PARP12
-
Official Full Name
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 12 -
Synonyms
PARP12;poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 12;ZC3HDC1, zinc finger CCCH type domain containing 1;poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 12;FLJ22693;PARP 12;ZC3H1;zinc finger CCCH type domain containing 1;zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 1
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARP12-12370M | Recombinant Mouse PARP12 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PARP12-432H | Recombinant Human PARP12, GST-tagged | Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | Full L. |
|
| PARP12-433H | Recombinant Human PARP12, His-GST tagged | Sf9 Cells | Human | GST&His | 500-701 a.a. |
|
| PARP12-5643H | Recombinant Human PARP12 protein, His&Myc-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&Myc | 1-701a.a. |
|
| PARP12-6503M | Recombinant Mouse PARP12 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PARP12-6503M-B | Recombinant Mouse PARP12 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PARP12 protein?
PARP12 protein, also known as ARTD12, is an enzyme that belongs to the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) family. PARP enzymes play a crucial role in cellular processes such as DNA repair, gene transcription, and cell survival. PARP12 is specifically involved in the antiviral response and innate immune signaling.
What is the function of PARP12 protein?
The main function of PARP12 is to modify target proteins through the addition of poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) chains. This post-translational modification regulates protein-protein interactions, protein localization, and protein function. PARP12 acts as an RNA-binding protein and is essential for the production of type I interferons, which are important in the defense against viral infections.
PARP12 related signaling pathway
The specific signaling pathway associated with PARP12 is not well-characterized. However, studies suggest that PARP12 may play a role in the regulation of immune responses and cellular stress pathways. It has been shown to be involved in the innate immune response by interacting with and modulating the activity of various signaling molecules, including interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1). PARP12 has also been implicated in the regulation of cellular stress responses, such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and oxidative stress.
PARP12 Related Diseases
- Cancer: PARP12 has been found to play a role in DNA repair and maintenance of genomic stability. Dysregulation or mutations in PARP12 may contribute to the development of certain types of cancer, such as breast, ovarian, or prostate cancer.
- Autoimmune diseases: PARP12 has also been implicated in the regulation of immune responses. Dysregulation of PARP12 may contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Neurological disorders: PARP12 has been associated with neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. It may play a role in the pathogenesis of conditions like Alzheimer's disease or Parkinson's disease.
- Cancer: PARP12 has been implicated in cancer development and progression. It has been shown to interact with other proteins involved in DNA repair, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2. Targeting PARP12 could have potential therapeutic benefits in cancer treatment, especially in combination with existing DNA-damaging agents or PARP inhibitors.
- Viral infections: PARP12 has been shown to play a role in antiviral immune responses. It can modulate the activity of viral RNA sensors, such as RIG-I and MDA5, and regulate the production of interferons and inflammatory cytokines. Understanding the role of PARP12 in viral infections could lead to the development of new antiviral strategies.
- Autoimmune diseases: PARP12 has been suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It may regulate the activation and function of immune cells, contributing to the dysregulated immune response seen in these conditions.
- Cancer: PARP12 has been implicated in cancer development and progression. It has been shown to interact with other proteins involved in DNA repair, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2. Targeting PARP12 could have potential therapeutic benefits in cancer treatment, especially in combination with existing DNA-damaging agents or PARP inhibitors.
- Viral infections: PARP12 has been shown to play a role in antiviral immune responses. It can modulate the activity of viral RNA sensors, such as RIG-I and MDA5, and regulate the production of interferons and inflammatory cytokines. Understanding the role of PARP12 in viral infections could lead to the development of new antiviral strategies.
- Autoimmune diseases: PARP12 has been suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It may regulate the activation and function of immune cells, contributing to the dysregulated immune response seen in these conditions.
Case Study
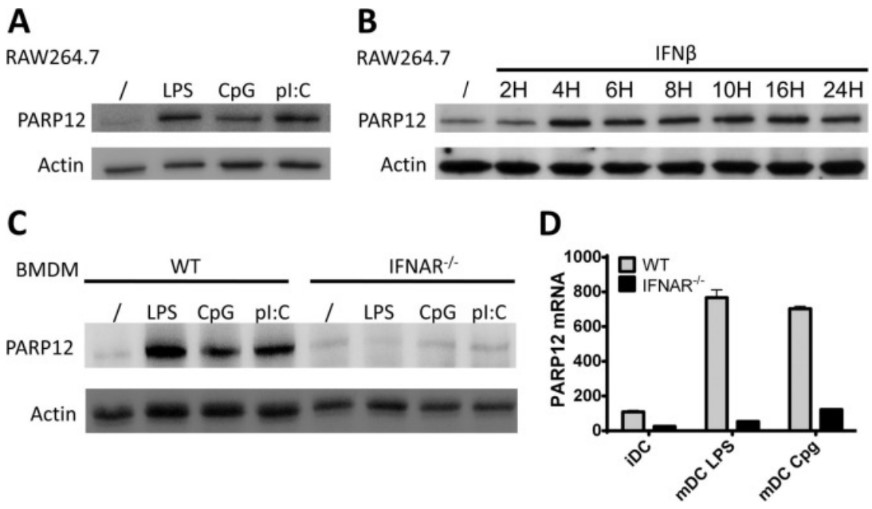
(Iain Welsby, 2014)
Fig1. Expression of PARP12 is type-I interferon dependent. A, RAW264.7 macrophages were left untreated or activated for 8 h with LPS (10 μg/ml), CpG (100 ng/ml), or polyI:C (1 μg/ml), and PARP12 protein expression was detected by Western blot with the MP12 antibody. Actin was blotted as loading control. B, RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with IFNβ for the indicated time and expression of PARP12 was detected as in A.
