GATA1
-
Official Full Name
GATA binding protein 1 (globin transcription factor 1) -
Overview
This gene encodes a protein which belongs to the GATA family of transcription factors. The protein plays an important role in erythroid development by regulating the switch of fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked dyserythropoietic anemia and thrombocytopenia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
GATA1;GATA binding protein 1 (globin transcription factor 1);GF1;GF-1;NFE1;XLTT;ERYF1;NF-E1;XLANP;XLTDA;GATA-1;erythroid transcription factor;GATA-binding factor 1;NF-E1 DNA-binding protein;transcription factor GATA1;nuclear factor, erythroid 1;globin transcription factor 1;erythroid transcription factor 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GATA1-2481R | Recombinant Rat GATA1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| GATA1-28476TH | Recombinant Human GATA1, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 70-413 a.a. |
|
| Gata1-474M | Recombinant Mouse Gata1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Asp20~Thr265 |
|
| Gata1-475R | Recombinant Rat Gata1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | Asp42~Asn292 |
|
| GATA1-6222M | Recombinant Mouse GATA1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| GATA1-7013C | Recombinant Chicken GATA1 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| GATA1-689HCL | Recombinant Human GATA1 cell lysate | Human | Non |
|
||
| GATA1-1962HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human GATA1 Protein, N-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. |
|
| GATA1-2137R | Recombinant Rat GATA1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| GATA1-2137R-B | Recombinant Rat GATA1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| GATA1-3481M | Recombinant Mouse GATA1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| GATA1-3481M-B | Recombinant Mouse GATA1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| GATA1-6938HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GATA1 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 413 amino acids |
|
Background
What is GATA1 protein?
GATA1 (GATA binding protein 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the chromosome X. This protein enables several functions, including DNA binding activity; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific; and p53 binding activity. Involved in several processes, including platelet aggregation; regulation of cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process; and regulation of definitive erythrocyte differentiation. Acts upstream of or within several processes, including hemopoiesis; positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation; and regulation of primitive erythrocyte differentiation. Located in nucleus. Is expressed in several structures, including alimentary system; central nervous system; ear; early conceptus; and genitourinary system. The GATA1 protein is consisted of 413 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 42.8 kDa.
What is the function of GATA1 protein?
GATA1 is essential for the process of erythropoiesis, where it regulates the expression of genes required for the development of red blood cells from hematopoietic stem cells. As a transcription factor, GATA1 binds to specific DNA sequences in gene promoters and enhancers to regulate gene expression, which is critical for the differentiation of red blood cells. GATA1 has been implicated in the regulation of apoptosis in red blood cells, which is important for maintaining the proper balance of cell production and cell death. It is involved in the maturation of red blood cells, ensuring that they achieve the correct shape and size and can carry out their oxygen transport function effectively. GATA1 interacts with other proteins, such as HES6, to form complexes that are essential for the transcriptional regulation of genes involved in erythropoiesis
GATA1 Related Signaling Pathway
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells. GATA1 is a key downstream effector of EPO signaling, regulating genes necessary for erythropoiesis. GATA1 has been shown to promote the survival of developing red blood cells by regulating anti-apoptotic genes. GATA1 is involved in the regulation of genes related to glycolysis and red blood cell metabolism, which are critical for the energy needs of these cells. GATA1 interacts with other transcription factors and cofactors to form complex gene regulation networks that control erythropoiesis. GATA1 may also be involved in epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, which can affect gene expression during erythropoiesis.
