterations and mutations in the TUBA1A gene can lead to a wide variety of diseases and neurodevelopmental disorders. Studies have found that heterozygous missense mutations in TUBA1A are associated with malformations of cortical development, leading to disorders like lissencephaly, polymicrogyria, or microlissencephaly. Patients present with severe intellectual disability, epilepsy, and motor delay. TUBA1A mutations have also been linked with familial and sporadic isolated lissencephaly sequence (ILS).
Applications of TUBA1A Protein in Biomedicine
In biomedical research, TUBA1A protein and its mutations serve as significant areas of interest for understanding disease mechanisms and pursuing targeted therapeutic interventions. Its role in neurodevelopmental disorders makes it crucial for studying brain growth and connectivity disorders, paving the way for personalized medicine.
The current research focuses on using gene editing techniques, like CRISPR-Cas9, to study the effect of specific TUBA1A mutations in laboratory models hence, providing a comprehensive understanding of cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying brain malformations.
In addition, their involvement in microtubule dynamics makes Tubulin proteins (including TUBA1A) primary targets for chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. Drugs like paclitaxel (also known as Taxol) and Vinca alkaloids, which target and disrupt microtubule function, are used in clinical oncology, thus projecting TUBA1A and other Tubulin proteins as potential drug targets.
Despite the complexity associated with TUBA1A protein and its associated pathways, understanding it is crucial in elucidating the mysteries tied to neurodevelopmental disorders and establishing potential therapeutic strategies. Unraveling the secrets of such proteins gives a promising pathway to conquering many disease states, underlining their importance in biomedical research.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUBA1A-18H | Recombinant Human TUBA1A protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| TUBA1A-3184H | Recombinant Human TUBA1A protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| TUBA1A-533HF | Recombinant Full Length Human TUBA1A Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| TUBA1A-17608M | Recombinant Mouse TUBA1A Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| TUBA1A-9752M | Recombinant Mouse TUBA1A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| TUBA1A-6354R | Recombinant Rat TUBA1A Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Schröter, J., Popp, B., Brennenstuhl, H., Döring, J. H., Donze, S. H., Bijlsma, E. K., Van Haeringen, A., Huhle, D., Jestaedt, L., Merkenschlager, A., Arelin, M., Gräfe, D., Neuser, S., Oates, S., Pal, D. K., Parker, M. J., Lemke, J. R., Hoffmann, G. F., Kölker, S., . . . Syrbe, S. (2022). Complementing the phenotypical spectrum of TUBA1A tubulinopathy and its role in early-onset epilepsies. European Journal of Human Genetics, 30(3), 298-306. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-021-01027-0

