RASA1
-
Official Full Name
RAS p21 protein activator (GTPase activating protein) 1 -
Overview
The mammalian proto-oncogene Ras encodes 21 kDa proteins (p21Ras) which exists in either a physiologically quiescent GDP-binding state or a GTP binding signal-emitting state. Interaction of p21Ras with GTPase activating protein (GAP) can increase hydrolys -
Synonyms
RASA1;RAS p21 protein activator (GTPase activating protein) 1;RASA;ras GTPase-activating protein 1;capillary malformation arteriovenous malformation;CM AVM;GAP;p120GAP;p120RASGAP;triphosphatase-activating protein;PKWS;CMAVM;CM-AVM;RASGAP;DKFZp434N071
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect cells
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- His
- T7
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is RASA1 Protein?
RASA1, often referred to in scientific circles, is a protein that doesn’t usually make headlines but has a pretty important job. It's basically a regulator that controls signals relayed inside cells. Imagine it as a traffic cop managing the flow of information. RASA1 specifically works with something called the RAS pathway, which is crucial for cell growth and development. When RASA1 is doing its job right, it helps keep cell proliferation in check, preventing things from getting out of hand—like those cells dividing uncontrollably, which could lead to tumors. Researchers have found that variations or issues with RASA1 might be linked to certain genetic conditions and cancers. So, while you might not hear about RASA1 every day, it plays a vital role in making sure our cells communicate and grow properly without going off track.What is the Function of RASA1 Protein?
The RASA1 protein is a bit like a cellular watchdog, keeping an eye on how signals are passed within cells. Think of it as the cell's internal regulator that ensures everything runs smoothly and doesn't spiral out of control. RASA1 specifically manages the RAS signaling pathway, which is super important for deciding when cells should grow, divide, or even just chill out. By acting like a brake, RASA1 makes sure cells don’t grow and divide like crazy, which could lead to tumors. So, when RASA1 is doing its thing, it prevents those wild cellular parties that can cause problems. If RASA1 isn’t functioning well, that’s when cells might start misbehaving, possibly leading to cancers. In short, RASA1’s role is all about maintaining balance and order inside our cells, ensuring they respond appropriately to growth signals.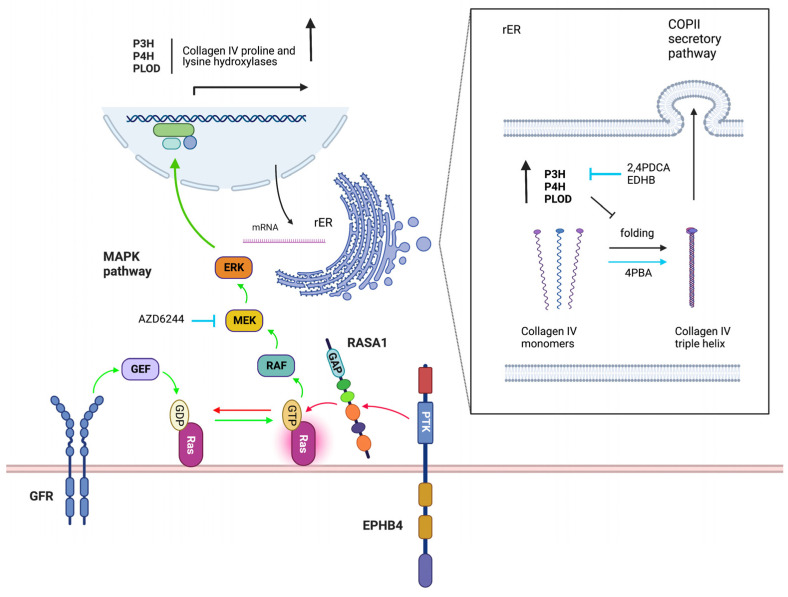
Fig1. Control of EC collagen IV secretion by EPHB4 and RASA1. (Di Chen, 2023)
RASA1 Related Signaling Pathway
RASA1 is closely tied to the RAS signaling pathway, which is crucial for how our cells manage growth and respond to their environment. Imagine this pathway as a busy communication highway inside your cells, where RASA1 acts like an intelligent traffic controller. It helps ensure that the signals telling cells to grow, divide, or develop are kept in check. By controlling these signals, RASA1 prevents cells from going haywire and dividing unchecked, which can lead to cancer or other disorders. Any hiccup in this system, like when RASA1 isn’t working right, can cause major traffic jams on this cellular highway, leading to chaotic cell growth. So, the proper functioning of RASA1 in this signaling pathway is key to keeping cells behaving normally, and any breakdown can have big impacts on health.RASA1 Related Diseases