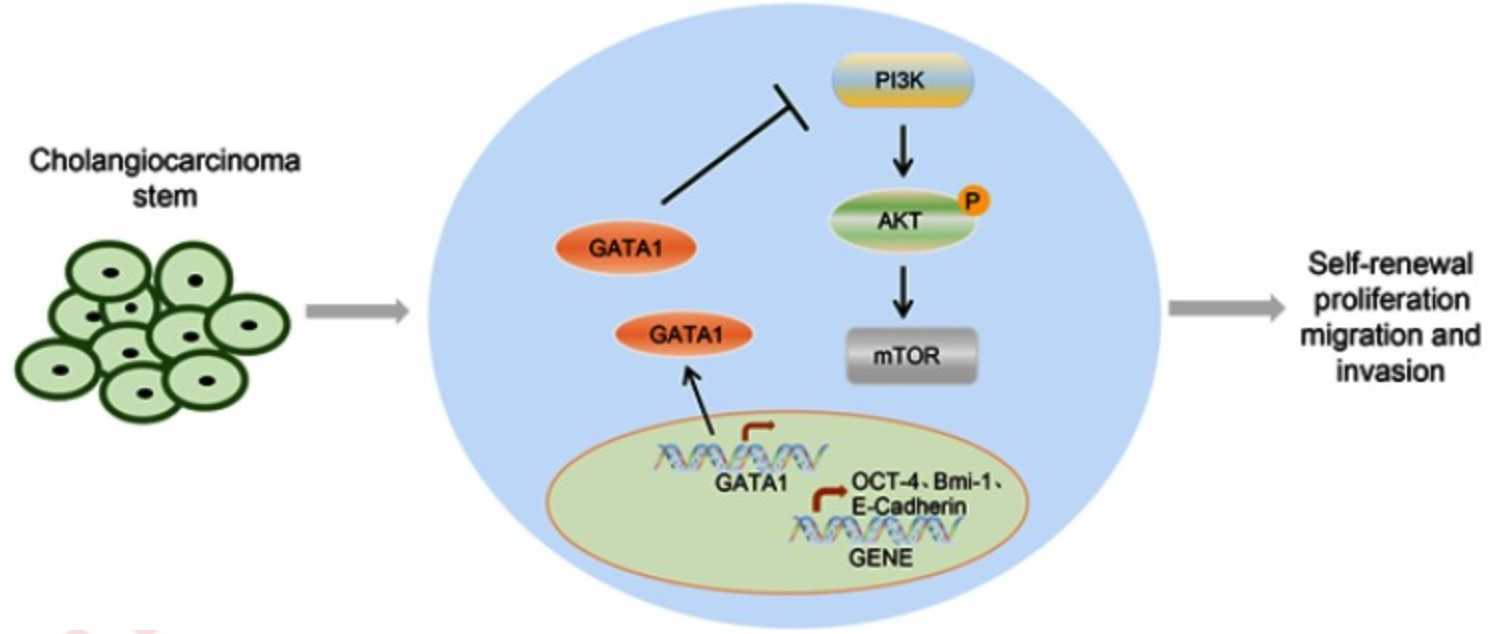
Fig1. Mechanism map of GATA1 in CCA stem cells. (Guang Shi, 2019)
GATA1 Related Diseases
GATA1-Related Cytopenia is an X-linked disorder characterized by thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) and anemia, which can range from mild to severe. Children with Down syndrome who develop somatic mutations in GATA1 are at risk for transient myeloproliferative disease and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Mutations in GATA1 can cause thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by a low number of platelets that can lead to increased bleeding risk. GATA1 mutations have been associated with certain types of neoplasms that affect both the red blood cell and myeloid lineages.
Bioapplications of GATA1
Modulating the activity of GATA1 could be a strategy for developing drugs that treat diseases associated with GATA1 dysregulation. GATA1 plays a key role in the development of erythroid cells, the precursor of red blood cells. Therefore, the study of GATA1 and its regulatory network is very important for understanding and treating diseases related to erythropoietic production, such as anemia, leukemia, etc. For example, studies have found that GATA1 is involved in the regulation of heme levels, which is essential to ensure the normal differentiation and maturation of red blood cells.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zi Wang, 2023
Normal erythropoiesis requires the precise regulation of gene expression patterns, and transcription cofactors play a vital role in this process. Deregulation of cofactors has emerged as a key mechanism contributing to erythroid disorders. Through gene expression profiling, the researchers found HES6 as an abundant cofactor expressed at gene level during human erythropoiesis. HES6 physically interacted with GATA1 and influenced the interaction of GATA1 with FOG1. Knockdown of HES6 impaired human erythropoiesis by decreasing GATA1 expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and RNA sequencing revealed a rich set of HES6- and GATA1-co-regulated genes involved in erythroid-related pathways. They also discovered a positive feedback loop composed of HES6, GATA1 and STAT1 in the regulation of erythropoiesis. Notably, erythropoietin (EPO) stimulation led to up-regulation of these loop components. Increased expression levels of loop components were observed in CD34+ cells of polycythemia vera patients. Interference by either HES6 knockdown or inhibition of STAT1 activity suppressed proliferation of erythroid cells with the JAK2V617F mutation.
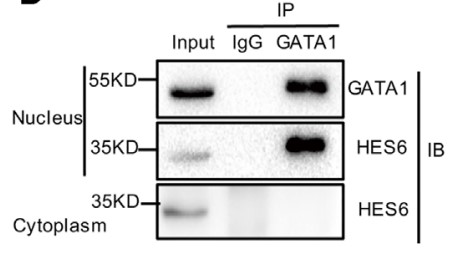
Fig1. Co-IP results confirmed that the HES6 and GATA1 interaction occurred in the nucleus but not in the cytoplasm.
 and GATA1 (blue) ChIP-seq reads.jpg)
Fig2. Averaged profiles of HES6 (green) and GATA1 (blue) ChIP-seq reads centered on the transcription start site.
