What is VCP Protein
The Valosin-containing Protein (VCP), also referred to as p97, Cdc48, or Ter94 in different species. Its significance lies in governing cellular processes and its link to an array of diseases.
The decoding of VCP happened in the late 1980s through studies investigating cell cycle progression in yeast. Initially termed Cdc48 (Cell division cycle 48), it was later identified in humans as VCP, owing to the presence of the valosin drug molecule.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure
The VCP gene is located on chromosome 9p13.3, spanning around 33 kilobases with 17 exons and producing a 97kDa protein that comprises of 806 amino acids. VCP exhibits a unique tripartite architecture - a dual ATPase domain (D1 and D2 domain), interspersed by a non-catalytic ridge, and a versatile amino-terminal domain (NTD).
Each domain plays a crucial role in its function. The NTD acts as a principal interaction platform for many adaptive proteins partners, while the D1 and D2 domains facilitate VCP's ATPase activity. Proper co-functioning of these domains is pivotal for the physiological and biological role of VCP.
Function of VCP Protein
VCP's primary function involves segregating ubiquitinated substrates from protein complexes or cellular structures. It chaperones the extraction, unfolding, and degradation of misfolded, damaged, or unnecessary proteins. VCP plays an indispensable role in various cellular processes, including endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD), DNA damage response (DDR), cell cycle control, and protein homeostasis. It's essentially a molecular "jack of all trades," contributing to the overall cellular structural integrity and function.
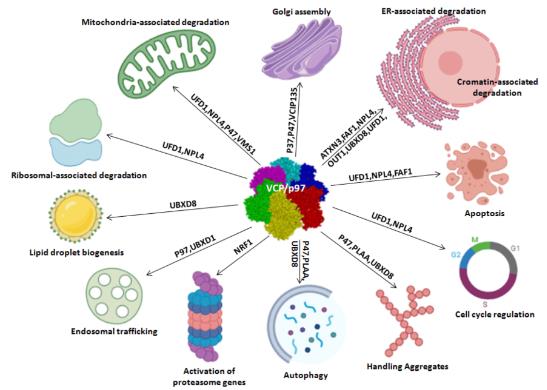
Fig1. Biological functions of VCP/p97 (Costantini, S., et al. 2020)
VCP Protein Related Signaling Pathway
VCP functions draw on an interplay of various signaling pathways. The primary one involves the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), responsible for protein degradation. VCP interacts with ubiquitin chains, aids in the extraction of ubiquitinated proteins from their native complexes, and delivers them to the proteasome for degradation – a crucial function for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Another critical pathway is the autophagy-lysosomal pathway, where VCP regulates the maturation of autophagosomes, cellular components involved in removing damaged organelles or protein aggregates.
VCP Protein-Related Diseases
VCP mutations can disrupt the normal functioning of cellular processes, leading to an array of illnesses. The most prominent VCP-related disease is the Inclusion Body Myopathy associated with Paget's disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia (IBMPFD), an adult-onset neurodegenerative disorder. VCP mutations can also lead to ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis), a severe neurodegenerative disease affecting motor neuron cells.
Further, VCP overexpression has been identified in several cancers, including breast, lung, and prostate, correlating with poor prognosis. Such findings link VCP to tumorigenesis and tumor progression.
Applications of VCP Protein in Biomedicine
Since its relation to various diseases, VCP protein has emerged as a promising therapeutic target in the biomedical field. Pharmacological inhibitors of VCP, such as DBeQ and NMS-873, have affirmed potential implications in cancer treatment by selectively killing cancer cells.
In the realm of neurodegenerative diseases like ALS and IBMPFD, small molecules and VCP modulators have shown promise in attenuating disease progression. Conceptually, such therapies may help restore normal VCP function, providing a significant leap forward in the race against these diseases.
In light of its wide-ranging functions, VCP's importance in cellular biology and disease pathology is undeniable. Though its journey from cellular biology to clinical medicine is far from complete, the potential of transcribing this 'jack of all trades' into a masterstroke against disease holds immense promise. The extensive research efforts invested in understanding VCP's role will hopefully offer profound insights, enhancing our abilities to combat diseases and enrich human health.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCP-3656H | Recombinant Human VCP, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| VCP-7934H | Recombinant Human VCP protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| VCP-506H | Recombinant Human VCP protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| VCP-195H | Recombinant Human VCP Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Insect cell | GST |
| VCP-9955HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human VCP protein, Flag-tagged | Human | Mamanlian cells | Flag |
| VCP-17998M | Recombinant Mouse VCP Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| VCP-10004M | Recombinant Mouse VCP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Vcp-6911M | Recombinant Mouse Vcp Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Costantini, S., Capone, F., Polo, A., Bagnara, P., & Budillon, A. (2020). Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97: A Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 10177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810177

