What is UBC9 Protein
The UBC9 protein, officially known as Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme E2I, is a crucial player in the intricate world of molecular biology. Also recognized by its synonyms such as UBE2I and UBC9p, this protein belongs to the family of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, or E2 enzymes, are vital components of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, responsible for maintaining cellular protein homeostasis.
UBC9 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, UBC9 is a small protein, comprised of approximately 158 amino acids. It exhibits a characteristic fold, forming a compact structure essential for its function. Classification places UBC9 within the E2 enzyme family, and recent research advances have shed light on its diverse roles in cellular processes.
UBC9 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of UBC9 are multifaceted, reflecting its involvement in various cellular mechanisms. Its primary role lies in the regulation of protein sumoylation, a post-translational modification process akin to ubiquitination. Sumoylation involves the attachment of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) proteins to target proteins, modifying their function, localization, or interaction with other molecules.
UBC9 acts as the key mediator in the sumoylation process, facilitating the transfer of SUMO from the E1 enzyme to the target protein. This modification influences diverse cellular processes, including DNA repair, transcriptional regulation, and cell cycle progression. Additionally, UBC9 is implicated in the maintenance of genomic stability and the response to cellular stress.
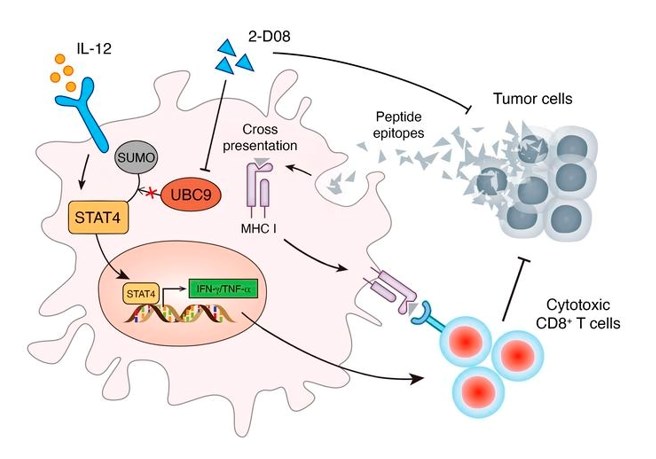
Figure 1. UBC9 deficiency enhances immunostimulatory macrophage activation and subsequent antitumor T cell response in prostate cancer. (Xiao J, et al., 2023)
UBC9 Related Signaling Pathway
Understanding the signaling pathway associated with UBC9 provides insights into its regulatory networks. UBC9 participates in intricate crosstalk with other cellular components, influencing diverse pathways. Notably, the interaction of UBC9 with specific transcription factors and nuclear receptors modulates gene expression, affecting cellular responses to environmental stimuli.
Moreover, UBC9 is intricately connected to the DNA damage response pathway. Its role in coordinating the repair of damaged DNA highlights its significance in maintaining genomic integrity. Dissecting the UBC9 signaling pathway offers potential therapeutic targets for diseases associated with its dysregulation.
UBC9 Related Diseases
As with any molecular player, disruptions in UBC9 function can lead to pathological consequences. Research has unveiled associations between UBC9 dysfunction and various diseases. For instance, aberrant sumoylation mediated by UBC9 has been linked to cancer development. Dysregulation of UBC9 is observed in several cancer types, influencing the activity of key proteins involved in cell proliferation and survival.
Furthermore, neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, showcase altered UBC9 levels. The impact of UBC9 on protein aggregation and clearance mechanisms in neurons underscores its significance in maintaining neuronal health.
UBC9's Applications in Biomedicine
Beyond its fundamental role in cellular processes, UBC9 has garnered attention for its applications in biomedical research and development. The protein's involvement in disease pathways positions it as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target.
In diagnostics, UBC9's altered expression in various diseases serves as a biomarker for disease progression and prognosis. Researchers are exploring its utility in developing diagnostic tools that provide early indications of diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
The versatile nature of UBC9 extends to vaccine development. Understanding its role in modulating immune responses opens avenues for designing vaccines that leverage UBC9 to enhance the body's ability to combat infections and diseases.
Furthermore, UBC9 is a promising target for therapeutic interventions. Small molecules and inhibitors that selectively modulate UBC9 activity are under investigation for their potential in cancer therapy and neurodegenerative disease treatments. The development of targeted therapeutics capitalizes on UBC9's involvement in disease-specific pathways.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC9-3524H | Recombinant Human UBC9, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | |
| Ubc9-14H | Recombinant Human Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme 9, His | Human | E.coli | |
| UBC9-3407H | Recombinant Human UBC9 protein, His-tagged | Human |
Reference
- Xiao J, et al. UBC9 deficiency enhances immunostimulatory macrophage activation and subsequent antitumor T cell response in prostate cancer. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2023, 133(4).

