What is VEGFE Protein
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor E (VEGFE), also known by its official name VEGFA, is a key player in the family of vascular endothelial growth factors. Commonly referred to as VEGF, this protein has several synonyms, including VPF (vascular permeability factor) and MVCD1 (macular degeneration, age-related, 1). Its official nomenclature, VEGFA, highlights its role in promoting angiogenesis, a critical process in the development of new blood vessels.
VEGFE Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
VEGFE is characterized by a conserved structural motif known as the VEGF homology domain (VHD). This domain is crucial for its interaction with the VEGF receptors (VEGFRs) present on the surface of endothelial cells. Structurally, VEGFE is classified into several isoforms, with VEGFA being the most prominent. The isoforms differ in their amino acid compositions, resulting in diverse biological activities.
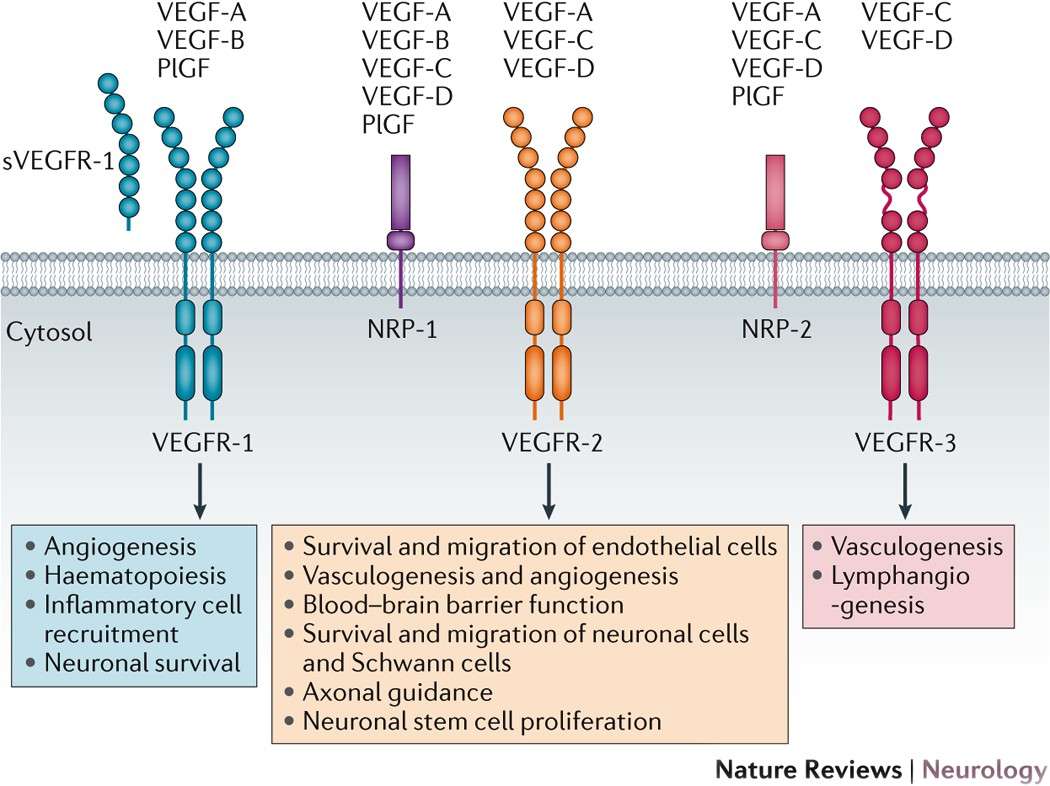
Figure 1. The VEGF family of growth factors. (Lange C, et al., 2016)
Recent Research Advances about VEGFE Protein
Recent research has shed light on the complexity of VEGFE signaling. Advances in structural biology techniques, such as cryo-electron microscopy, have enabled a more detailed understanding of the interaction between VEGFE and its receptors. Moreover, studies exploring the expression patterns of VEGFE isoforms in various tissues have expanded our knowledge of its diverse roles beyond angiogenesis.
VEGFE Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
VEGFE's primary function revolves around angiogenesis, the process of forming new blood vessels from existing ones. It stimulates endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and survival, contributing to the vascularization of tissues during development and wound healing. Additionally, VEGFE enhances vascular permeability, facilitating the movement of nutrients and immune cells across blood vessel walls.
VEGFE exerts its effects by binding to VEGFRs, specifically VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, on the surface of endothelial cells. This interaction triggers downstream signaling pathways, including the MAPK and PI3K-Akt pathways, which regulate cell survival, proliferation, and migration. The intricate balance of these pathways is crucial for the precise control of angiogenesis and vascular homeostasis.
VEGFE Related Signaling Pathway
The VEGFE signaling pathway is initiated by binding to VEGFRs, leading to the activation of intracellular signaling cascades. Notably, the MAPK and PI3K-Akt pathways play pivotal roles in mediating the cellular responses to VEGFE. These pathways orchestrate gene expression, cell proliferation, and migration, finely tuning the angiogenic process.
VEGFE Related Diseases
VEGFE dysregulation is implicated in various diseases, emphasizing its significance in maintaining vascular health. Conditions such as cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration are associated with abnormal angiogenesis driven by an imbalance in VEGFE signaling. Understanding these disease mechanisms provides potential therapeutic targets for intervention.
VEGFE's Applications in Biomedicine
- Diagnostic Development
In the realm of diagnostics, VEGFE has emerged as a biomarker for certain diseases characterized by aberrant angiogenesis. Detection of elevated VEGFE levels in patient samples can aid in the diagnosis and prognosis of conditions such as certain cancers, providing valuable information for personalized treatment strategies.
- Vaccine Development
The unique properties of VEGFE make it a promising candidate for vaccine development. Research is underway to harness its angiogenic capabilities for therapeutic purposes, aiming to stimulate controlled angiogenesis to promote tissue repair and regeneration. This innovative approach holds potential for addressing ischemic conditions and other disorders involving impaired blood vessel formation.
- Therapeutics
VEGFE-targeted therapies, such as anti-VEGF drugs, have revolutionized the treatment landscape for various diseases. In oncology, these drugs inhibit tumor angiogenesis, suppressing the blood supply essential for tumor growth. Beyond cancer, anti-VEGF therapies are employed in the management of retinal diseases, offering hope to patients with conditions like wet age-related macular degeneration.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFE-52 | Recombinant Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-E (Orf Virus) | N/A | E.coli | N/A |
Reference
- Lange C, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor: a neurovascular target in neurological diseases. Nature Reviews Neurology. 2016, 12(8): 439-454.