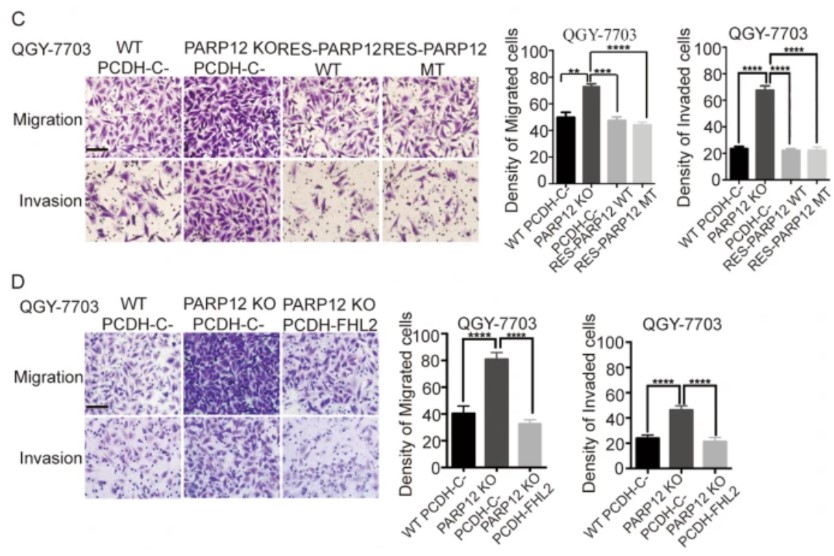
(Changjuan Shao, 2018)
Fig2. Wild-type and enzyme-inactive mutant PARP12 reconstitutions decreased the migration and invasion of PARP12-deficient QGY-7703 cells. Representative images of migrated and invaded cells are shown and originally magnified 400×. The histograms show the mean numbers of migrated and invaded cells from three independent tests (mean ± s.d.). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Scale bars = 50 μm. d FHL2 overexpression decreased the migration and invasion of PARP12-deficient QGY-7703 cells. Representative images of migrated and invaded cells are shown and originally magnified 400×. The histograms show the mean numbers of migrated and invaded cells from three independent tests
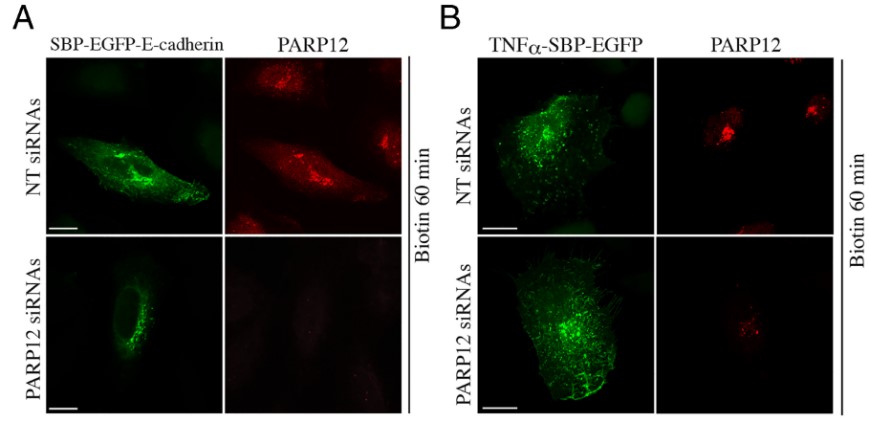
(Giovanna Grimaldi, 2021)
Fig3. Exocytosis of E-cadherin is specifically controlled by PARP12 and Golgin-97. (A–D) HeLa cells expressing the indicated RUSH-based constructs show an increased amount of EGFP–E-cadherin (A), but not EGFP–TNFα (B), at the Golgi complex after 60 min of biotin addition in the absence of PARP12.
Involved Pathway
PARP12 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PARP12 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PARP12 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
PARP12 has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity,metal ion binding,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PARP12 itself. We selected most functions PARP12 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PARP12. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | CAR1,PPM1DA,PM20D1.2,COL27A1A,PLA2G4F,BMX,ZSCAN2,PRKCH,ACSM1,ANTXR1 |
| NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | ART5,GIG2G,PARP14,GIG2I,GIG2D,GIG2P,GIG2K,PARP11,PARP2,PARP15 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | FLYWCH2,NAP1L1,GANAB,ANP32A,TSFM,SCAF4,DZIP3,KIAA1324,NAT10,ADD1 |
Interacting Protein
PARP12 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PARP12 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PARP12.
MLH1;BCL6;SUMO1;CBX2
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References