RASA1 is an important player in maintaining cellular balance, and when things go wrong with it, a bunch of health issues can pop up. Since RASA1 keeps the RAS pathway in check—kind of like making sure that cells don't grow and divide out of control—any malfunction can lead to problems like cancer. Think of it this way: if RASA1 isn’t doing its job properly, cells might start dividing wildly because they aren't getting the proper signals to stop. Beyond cancer, mutations or issues with RASA1 are also linked to certain genetic conditions, such as capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome. This condition can lead to abnormalities in blood vessels, causing visible marks on the skin or even affecting internal organs. So, while RASA1 may not always be in the spotlight, its role in keeping cellular operations smooth is crucial, and its dysfunction can lead to some significant health challenges.Bioapplications of RASA1
RASA1 might not be mainstream, but it’s gaining attention for its potential in medical research. As a key player in the RAS signaling pathway, RASA1 helps keep cellular growth in line, which makes it a hot topic for developing new treatments. Researchers are looking into how manipulating RASA1 could lead to breakthroughs in cancer therapy, aiming to control cell division and prevent tumors. Beyond cancer, studying RASA1 could also offer insights into treating genetic conditions that affect blood vessels, such as capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome. By focusing on these bioapplications, scientists hope to leverage RASA1's regulatory role to create new intervention strategies for various health issues.Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen D. et al. Circ Res. 2024
EPHB4 (ephrin receptor B4) and RASA1 (p120 Ras GTPase-activating protein) are essential for developing lymphatic vessel (LV) valves, but their exact functions are unclear. This study investigates their roles using mice lacking EPHB4 in LVs and those with a version that can’t bind RASA1 (EPHB4 2YP). We found that losing EPHB4 disrupts both the formation and maintenance of LV valves. Similarly, EPHB4 2YP mice showed impaired valve development. Blocking the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway corrected these issues. In human lymphatic cells, reducing EPHB4 or RASA1 disrupted the response to oscillatory shear stress, affecting LV specification. This effect was also seen when cells were treated with Yoda1, which normally increases LV valve numbers but didn’t work in EPHB4 2YP embryos.-
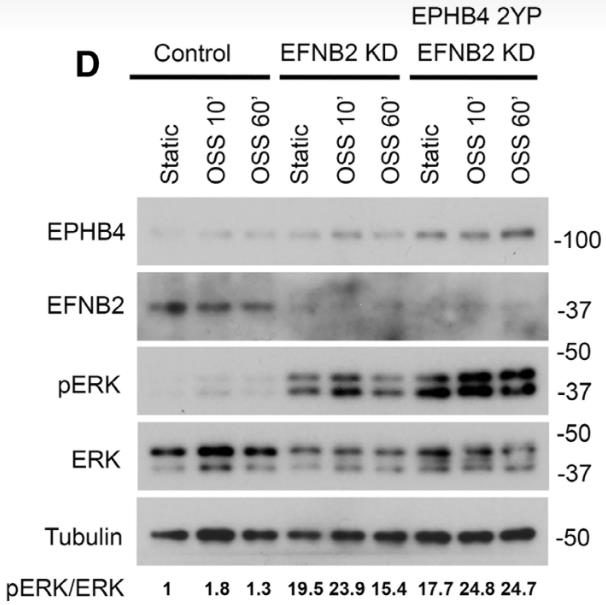 Fig1. Western blot analysis of OSS-induced MAPK activation.
Fig1. Western blot analysis of OSS-induced MAPK activation. -
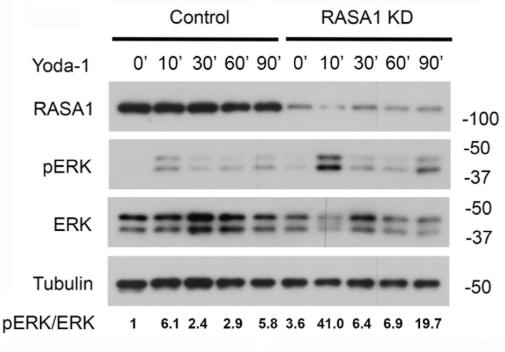 Fig2. Yoda1-induced MAPK activation in HDLEC treated with control or RASA1 siRNA.
Fig2. Yoda1-induced MAPK activation in HDLEC treated with control or RASA1 siRNA.
Case Study 2: Xu X. et al. Biochem Genet. 2024
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), linked to infertility, involves high androgens, lack of ovulation, and insulin resistance. Researchers explored how lncRNA XIST affects KGN cells in PCOS through the miR-212-3p/RASA1 axis. Typically, XIST is low, while miR-212-3p is high, reducing RASA1 levels. XIST suppresses miR-212-3p, which otherwise decreases RASA1. Increasing XIST levels reduces cell growth and boosts apoptosis, but these effects reverse with miR-212-3p mimics. Inhibiting miR-212-3p has the opposite effect, countered by RASA1-siRNA.-
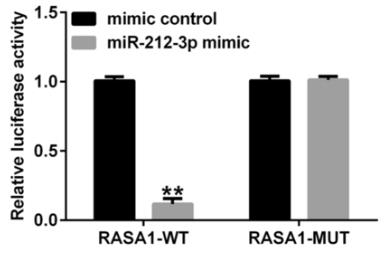 Fig3. Dual-luciferase reporter assay verified the association between miR-212-3p and RASA1.