Case Study 2: Zhenyu Chang, 2019
Gemcitabine-based chemotherapy is the first-line treatment for pancreatic cancer. However, chemoresistance is a major obstacle to drug efficacy, leading to poor prognosis. Little progress has been achieved although multiple mechanisms are investigated. Therefore, effective strategies are urgently needed to overcome drug resistance. Here, the researchers demonstrate that the transcription factor GATA binding protein 1 (GATA1) promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through antiapoptotic pathway. GATA1 is highly expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues, and GATA1 status is an independent predictor of prognosis and response to gemcitabine therapy. Further investigation demonstrates GATA1 is involved in both intrinsic and acquired gemcitabine resistance in PDAC cells. Mechanistically, they find that GATA1 upregulates Bcl-XL expression by binding to its promoter and thus induces gemcitabine resistance through enhancing Bcl-XL mediated antiapoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, in PDAC patients, Bcl-XL expression is positively correlated with GATA1 level and predicts clinical outcomes and gemcitabine response.

Fig3. Western blot assay of GATA1 in PDAC and normal pancreatic cell lines.
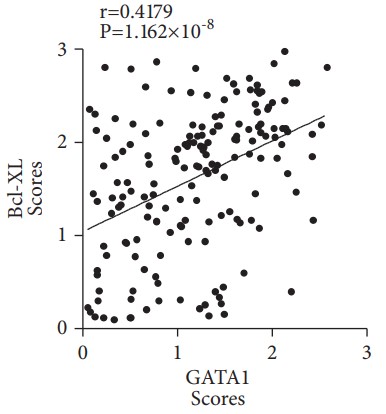
Fig4. Correlation between GATA1 and Bcl-XL expression was analyzed in 172 PDAC samples by Spearman rank correlation analysis.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GATA1-1962HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Gata1-474M)
Involved Pathway
GATA1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GATA1 participated on our site, such as C-MYB transcription factor network,Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production,Hemostasis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GATA1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Notch-mediated HES/HEY network | YY1,MYOD1,GATA6,CTBP1,TLE1,HES6,HEY1,MYB,RCAN1,BGLAP |
| C-MYB transcription factor network | ADORA2B,CEBPA,MYC,MYB,SMARCA2,CREBBP,SKI,PRTN3,COL1A2,MYF6 |
| IL-3 Signaling Pathway | KCNIP3B,BIRC5A,GATA1A,KCNIP3,SPI1B,GNB2L1,PILRB,GATA2A,CISH,BMX |
| Signaling events mediated by HDAC Class II | ANKRA2,BCOR |
| Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production | KIFAP3,KIF20A,ITPK1,GATA2A,DOCK7,MAFG,KIF5A,CABLES1,KIF4,HBBE2 |
| Signaling events mediated by HDAC Class I | SIRT4,SIRT2,NR2C1,MXD1,GATA2,TFCP2,PRMT5,FKBP3,SIRT5,SIRT7 |
| Hemostasis | KIF2A,HBBE1.1,CLEC1B,KIF2B,SLC3A2A,ATP2B1B,DOCK7,KIF4,D-AKAP2,DGKG |
Protein Function
GATA1 has several biochemical functions, for example, C2H2 zinc finger domain binding,DNA binding,DNA binding, bending. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GATA1 itself. We selected most functions GATA1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GATA1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | SP8B,ZFP146,SIX6A,FOXQ2,GATA4,HIST4H4,POLE3,DNASE1L3,ACD,APEX1 |
| RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | DMBX1,ZIK1,CREBBP,AASS,PRDM15,ETV3,CREB3L3,TAL2,ONECUT3,FOXF2 |
| enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding | ISL1,GATA3,LMO4,TFAP2B,KLF6A,TBX19,TWIST1B,KLF7B,MYT1,YY1 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding | GATA1A,TRPS1,DHX9,TAL1,MTDH,GSK3B,CHST13,KLF4,ID4,MKX |
| p53 binding | ZFP346,RCHY1,DAXX,KDM1A,HTT,TRIM24,CDKN2A,BRD7,TP53RK,TAF9 |
| transcriptional repressor activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | SNAI1,PROX1A,HAND1,ETS2,SNAI2,NFIL3-5,TBX15,MXD1,NFIL3-6,ATF7 |
| core promoter binding | MYOG,NKX3-1,HDAC5,HNRNPU,CLOCK,NPAS2,IRF9,DHX36,E2F8,PSPC1 |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | NFAT5,SOX12,ATF2,NFIB,YBX1,KLF5,NKX2-8,GLI2,PGR,EBF2 |
| zinc ion binding | NR2F1B,RORC,PHF2,ZFAND3,MARCH1,ZDHHC24,UBR3,HHIP,MORC2B,OAS1A |
Interacting Protein
GATA1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GATA1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GATA1.
FRS3;PRKAB2;HOXA1;KRTAP10-5;CCDC24;FBF1;RADIL
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, KP; Zhao, LQ; et al. Differential co-expression analysis of rheumatoid arthritis with microarray data. MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10:2421-2426(2014).
- Battista, JM; Tallmadge, RL; et al. Hematopoiesis in the equine fetal liver suggests immune preparedness. IMMUNOGENETICS 66:635-649(2014).