Fig3. Dual-luciferase reporter assay verified the association between miR-212-3p and RASA1. -
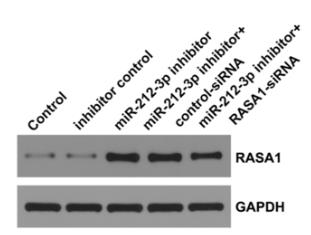 Fig4. Detection of RASA1 expression using Western blot.
Fig4. Detection of RASA1 expression using Western blot.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RASA1-28974TH)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RASA1-28974TH) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RASA1-7177H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RASA1-7177H)
Involved Pathway
RASA1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RASA1 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Axon guidance, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RASA1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ras signaling pathway | HTR7,PDGFRB,FGFR4,ANGPT4,MAPK8,PLA2G6,MLLT4,SHC4,ANGPT2,FGF1 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | FGF20,ELK4,CACNA2D3,PPM1BB,FGF17,MAP2K6,PRKACA,MAP2K2,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,PPM1AA |
| Axon guidance | SCN2B,AKAP9,EPHA6,NCK1,SEMA3G,NRG2A,AGRN,PPP3R2,ADAM10,KBTBD7 |
-
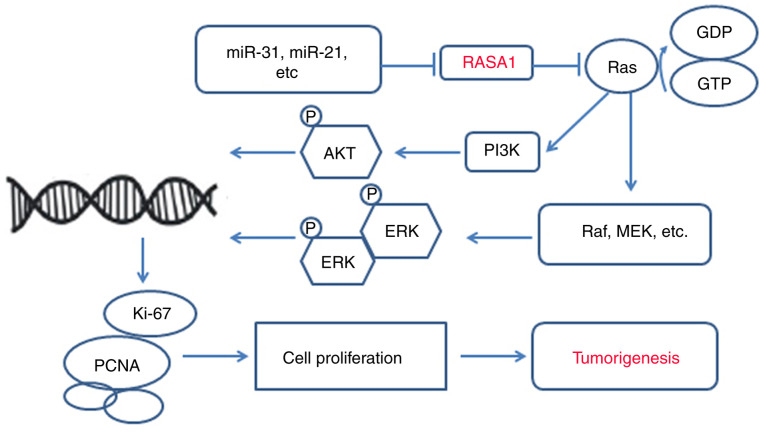 Fig1. The potential role of RASA1 in tumorigenesis. (Yanhua Zhang, 2020)
Fig1. The potential role of RASA1 in tumorigenesis. (Yanhua Zhang, 2020) -
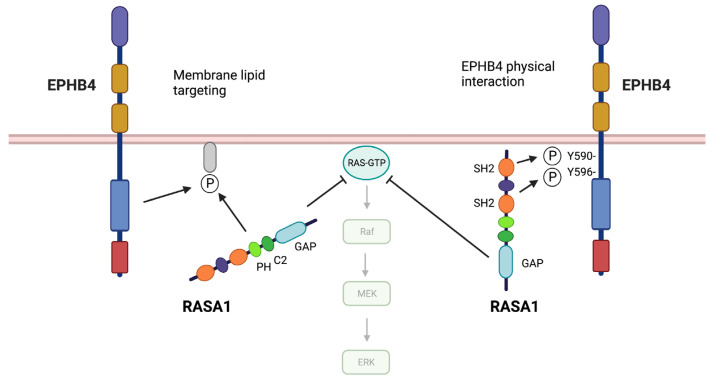 Fig2. Models of EPHB4 and RASA1 cooperation in EC. (Di Chen, 2023)
Fig2. Models of EPHB4 and RASA1 cooperation in EC. (Di Chen, 2023)
Protein Function
RASA1 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTPase activator activity,GTPase binding,glycoprotein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RASA1 itself. We selected most functions RASA1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RASA1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GTPase activator activity | ARAP1,RGS20,TBC1D25,CHN2,DOCK4,CDC42EP1,SMAP1,ARHGAP33,TBC1D21,ARHGAP12 |
| glycoprotein binding | SDC1,FYN,SERPINA1,LGALS1,EDEM2,SDCBP,FBXO17,B2M,ERBB2,BBC3 |
| receptor binding | DIAPH1,ADCYAP1,FZD1,GCG,GIPC1,NRG2A,PVRL1,PVRL3,DVL3,TMEM38A |
| protein binding | ZNF136,PASK,CDT1,USP22,SUCLA2,IMP4,RPLP0,SULT1A3,LZTS1,UCP3 |
| potassium channel inhibitor activity | PTI,NEDD4L,KCNA5,ENSA,KCNK2,CAV3 |
| GTPase binding | LCP1,SPTBN1,RAB3D,GNB3,GNB1,EPRS,IARS,VPS41,BNIP3,AIMP1 |
Interacting Protein
RASA1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RASA1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RASA1.
DLC1;NCK1;PDGFRB;ERBB2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



